Date: 26 November 2013
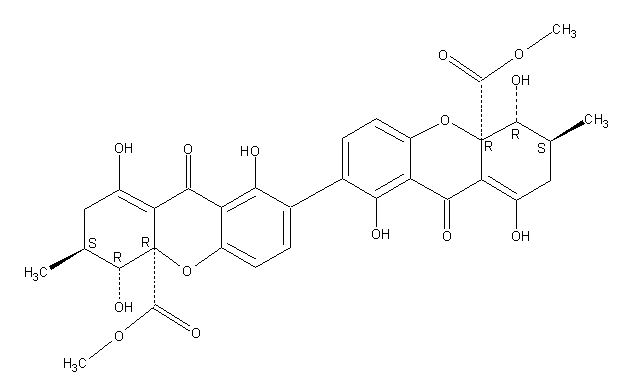
Secondary metabolites, structure diagram: Trivial name – secalonic acid D
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
Species: A. aculeatus, A. ochraceus, A. uvarumSystematic name: [7,7′-Bi-4aH-xanthene]-4a,4’a-dicarboxylic acid, 2,2′,3,3′,4,4′,9,9′-octahydro-1,1′,4,4′,8,8′-hexahydroxy-3,3′-dimethyl-9,9′-dioxo-, dimethyl ester, (3S,3’S,4R,4’R,4aR,4’aR)-Molecular formulae: C32 H30 O14Molecular weight: 638.581Chemical abstracts number: 35287-69-5Selected references: Andersen, Raymond; Buechi, George; Kobbe, Brunhilde; Demain, Arnold L. (Dep. Chem., Massachusetts Inst. Technol., Cambridge, Mass., USA). J. Org. Chem., 42(2), 352-3 (English) 1977.Kurobane I, Vining LC, McInnes AG. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 1979 Dec;32(12):1256-66. Biosynthetic relationships among the secalonic acids. Isolation of emodin, endocrocin and secalonic acids from Pyrenochaeta terrestris and Aspergillus aculeatus.Toxicity: mouse LD50 intraperitoneal 26500ug/kg (26.5mg/kg) EFFECTS: VASCULAR: REGIONAL OR GENERAL ARTERIOLAR OR VENOUS DILATION LUNGS, THORAX, OR RESPIRATION: CHANGES IN PULMONARY VASCULAR RESISTANCE LUNGS, THORAX, OR RESPIRATION: OTHER CHANGES Applied and Environmental Microbiology. Vol. 39, Pg. 285, 1980. mouse LD50 intravenous 25mg/kg (25mg/kg) EFFECTS: BEHAVIORAL: CONVULSIONS OR EFFECT ON SEIZURE THRESHOLD BEHAVIORAL: FOOD INTAKE (ANIMAL) SKIN AND APPENDAGES (SKIN): HAIR: OTHER Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health. Vol. 5, Pg. 1159, 1979.mouse LDLo oral 30mg/kg (30mg/kg) EFFECTS: SENSE ORGANS AND SPECIAL SENSES: OTHER CHANGES: OLFACTION LIVER: HEPATITIS (HEPATOCELLULAR NECROSIS), ZONAL LUNGS, THORAX, OR RESPIRATION: OTHER CHANGES Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology. Vol. 48, Pg. A14, 1979. rat LD50 oral 22mg/kg (22mg/kg) EFFECTS: SENSE ORGANS AND SPECIAL SENSES: OTHER CHANGES: OLFACTION LIVER: HEPATITIS (HEPATOCELLULAR NECROSIS), ZONAL LUNGS, THORAX, OR RESPIRATION: OTHER CHANGES Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology. Vol. 48, Pg.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
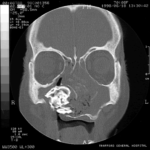
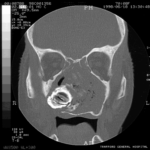
Patient MB X rays and CT scans. Chronic calcified maxillary sinusitis, patient had a palate defect.A. fumigatus cultured.
Images A&B Plain X rays antero-posterior and lateral, pre-operatively of Pt MB aged 76 who presented with unilateral nasal stuffiness and difficulty getting dentures fitted. She had hda these symptoms for many years. A large irregular calcified mass can be seen replacing the right maxillary sinus.
Images C D & E Coronal CT scan images of Pt MB showing a completely obstructed nasal cavity bilaterally and loss of internal nasal architecture. On the right side is large lamellar calcified lesion embedded in the extensive inflammatory material. Loss of bony margins is seen in numerous locations. This material was all removed surgically and showed mostly necrotic debris with Charcot-Leyden crystals and a few eosinophils and degenerate fungal hyphae. Aspergillus fumigatus was cultured from the material, especially infero-laterally on the right.
Image F Photograph through the mouth post-operatively showing the palate and a large defect in its right side. Through the defect can be seen the interior of the right maxillary sinus and nasal cavity with the inferior turbinate just visible.
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
-
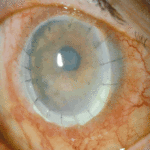
Aspergillus keratitis. Severe aspergillus infection with large area of corneal ulceration and deep stromal involvement

-
Sequence of images showing ocular surface change which unusually predisposed to severe fusarium keratitis in an elderly woman. Successful treatment involved full thickness corneal transplantation shown 2 weeks and then 2 years after surgery.

-
Sequence of images showing ocular surface change which unusually predisposed to severe fusarium keratitis in an elderly woman. Successful treatment involved full thickness corneal transplantation shown 2 weeks and then 2 years after surgery.
-
Sequence of images showing ocular surface change which unusually predisposed to severe fusarium keratitis in an elderly woman. Successful treatment involved full thickness corneal transplantation shown 2 weeks and then 2 years after surgery.
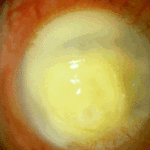
-
Sequence of images showing ocular surface change which unusually predisposed to severe fusarium keratitis in an elderly woman. Successful treatment involved full thickness corneal transplantation shown 2 weeks and then 2 years after surgery
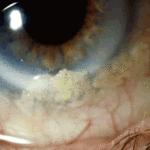
-
Aspergillus keratitis. Shrunken eye as a consequence of this infection