Date: 26 November 2013
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
Dr Jenny Bartholomew is a Research Associate in the Institute of Inflammation and Repair, University of Manchester. A Manchester graduate – she formerly worked as a University Lecturer at Monash University, Melbourne for four years where she undertook research into the immunology of connective tissue damage and repair in rheumatoid arthritis, identifying TNF alpha in inflamed cartilage in an animal model of arthritis.
On returning to Manchester she moved to Christie Hospital, Manchester as a Research Fellow and University teacher where her main research interests were studying the immunological responses to human papillomavirus (HPV 16/18) in cervical cancer. Using recombinant vaccinia virus to express viral proteins from HPV, the major oncoproteins from HPV were studied and used in the development of the cervical cancer vaccine.
For the last 12 years she has been involved in Aspergillus research, providing clinical and scientific information to patients, doctors and scientists, she manages and publishes the Aspergillus website. This is a complex educational resource providing the latest research, technology and information for a wide diversity of users. She has a particular interest in video media and produces a broad range of video interviews from patients and clinics for educational use.
She is now engaged in global health programme. Jenny has launched the LIFE (Leading International Fungal Education) programme commencing with a public engagement and awareness project in 2012, combining Science with Art, aimed at educating young people about harmful fungi.
This was followed by the LIFE online resource (http://life-worldwide.org) for health care professionals encompassing all fungi, the infections they cause, diagnosis and treatments. This resource has a news flow about global health and is targeting global education about fungi and serious infections they can cause. The site is now being translated into Spanish and other languages will follow soon. She launched the Global Action Fund for Fungal Infection site (http://gaffi.org) in July 2013 – GAFFI is a foundation based in Geneva, focused on advocacy for access to diagnostics and treatment in every country.
Aspergillus website, Life worldwide organisation, GAFFI , National Aspergillosis Centre, Mycology Reference Laboratory and Fungal Infection Trust.
Some of my Publications:
- Bartholomew, J S, J M Evanson and DE Woolley . Rheumatol. Int., II: 37-40, 1991 Serum IgE Anti-cartilage Collagen Antibodies in Rheumatoid Patients.
- Bartholomew,J S,J M Evanson and DE Woolley . Allergy Digests, 2: 30-31, 1992 Collagen Specific IgE Antibodies in Rheumatoid Patients.
- Stacey,S N, J S Bartholomew, A Ghosh, P L Stern, M Mackett and J R Arrand. J.Gen. Vir., 73: 2337-2345, 1992 Expression of human papillomavirus type 16 E6 protein by recombinant baculovirus and use for detection of anti-E6 antibodies in human sera.
- Stacey,S N, A Ghosh, J S Bartholomew, R W Tindle, P L Stern, M Mackett and J R Arrand. J. Med. Virol., 40: 14-21, 1993. Expression of human papillomavirus type 16 E7 protein by recombinant baculovirus and use for the detection of E7 antibodies in sera from cervical carcinogen patients.
- Bartholomew,JS, S N Stacey, B Coles, D Burt, I R Arrand and P L Stern. European Journal of Immunology, 24: 3175-3179, 1994 Identification of a naturally processed HLA-A0201 restricted viral peptide from cells expressing human papillomavirus type 16 E6 oncoprotein.
- Bartholomew J and P L Stern.
In: Modulation of MHC Antigen Expression and Disease. Eds E G Blair, D J Maudsley and C P Pringle, 233-250, 1994 MHC expression in HPV associated cervical cancer. - Ellis JRM, P I Keating, J Baird, E F Hounsell, D V Renouf, M Rowe, D Hopkins, M F Duggan-Keen, J.S Bartholomew, L S Young and P L Stern. Nature Medicine, 1,464-470, 1995 An HP V 16 variant is associated with cervical carcinoma in HLA-B7 positive women.
- Bartholomew,JS, S. Glenville, S. Sarkar, D.I. Burt, M.A. Stanley, F. Ruiz-Cabens, J. Chengang, F. Garrido and P .L. Stern. Cancer Res. March 1, 1997. Integration of high-risk human papillomavirus DNA is linked to the down-regulation of Class I Human leukocyte antigens by steroid hormones in cervical tumour cells.
- Brady CS. Bartholomew JS. Burt DJ. Duggan-Keen MF. Glenville S. Telford N. Little AM. Davidson JA. Jimenez P. Ruiz-Cabello F. Garrido F. Stern PL.
Tissue Antigens. 55(5):401-11, 2000 May. Multiple mechanisms underlie HLA dysregulation in cervical cancer. - Fungi: friends or foes? Biological Sciences Review 17(1) 24-28, 2004
-
Mabey Gilsenan JE, Atherton G, Bartholomew J, Giles PF, Attwood TK, Denning DW, Bowyer P.
Aspergillus genomes and the aspergillus cloud Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Jan;37(Database issue):D509-14. Epub 2008 Nov 27
E-mail: jennifer.bartholomew@manchester.ac.uk
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
5 sputum samples were positive for A. niger, a bronchoscopy was normal and culture and microscopy were negative. Rx voriconazole, 200mg bd was given. An excellent clinical response was seen.
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
-
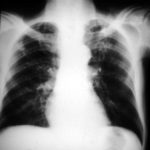
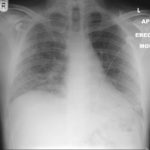
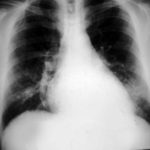
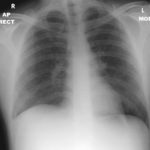
The patient was a 37-year old man in whom P.carinii pneumonia developed in August 1987, followed by esophageal candidiasis and upper gastrointestinal bleeding in September. Chronic perineal herpes led to the formation of rectourethral fistula and multiple episodes of urosepsis, for which he was given long-term ciprofloxacin therapy to suppress bacterial colonization of the bladder. He discontinued heavy alcohol use in September 1987 and smoked marijuana occasionally.On April 23 1989, the patient was admitted to the hospital with a two-month history of increasing dry cough with shortness of breath. He reported transient fever (temperature to 41°C). He was admitted with leukopenia, with his neutrophil count falling to 16 x 106/l on the second hospital day. A chest film showed bilateral fluffy lower-lobe infiltrates (this image). Zidovudine was discontinued. The patient had a rapidly downhill course despite intravenous treatment with trimethioprim-sulfamethoxazole. A bronchoscopy on the sixth hospital day revealed what appeared to be a foreign body in the left lower-lobe bronchus. It was removed, together with much necrotic, mucoid debris. On microscopic examination, the “foreign body” was necrotic, containing large numbers of hyphae and conidia in a manner typical of an aspegilloma or fungal cast. The culture grew A.fumigatus.
Clinical and radiologic improvement followed bronchoscopy, and itraconazole therapy was begun because of the concern about invasive aspergillosis in the setting of marked neutropenia. The patient tolerated the medication well at a dose of 200 mg twice daily, and the chest film became normal over the subsequent six weeks, after which itraconazole was discontinued. A sputum specimen cultured for fungus four weeks after the start of therapy was negative. After the initial improvement with itraconazole, the patient had recurrent urosepsis, associated with dehydration and marked confusion. Nine weeks after the discontinuation of itraconazole, he died of progressive dementia complicated by recurrent pneumonia and sepsis. There was no postmortem examination.
This patient was described (pt 11) and this chest radiograph reproduced in Denning DW, Follansbee S, Scolaro M, Norris S, Edelstein D, Stevens DA. Pulmonary Aspergillosis in the Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome. N Engl J Med 1991; 324: 654-662.
 ,
, 
-
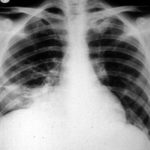
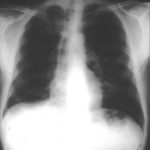
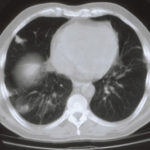
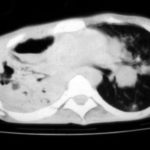
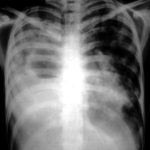
Image A. This 25 year old woman was previously well and presented with a pneumonia of uncertain aetiology. She has infiltrates in right upper-lobe and left middle and lower zones. The diagnosis was later made of chronic invasive pulmonary aspergillosis by bronchoscopy . Subsequently she was diagnosed with adult-onset chronic granulomatous disease with neutrophil function assays.
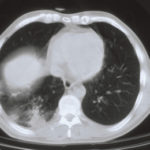
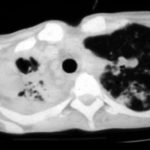
Image B. CT scan of the thorax just below the carina, showing almost complete opacification of the right lung and marked nodular shadowing around the hilum of the left lung.
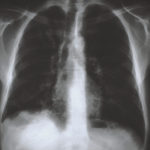
Image C. Progression of pulmonary infiltrates are seen seven weeks later, despite administration of amphotericin B.
Image D. CT scan of the thorax above the carina showing near complete opacification of the right lung and multiple discrete nodular shadows in the left lung.
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
-
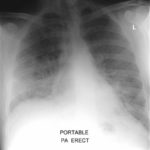
02/10/09 X -ray shows improvement in appearances from initial presentation with complete chest radiographic resolution by 07/11/2008
-
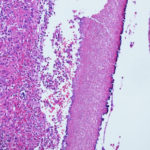
Subacute IPA in rhematoid nodules of the lung. in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. Histology sections stained with H&E