Date: 26 November 2013
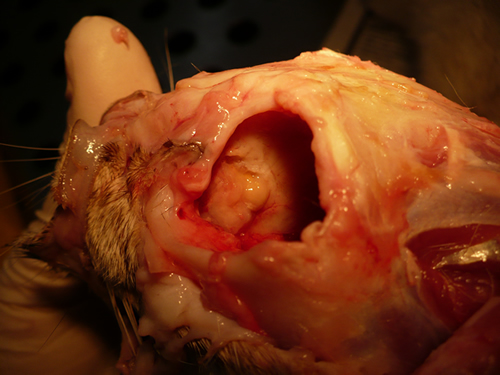
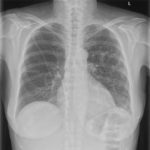
Nasal, sinus and orbital aspergillosis in a cat. The left nasal cavity and sinus were full of pus and debris and there was severe bone erosion from the nasal cavity into the rostromedial orbitthrough which pus was protruding
Copyright:
(Kindly provided by Martin L. Whitehead, BSc, PhD, BVSc, CertSAM, MRCVS & Peter W. Kettlewell, BVSc, MSc, MRCVS. Chipping Norton Veterinary Hospital, Albion Street, Chipping Norton, Oxon, OX7 5BN.)
Notes:
History : Nasal aspergillosis is relatively common in dogs but rare in cats. Our veterinary hospital in Oxfordshire was recently presented with a 13-year old female Burmilla cat with a history of left-side unilateral nasal discharge, a watery left eye with slight blepharospasm, occasional ‘twitching movements’ of the head, weight loss, inappetance and depression. Clinical examination was unremarkable except for left-side mucopurulent nasal discharge, left-side mild serous ocular discharge, and a soft subcutaneous swelling over the left frontal sinus. Haematology, blood biochemistry and urinalysis revealed diabetes mellitus but was otherwise unremarkable. Radiography under general anaesthesia revealed a diffuse soft tissue density within the left nasal cavity and left frontal sinus. Rhinoscopy revealed mucopurulent discharge on the left side but was otherwise unremarkable. Aspiration of the swelling over the left frontal sinus produced pus and this abscess was lanced and flushed. The frontal sinus was trephined and the sinus and nasal cavity flushed with saline. Tests for feline immunodeficiency virus and feline leukaemia virus and serology for Aspergillus were not carried out. The cat was started on insulin, ibafloxacin (Ibaflin, Intervet) and meloxicam (Metacam, Boehringer). Cytology of the material flushed from the frontal sinus and nasal cavity revealed fungal hyphae consistent with Aspergillus species and culture of this material yielded growth of a fungus which was morphologically similar to A. candidus (Awaiting molecular typing results). The cat was then started on oral itraconazole (Itrafungol, Janssen) 10 mg/kg p.o. SID. The abscess over the rostral frontal sinus did not heal and a second abscess appeared over the nasal bone just dorsal to the nose. Infusion of the frontal sinus and nasal cavity with topical antifungal medication was discussed with the owners, but as the cat was deteriorating they requested euthanasia. On post-mortem examination the right nasal cavity, frontal sinus and orbit were unaffected. The left nasal cavity and sinus were full of pus and debris and there was severe bone erosion from the nasal cavity into the rostromedial orbit through which pus was protruding. There was also severe bone erosion rostrally through the nasal bone and less severe bone erosion dorsally over the rostral part of the frontal sinus, these sites of bone erosion being at the location of the two subcutaneous abscesses.Feline nasal aspergillosis is extremely rare in the UK and to our knowledge this is the first reported case of orbital aspergillosis in the UK although nasal aspergillosis has been reported in other countries.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
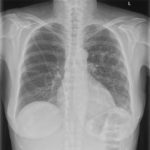
PtDS2 –Repeated chest infections arrested by itraconazole therapy in ABPA and bronchiectasis
DS2 developed asthma age 24 and now aged 62. From about age 30 she started getting repeated chest infections and a few years later ABPA and bronchiectasis was diagnosed. Infections continued requiring multiple courses of antibiotics annually. At one point DS2 developed a pneumothorax, possibly because of excess coughing. She has chronic rhinitis and mannose binding lectin deficiency. In May 2011, she started itraconazole therapy, and has needed no antibiotic courses for her chest since. Her rhinitis with sinusitis occasionally bothers her. She is delighted to have gone 18 months with no chest infections.
 ,
,  ,
, 
-
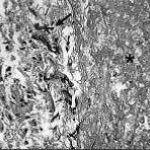
Aspergillus hyphae (arrow) in the lumen without invasion of the necrotic bronchial wall (*) (Nicod 2001).
-
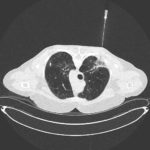
fibrinonecrotic material (arrow) from the airway shown in A, with subocclusion of the bronchial lumen (*)
-
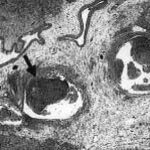
Fibrinous or pseudomembranous bronchitis (arrow) with subocclusion of the airways (* indicates subocclusion of the airways by pseudomembranes)

-
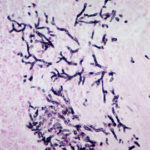
Bronchoscopic biopsy demonstrated septate hyphae with branching at 45o (methenamine silver stain ×400).