Date: 26 November 2013
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
Dr Jenny Bartholomew is a Research Associate in the Institute of Inflammation and Repair, University of Manchester. A Manchester graduate – she formerly worked as a University Lecturer at Monash University, Melbourne for four years where she undertook research into the immunology of connective tissue damage and repair in rheumatoid arthritis, identifying TNF alpha in inflamed cartilage in an animal model of arthritis.
On returning to Manchester she moved to Christie Hospital, Manchester as a Research Fellow and University teacher where her main research interests were studying the immunological responses to human papillomavirus (HPV 16/18) in cervical cancer. Using recombinant vaccinia virus to express viral proteins from HPV, the major oncoproteins from HPV were studied and used in the development of the cervical cancer vaccine.
For the last 12 years she has been involved in Aspergillus research, providing clinical and scientific information to patients, doctors and scientists, she manages and publishes the Aspergillus website. This is a complex educational resource providing the latest research, technology and information for a wide diversity of users. She has a particular interest in video media and produces a broad range of video interviews from patients and clinics for educational use.
She is now engaged in global health programme. Jenny has launched the LIFE (Leading International Fungal Education) programme commencing with a public engagement and awareness project in 2012, combining Science with Art, aimed at educating young people about harmful fungi.
This was followed by the LIFE online resource (http://life-worldwide.org) for health care professionals encompassing all fungi, the infections they cause, diagnosis and treatments. This resource has a news flow about global health and is targeting global education about fungi and serious infections they can cause. The site is now being translated into Spanish and other languages will follow soon. She launched the Global Action Fund for Fungal Infection site (http://gaffi.org) in July 2013 – GAFFI is a foundation based in Geneva, focused on advocacy for access to diagnostics and treatment in every country.
Aspergillus website, Life worldwide organisation, GAFFI , National Aspergillosis Centre, Mycology Reference Laboratory and Fungal Infection Trust.
Some of my Publications:
- Bartholomew, J S, J M Evanson and DE Woolley . Rheumatol. Int., II: 37-40, 1991 Serum IgE Anti-cartilage Collagen Antibodies in Rheumatoid Patients.
- Bartholomew,J S,J M Evanson and DE Woolley . Allergy Digests, 2: 30-31, 1992 Collagen Specific IgE Antibodies in Rheumatoid Patients.
- Stacey,S N, J S Bartholomew, A Ghosh, P L Stern, M Mackett and J R Arrand. J.Gen. Vir., 73: 2337-2345, 1992 Expression of human papillomavirus type 16 E6 protein by recombinant baculovirus and use for detection of anti-E6 antibodies in human sera.
- Stacey,S N, A Ghosh, J S Bartholomew, R W Tindle, P L Stern, M Mackett and J R Arrand. J. Med. Virol., 40: 14-21, 1993. Expression of human papillomavirus type 16 E7 protein by recombinant baculovirus and use for the detection of E7 antibodies in sera from cervical carcinogen patients.
- Bartholomew,JS, S N Stacey, B Coles, D Burt, I R Arrand and P L Stern. European Journal of Immunology, 24: 3175-3179, 1994 Identification of a naturally processed HLA-A0201 restricted viral peptide from cells expressing human papillomavirus type 16 E6 oncoprotein.
- Bartholomew J and P L Stern.
In: Modulation of MHC Antigen Expression and Disease. Eds E G Blair, D J Maudsley and C P Pringle, 233-250, 1994 MHC expression in HPV associated cervical cancer. - Ellis JRM, P I Keating, J Baird, E F Hounsell, D V Renouf, M Rowe, D Hopkins, M F Duggan-Keen, J.S Bartholomew, L S Young and P L Stern. Nature Medicine, 1,464-470, 1995 An HP V 16 variant is associated with cervical carcinoma in HLA-B7 positive women.
- Bartholomew,JS, S. Glenville, S. Sarkar, D.I. Burt, M.A. Stanley, F. Ruiz-Cabens, J. Chengang, F. Garrido and P .L. Stern. Cancer Res. March 1, 1997. Integration of high-risk human papillomavirus DNA is linked to the down-regulation of Class I Human leukocyte antigens by steroid hormones in cervical tumour cells.
- Brady CS. Bartholomew JS. Burt DJ. Duggan-Keen MF. Glenville S. Telford N. Little AM. Davidson JA. Jimenez P. Ruiz-Cabello F. Garrido F. Stern PL.
Tissue Antigens. 55(5):401-11, 2000 May. Multiple mechanisms underlie HLA dysregulation in cervical cancer. - Fungi: friends or foes? Biological Sciences Review 17(1) 24-28, 2004
-
Mabey Gilsenan JE, Atherton G, Bartholomew J, Giles PF, Attwood TK, Denning DW, Bowyer P.
Aspergillus genomes and the aspergillus cloud Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Jan;37(Database issue):D509-14. Epub 2008 Nov 27
E-mail: jennifer.bartholomew@manchester.ac.uk
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
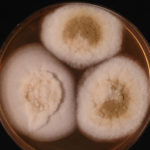
A Colonies on MEA after one week, B conidial head x920, C atypical reduced conidial head x920, D conidial head x 920.

-
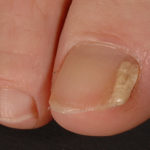
A case of onychomycosis associated with Aspergillus ochraceopetaliformis as described in Med Mycol. 2009 Mar 9:1-5, 2009,Brasch J, Varga J, Jensen JM, Egberts F & Tintelnot K
-
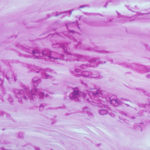
Histology of the infected nail (PAS stain) showing thick fungal elements and septate hyphae within nail material.
-
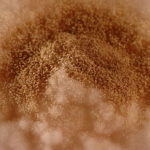
culture and identified in a case of onychomycosis – Culture at higher magnification.
-
culture and identified in a case of onychomycosis – Culture of Aspergillus ochraceopetaliformis on Sabouraud agar with cycloheximide at 26C
-
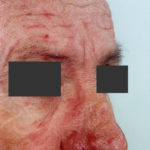
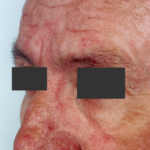
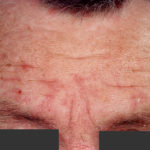
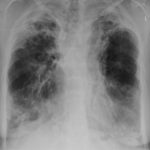
This patient with chronic cavitary pulmonary aspergillosis was treated with itraconazole, with some success, but considerable gastrointestinal disturbance (diarrhoea, flatulence and uncomfortable feeling in his abdomen). He also developed a facial rash. Itraconazole was stopped and he reverted to voriconazole which he was unable to take because of a severe feeling of being generally unwell. His facial rash resolved. Application was made for funding posaconazole. He started this and after 6 weeks an almost identical facial rash to that seen with itraconazole appeared. He tolerated posaconazole well in other respects, and his chronic cavitary pulmonary aspergillosis is now significantly better (symptomatically and serologically). July 2007
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
-
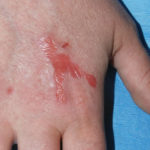
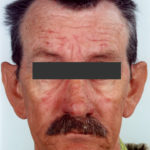
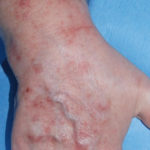
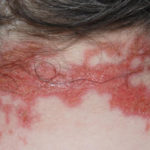
This patient with ABPA and chronic cavitary pulmonary aspergillosis has been stabilized on voriconazole treatment for >5 years. She had a degree of photosensitivity most of that time, noticed early in the course of voriconazole treatment. She is oxygen and wheelchair dependent and doesn’t go outside very much, so most of her light exposure has been indoor light. She developed rough scaly patches over her face, neck and lower arms. Dermatological review indicated multiple solar keratoses”. Skin biopsy from the right forearm confirmed this clinical diagnosis – “skin showing hyperkeratosis with a little parakeratosis and acanthosis. The keratinocytes have a glassy appearance but show nuclear atypia with dyskeratotic cells, and occasional suprabasal mitoses. The intraepidermal sweat ducts are spared. Appearances suggest an actinic keratosis with moderate to severe dysplasia.” These features are characteristic of a low grade premalignant change.
She was treated with local 5-fluorouracil cream (Efudix) (3 cycles) to the affected lesions. These photos were taken at the apogee of inflammation. The inflammation resolved after discontinuing the cream. This reaction is expected with application of this mild chemotherapy agent. Alternative or supplementary treatments include cryotherapy, curettage and cautery, if necessary. Following treatment her skin was much softer and considerably improved. Voriconazole has been stopped, and posaconazole substituted.
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,