Date: 26 November 2013
D Sinusitis radiology with fluid level
Copyright:
Fungal Infection Trust
Notes:
Bronchography (A & B)is an old technique for visualising the bronchial tree, by introducing radio-opaque dye into the airways and then taking a chest Xray. It was the first means used to diagnose bronchiectasis, seen in these examples below. An historical description of the technique from 1922 can be seen here
Nowadays CT scanning of the chest is used for this purpose with 3D reconstruction in some cases.
White cell scan (C) This pair of white cell scans from different people show almost no white cells in the lungs on the left, as in a healthy person (the spleen is the ‘hottest area). The scan on the right shows grossly increased update, especially in the left lung (seen on the right). This is the typical feature of severe bronchiectasis with large amounts of neutrophils and other phagocytes present.
Sinusitis Plain X-ray (D) of the face showing the maxillary sinuses. The right maxillary sinus is complete fluid filled and the left side (seen on the right) has a fluid level. These features may be seen with severe acute bacterial sinusitis, but also other causes of sinusitis, including allergic rhinosinusitis.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
Light microscopic image of hyphae in an aspergilloma (10x magnification)

-
Light microscopic image of hyphae in an aspergilloma (400x magnification)
-
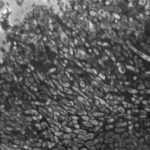
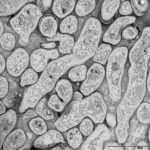
An aspergilloma (or fungal ball) is a mass of fungus found inside the body, for example inside cavities such as the lungs or sinuses, or as abscesses in organs such as the brain or kidney. They are made up of threadlike fungal strands (hyphae) that are densely packed but only around 1/200 of a millimetre in diameter. A mass of hyphae is called a mycelium.
In this image, a slice through an aspergilloma has been imaged using a transmission electron microscope.
-
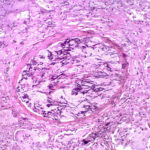
Aspergillus can punch through the lining of the lungs and invade the blood vessels below, in a process called angioinvasion. It can result in blockage (occlusion) of the blood vessel and damage to the local tissue through lack of oxygen (infarction). In severely immunocompromised patients, fragments can even break off and travel to other organs in the body.
In this image, a tissue section through a blocked blood vessel has been stained with the dyes haematoxylin (purple, binds DNA) and eosin (pink, binds proteins).
-
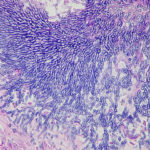
Showing the edge of a colony of aspergillus forming a fungal ball. The fungal hyphae exhibit dichotomous 45 degree angle branching and septae typical of Aspergillus.
-
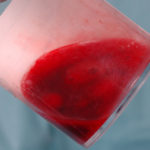
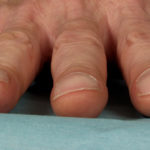
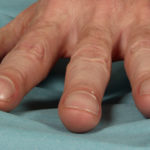
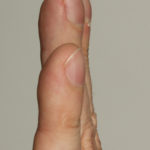
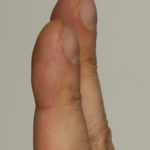
Pt CJ finger clubbing, this patient had chronic cavitary pulmonary aspergillosis, with an aspergilloma since 1988, following an episode of haemoptysis. Currently patient still has symptomatic disease.
Images E,F Blood stained sputum samples from this patient.
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
-
Disseminated, invasive aspergillosis showing dichotomously branching hyphae. Original magnification x300. Stained with Gomori Methenamine Silver (GMS).
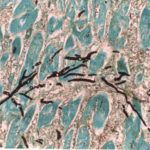
-
Disseminated, invasive aspergillosis showing dichotomously branching hyphae. Original magnification x150. Stained with Gomori Methenamine Silver (GMS).

-
Disseminated, invasive aspergillosis showing dichotomously branching hyphae. Original magnification x50. Stained with Gomori Methenamine Silver (GMS).

-
Light microscopical appearance of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis showing vessel occlusion with thrombus and distal infarction (Haematoxylin and eosin, x100)

