Date: 26 November 2013
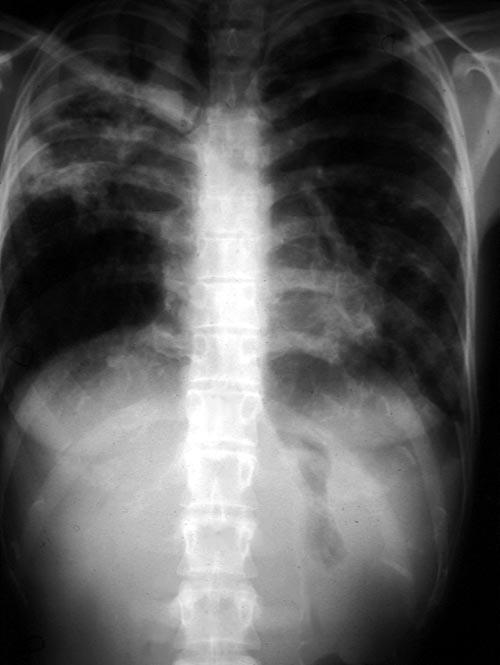
Image A. This 25 year old woman was previously well and presented with a pneumonia of uncertain aetiology. She has infiltrates in right upper-lobe and left middle and lower zones. The diagnosis was later made of chronic invasive pulmonary aspergillosis by bronchoscopy . Subsequently she was diagnosed with adult-onset chronic granulomatous disease with neutrophil function assays.
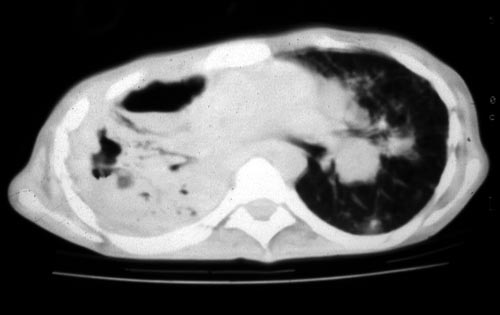
Image B. CT scan of the thorax just below the carina, showing almost complete opacification of the right lung and marked nodular shadowing around the hilum of the left lung.
Image C. Progression of pulmonary infiltrates are seen seven weeks later, despite administration of amphotericin B.
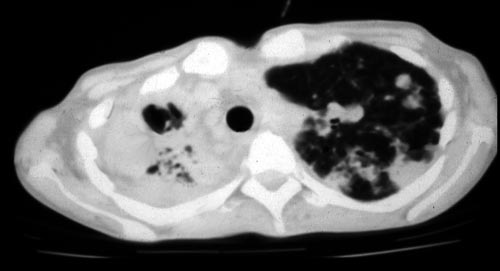
Image D. CT scan of the thorax above the carina showing near complete opacification of the right lung and multiple discrete nodular shadows in the left lung.
Copyright: n/a
Notes: n/a
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
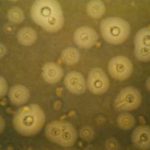
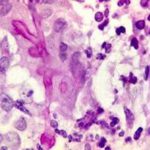
BAL specimen showing hyaline, septate hyphae consistent with Aspergillus, stained with Blankophor

-
Mucous plug examined by light microscopy with KOH, showing a network of hyaline branching hyphae typical of Aspergillus, from a patient with ABPA.

-
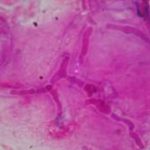
Corneal scraping stained with lactophenol cotton blue showing beaded septate hyphae not typical of either Fusarium spp or Aspergillus spp, being more consistent with a dematiceous (ie brown coloured) fungus
-
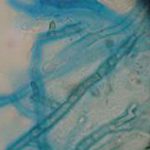
Corneal scrape with lactophenol cotton blue shows separate hyphae with Fusarium spp or Aspergillus spp.
-
A filamentous fungus in the CSF of a patient with meningitis that grew Candida albicans in culture subsequently.

-
Transmission electron micrograph of a C. neoformans cell seen in CSF in an AIDS patients with remarkably little capsule present. These cells may be mistaken for lymphocytes.
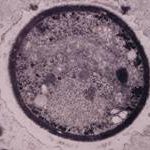
-
India ink preparation of CSF showing multiple yeasts with large capsules, and narrow buds to smaller daughter cells, typical of C. neoformans