Date: 26 November 2013
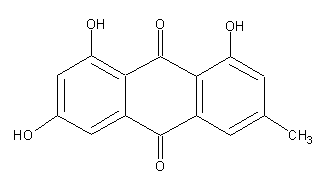
Secondary metabolites, structure diagram: Trivial name – Emodin/Archin/Emodol/Frandulic Acid
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
Species: A. aureus, A. sclerotiorum, A. terreus, A. wentiiSystematic name: 9,10-Anthracenedione, 1,3,8-trihydroxy-6-methyl- (9CI)Molecular formulae: C15H10O5Molecular weight: 270.237Chemical abstracts number: 518-82-1Selected references: Kiriyama, Noriki; Nitta, Keiichi; Sakaguchi, Yoshiaki; Taguchi, Yasuhisa; Yamamoto, Yuzuru (Fac. Pharm. Sci., Kanazawa Univ., Kanazawa, Japan). Chem. Pharm. Bull., 25(10), 2593-601 (English) 1977.Toxicity: Mean lethal dose of emodin orally administered to 1-day-old DeKalb cockerels was 3.7 mg/kg.BACKGROUND: Emodin, a widely available herbal remedy, was evaluated for potential effects on pregnancy outcome. METHODS: Emodin was administered in feed to timed-mated Sprague-Dawley (CD) rats (0, 425, 850, and 1700 ppm; gestational day [GD] 6-20), and Swiss Albino (CD-1) mice (0, 600, 2500 or 6000 ppm; GD 6-17). Ingested dose was 0, 31, 57, and approximately 80-144 mg emodin/kg/day (rats) and 0, 94, 391, and 1005 mg emodin/kg/day (mice). Timed-mated animals (23-25/group) were monitored for body weight, feed/water consumption, and clinical signs. At termination (rats: GD 20; mice: GD 17), confirmed pregnant dams (21-25/group) were evaluated for clinical signs: body, liver, kidney, and gravid uterine weights, uterine contents, and number of corpora lutea. Fetuses were weighed, sexed, and examined for external, visceral, and skeletal malformations/variations. RESULTS: There were no maternal deaths. In rats, maternal body weight, weight gain during treatment, and corrected weight gain exhibited a decreasing trend. Maternal body weight gain during treatment was significantly reduced at the high dose. In mice, maternal body weight and weight gain was decreased at the high dose. CONCLUSIONS: Prenatal mortality, live litter size, fetal sex ratio, and morphological development were unaffected in both rats and mice. At the high dose, rat average fetal body weight per litter was unaffected, but was significantly reduced in mice. The rat maternal lowest observed adverse effect level (LOAEL) was 1700 ppm; the no observed adverse effect level (NOAEL) was 850 ppm. The rat developmental toxicity NOAEL was > or =1700 ppm. A LOAEL was not established. In mice, the maternal toxicity LOAEL was 6000 ppm and the NOAEL was 2500 ppm. The developmental toxicity LOAEL was 6000 ppm (reduced fetal body weight) and the NOAEL was 2500 ppm. Copyright 2004 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
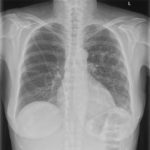
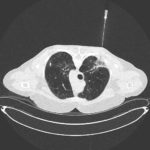
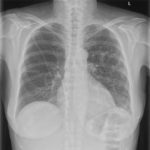
PtDS2 –Repeated chest infections arrested by itraconazole therapy in ABPA and bronchiectasis
DS2 developed asthma age 24 and now aged 62. From about age 30 she started getting repeated chest infections and a few years later ABPA and bronchiectasis was diagnosed. Infections continued requiring multiple courses of antibiotics annually. At one point DS2 developed a pneumothorax, possibly because of excess coughing. She has chronic rhinitis and mannose binding lectin deficiency. In May 2011, she started itraconazole therapy, and has needed no antibiotic courses for her chest since. Her rhinitis with sinusitis occasionally bothers her. She is delighted to have gone 18 months with no chest infections.
 ,
,  ,
, 
-
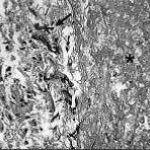
Aspergillus hyphae (arrow) in the lumen without invasion of the necrotic bronchial wall (*) (Nicod 2001).
-
fibrinonecrotic material (arrow) from the airway shown in A, with subocclusion of the bronchial lumen (*)
-
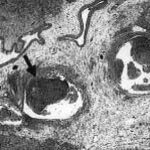
Fibrinous or pseudomembranous bronchitis (arrow) with subocclusion of the airways (* indicates subocclusion of the airways by pseudomembranes)

-
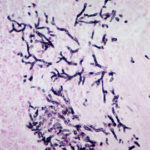
Bronchoscopic biopsy demonstrated septate hyphae with branching at 45o (methenamine silver stain ×400).