Date: 26 November 2013
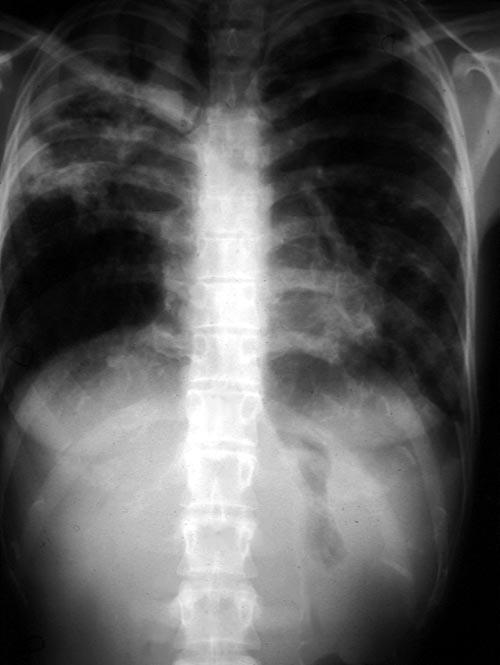
Image A. This 25 year old woman was previously well and presented with a pneumonia of uncertain aetiology. She has infiltrates in right upper-lobe and left middle and lower zones. The diagnosis was later made of chronic invasive pulmonary aspergillosis by bronchoscopy . Subsequently she was diagnosed with adult-onset chronic granulomatous disease with neutrophil function assays.
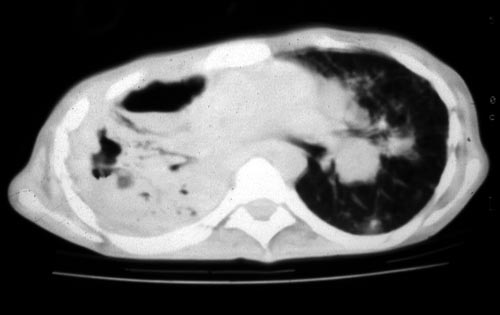
Image B. CT scan of the thorax just below the carina, showing almost complete opacification of the right lung and marked nodular shadowing around the hilum of the left lung.
Image C. Progression of pulmonary infiltrates are seen seven weeks later, despite administration of amphotericin B.
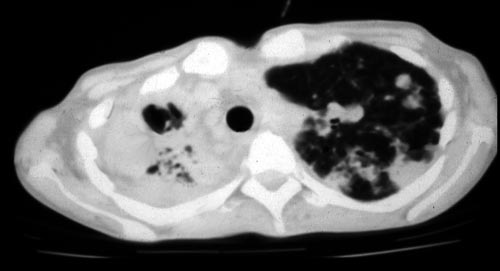
Image D. CT scan of the thorax above the carina showing near complete opacification of the right lung and multiple discrete nodular shadows in the left lung.
Copyright: n/a
Notes: n/a
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
Left= an agar air plate exposed for 2 minutes after the barley had been turned. showing numerous colonies of the fungus following incubation at 26C on 2% malt agar.Right= A sputum sample taken from a maltworker after exposure showing many fungal colonies when cultured on agar. His commensal yeast flora is seen towards the right base as cream/white colonies.

-
growing on contaminated barley malt. The deep blue-green heads made up of chains of conidia are seen on the left. On the right, conidiophores from which conidial chains are developed show typical clavate heads. Stain- Cotton blue in Lactophenol.

-
Sections of colonised alveoli
On the left, the conidiophores sporulate freely, on the right they are seen to cease development at the phialide stage. Carbon deposits are clearly seen here.A=alveolus, As=alveolar septum, C=conidiophore, P=phialide
-
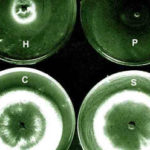
The growth isolated from the aspergilloma in the presence of living cells of the three bacterial species in culture.The most marked inhibition occurred with Pseudomonas aeruginosa(P) and Haemophilus influenzae(H) and to a much lesser extent with Staphylococcus aureus(S). C=control. Inhibitory factors were components of the bacterial slime layers.
-
aspergilloma removed from the lung cavity seen in section.Staining was with methenamine/silver and light green. The structure shows zonation probably due to variations in the growth rate of mycelium(deep brown). A mucus layer(stained green) containing cell debris and bacteria is seen shrouding the fungus. Bacterial genera were Staphylococcus, Haemophilus and Pseudodomonas.

-
Plugs cultured on agarA young colony of the fungus(AF) has a central patch of sporulation and is surrounded by colonies of bacteria and yeasts.

-
A part of the mycelium in a stained sputum plug showing the dichotomously branched hyphae of Aspergillus fumigatus.