Date: 26 November 2013
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
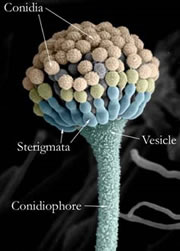
Aspergillus and other filamentous fungi produce clusters of spores known as fruiting bodies, which correspond with the mushrooms that other groups of fungi produce. They are very useful in diagnosing fungal diseases because their structures are strongly characteristic of different species.
Aspergillus was originally named for its fruiting body because it was thought that they resemble as aspergillum, which is a device used for sprinkling holy water.
In this picture, scanning electron microscopy has been used to visualise the fruiting body and false colour has been added to highlight the different parts.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
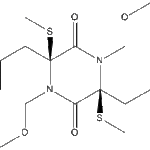
Secondary metabolites, structure diagram: Trivial name – Asterriquinone derivative 1
-
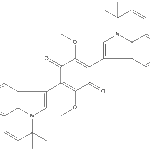
Secondary metabolites, structure diagram: Trivial name – Asterriquinone derivative 2
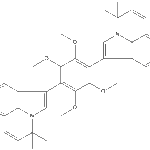
-
Secondary metabolites, structural diagram: Trivial name – Asterriquinones (1)

-
Secondary metabolites, structure diagram: Trivial name – Asterriquinones (2)
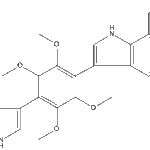
-
Secondary metabolites, structure diagram: Trivial name – Auranthine

-
Secondary metabolites, structure diagram: Trivial name – auroglaucine

-
Secondary metabolites, structure diagram: Trivial name – Austamide
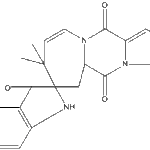
-
Secondary metabolites, structure diagram: Trivial name – b-Resorcylaldehyde-a-14C
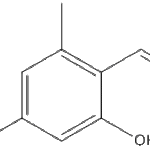
-
Secondary metabolites, structure diagram: Trivial name – b-Resorcylic-carboxy-14C acid
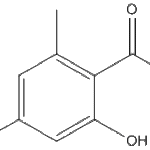
-
Secondary metabolites, structure diagram: Trivial name – benzylbismethylthiopiperazinedione metabolite 1