Date: 26 November 2013
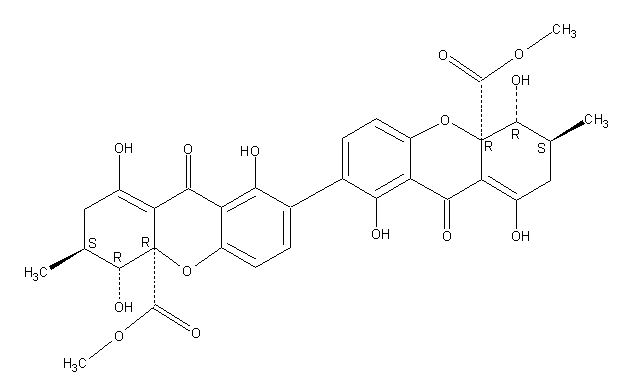
Secondary metabolites, structure diagram: Trivial name – secalonic acid D
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
Species: A. aculeatus, A. ochraceus, A. uvarumSystematic name: [7,7′-Bi-4aH-xanthene]-4a,4’a-dicarboxylic acid, 2,2′,3,3′,4,4′,9,9′-octahydro-1,1′,4,4′,8,8′-hexahydroxy-3,3′-dimethyl-9,9′-dioxo-, dimethyl ester, (3S,3’S,4R,4’R,4aR,4’aR)-Molecular formulae: C32 H30 O14Molecular weight: 638.581Chemical abstracts number: 35287-69-5Selected references: Andersen, Raymond; Buechi, George; Kobbe, Brunhilde; Demain, Arnold L. (Dep. Chem., Massachusetts Inst. Technol., Cambridge, Mass., USA). J. Org. Chem., 42(2), 352-3 (English) 1977.Kurobane I, Vining LC, McInnes AG. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 1979 Dec;32(12):1256-66. Biosynthetic relationships among the secalonic acids. Isolation of emodin, endocrocin and secalonic acids from Pyrenochaeta terrestris and Aspergillus aculeatus.Toxicity: mouse LD50 intraperitoneal 26500ug/kg (26.5mg/kg) EFFECTS: VASCULAR: REGIONAL OR GENERAL ARTERIOLAR OR VENOUS DILATION LUNGS, THORAX, OR RESPIRATION: CHANGES IN PULMONARY VASCULAR RESISTANCE LUNGS, THORAX, OR RESPIRATION: OTHER CHANGES Applied and Environmental Microbiology. Vol. 39, Pg. 285, 1980. mouse LD50 intravenous 25mg/kg (25mg/kg) EFFECTS: BEHAVIORAL: CONVULSIONS OR EFFECT ON SEIZURE THRESHOLD BEHAVIORAL: FOOD INTAKE (ANIMAL) SKIN AND APPENDAGES (SKIN): HAIR: OTHER Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health. Vol. 5, Pg. 1159, 1979.mouse LDLo oral 30mg/kg (30mg/kg) EFFECTS: SENSE ORGANS AND SPECIAL SENSES: OTHER CHANGES: OLFACTION LIVER: HEPATITIS (HEPATOCELLULAR NECROSIS), ZONAL LUNGS, THORAX, OR RESPIRATION: OTHER CHANGES Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology. Vol. 48, Pg. A14, 1979. rat LD50 oral 22mg/kg (22mg/kg) EFFECTS: SENSE ORGANS AND SPECIAL SENSES: OTHER CHANGES: OLFACTION LIVER: HEPATITIS (HEPATOCELLULAR NECROSIS), ZONAL LUNGS, THORAX, OR RESPIRATION: OTHER CHANGES Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology. Vol. 48, Pg.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
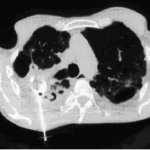
Image A. Scan shows large bore needle in one of the cavities on the right. The contrast media is mixed with amphotericin B and is whiter than surrounding lung tissue and fungal ball. The contrast surrounds the aspergilloma present in this cavity. Some of the contrast has fallen by gravity in another cavity anteriorly below the one being injected, showing communication between the cavities.
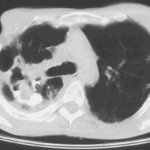
Image B. Scan showing contrast media mixed with amphotericin B injected into a multicystic cavity in the right upper lobe. The contrast (white) flows around the aspergilloma present in this cavity. The contrast falls by gravity posteriorly.
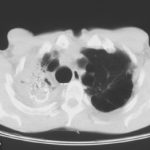
Image C. The opposite lung shows multiple empty cystic spaces with little normal lung.
Image D. There is substantial pleural thickening surrounding the irregular cavity containing the aspergilloma.
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
-
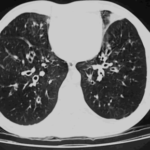
Extensive multilobar, varicose bronchiectasis, with some cyst formation most marked on the left anteriorly. Also some inhomogeneity of the pulmonary parenchyma secondary to air trapping in several affected segments.
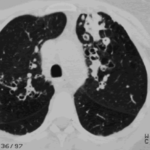
-
CT scans of thorax. Anterior left-sided bronchiectasis with extensive mucous plugging and with some proximal bronchiectasis and plugging on the right.

-
Bilateral multilobar varicose bronchiectasis affecting the segmental and small order bronchi, with some distal plugging.
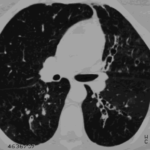
-
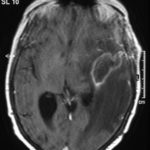
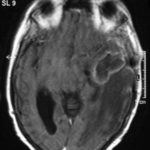
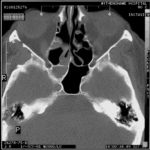
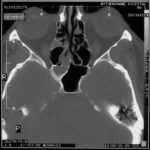
T1 weighted, gadolinium enhanced magnetic resonance brain scan. This 43 year-old alcoholic woman underwent laparoscopic cholecystectomy in January 2001. Ten days after surgery, she became confused, dysphasic and eventually had tonic-clonic seizures. A CT scan showed non-communicating hydrocephalus with ventriculitis. She underwent many complicated neurosurgical interventions, and received long term broad-spectrum antimicrobials and dexamethasone. One month later, she had generalized seizures, and a large abscess was observed on scan (see images). A heavy growth of A. fumigatus was retrieved from the abscess, and amphotericin B and 5-flucytosine were started. Antifungal therapy was changed voriconazole due to intolerance to amphotericin B and worsening disorientation. Voriconazole dosing (which varied from 300mg to 100mg twice daily) was guided by plasma concentrations as enzyme induction with rifampicin and carbamazepine, and reduction in clearance with alcoholic liver disease complicated her voriconazole dosing. Steroids were gradually reduced. She had a good recovery and completed 9 months of voriconazole.
Despite air filtration in the operating rooms, she apparently acquired an intra-operative infection, probably accelerated in presentation by concurrent dexamethasone. Rapid diagnosis and optimization of voriconazole dosing lead to a good outcome.
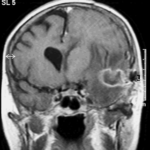 ,
, 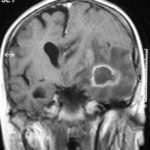 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
-
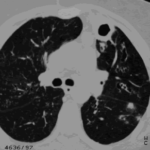
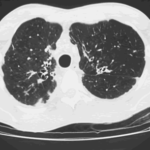
Allergic Broncho-pulmonary aspergillosis. Pt CT. Extensive severe saccular bronchiectasis of the left lower lobe and to a lesser extent of the left upper and right lower lobe.
-
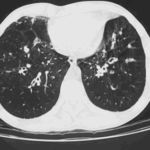
Ct scan of chest. This patient with severe ABPA, serologically and radiologically, developed a spectrum of lesions in the lung. In this cut, a cavitating infiltrate in the anterior segment of the left upper lobe was visualised together with some bronchial thickening and bronchiectasis in the left upper and lower lobe.


 ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,