Date: 26 November 2013
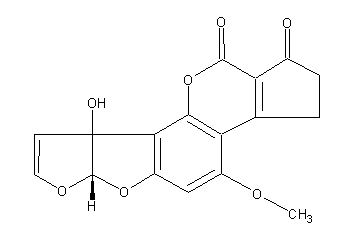
Secondary metabolites, structure diagram: Trivial name – aflatoxin M1
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
Species: A. flavus, A. parasiticusSystematic name: Cyclopenta[c]furo[3′,2′:4,5]furo[2,3-h][1]benzopyran-1,11-dione, 2,3,6a,9a-tetrahydro-9a-hydroxy-4-methoxy-, (6aR-cis)-Molecular formulae: C17H12O7Molecular weight: 328.28Chemical abstracts number: 6795-23-9Selected references: Nakazato, Mitsuo; Morozumi, Satoshi; Saito, Kazuo; Fujinuma, Kenji; Nishima, Taichiro; Kasai, Nobuhiko (Dep. Food Hyg. and Nutr., Tokyo Metrop. Res. Lab. Public Health, Tokyo 169, Japan). Eisei Kagaku, 37(2), 107-16 (English) 1991.Toxicity: Slightly less toxic than aflatoxin B1 with an oral LD50 for the one day-old duckling 0.46 mg/kg body-weight. Significantly less carcinogenic than aflatoxin B1.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
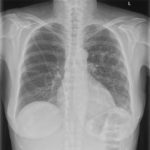
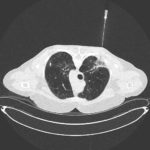
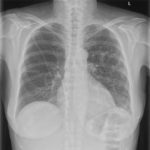
PtDS2 –Repeated chest infections arrested by itraconazole therapy in ABPA and bronchiectasis
DS2 developed asthma age 24 and now aged 62. From about age 30 she started getting repeated chest infections and a few years later ABPA and bronchiectasis was diagnosed. Infections continued requiring multiple courses of antibiotics annually. At one point DS2 developed a pneumothorax, possibly because of excess coughing. She has chronic rhinitis and mannose binding lectin deficiency. In May 2011, she started itraconazole therapy, and has needed no antibiotic courses for her chest since. Her rhinitis with sinusitis occasionally bothers her. She is delighted to have gone 18 months with no chest infections.
 ,
,  ,
, 
-
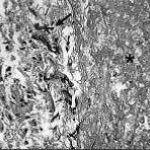
Aspergillus hyphae (arrow) in the lumen without invasion of the necrotic bronchial wall (*) (Nicod 2001).
-
fibrinonecrotic material (arrow) from the airway shown in A, with subocclusion of the bronchial lumen (*)
-
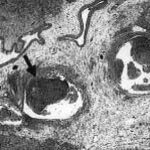
Fibrinous or pseudomembranous bronchitis (arrow) with subocclusion of the airways (* indicates subocclusion of the airways by pseudomembranes)

-
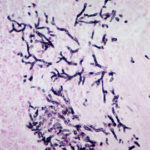
Bronchoscopic biopsy demonstrated septate hyphae with branching at 45o (methenamine silver stain ×400).