Submitted by Aspergillus Administrator on 22 October 2008

The European Science Foundation has announced the following in this weeks ‘Lancet‘ journal:
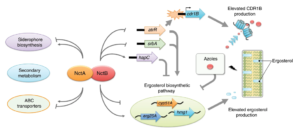
The European Science Foundation (ESF) has announced the start of a new pan-European collaboration, FUMINOMICS, to study the opportunistic pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus. This saprophytic filamentous fungus causes severe nosocomial infections that are increasingly problematic for clinicians; invasive aspergillosis is now the leading cause of early death in many transplant centres in Europe.
Jean-Paul Latgé (Institut Pasteur, Paris, France), chair of the new FUMINOMICS steering committee, added, “Our ability to carry out research into this pathogen has only become feasible recently because of the publication of the complete A fumigatus genome and new molecular and biochemical tools that make it possible to genetically modify the fungus in order to undertake large-scale studies including proteomic, transcriptomic analysis and the construction of mutant libraries”.
This collaboration has been made possible by the publicly available genomic sequence of Aspergillus fumigatus, such as that hosted by the Aspergillus Website (for whom Jean-Paul has been an editor for several years). The aims of the project are outlined as:
One of the main clinical objectives will be to investigate how the fungus grows in vivo, to discover the mechanisms that enable it to gain a foothold to establish disease. Another is to develop methods for better early diagnosis—aspergillosis is currently diagnosed very late and drug treatment fails because fungal burden is too high. “We also hope to identify new drug targets to tackle this opportunistic but deadly pathogen more effectively”
News archives
-
Title
Date


 ,
,  ,
,