Date: 26 November 2013
Secondary metabolites, structure diagram: Trivial name – malformins
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
Species: A. nigerSystematic name: Cyclo(D-cysteinyl-D-cysteinyl-L-valyl-D-leucyl-L-leucyl), cyclic (1®2)-disulfideMalformin AMolecular formulae: C23H39N5O5S2Molecular weight: 529.718Chemical abstracts number: 3022-92-2Selected references: Kim KW, Sugawara F, Yoshida S, Murofushi N, Takahashi N, Curtis RW. Structure of malformin B, a phytotoxic metabolite produced by Aspergillus niger. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 1993 May;57(5):787-91.Toxicity: mouse LD50 intraperitoneal 3100ug/kg (3.1mg/kg) EFFECTS: GASTROINTESTINAL: OTHER CHANGES. LIVER: OTHER CHANGES. KIDNEY, URETER, AND BLADDER: OTHER CHANGES Agricultural and Biological Chemistry. Vol. 39, Pg. 1325, 1975.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
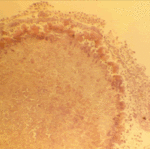
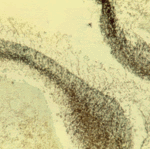
The periphery of the fungus ball is deeply eosinophilic because of the deposition of Splendore-Hoeppli material.
-
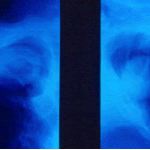
Single fungal ball, moving. Radiographic appearance of a fungus ball, showing movement as the patient’s position changes.
-
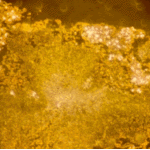
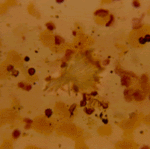
Oxalate crystals in the cavity wall surrounding an Aspergillus niger fungus ball (H&E, dark field, x 25).
-
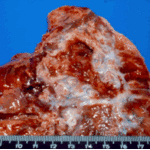
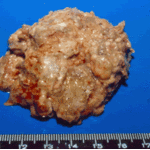
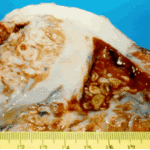
Aspergilloma patient. Gross pathology appearance of a fungus ball.
-
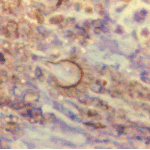
Conidiophores of Aspergillus fumigatus in the mass of the fungal ball surrounded by mycelia (H&E, x 400).
-
Aspergillus niger fungal ball. Calcium oxalate crystals in Aspergillus niger fungal ball. Also shown are darkly pigmented, rough-walled conidia associated with Aspergillus niger infection.
-
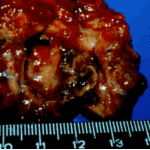
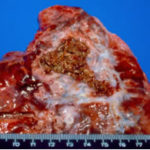
Aspergillus niger fungus ball within an old tuberculous cavern. This patient had diabetes, a disease commonly associated with A. niger infection.


 ,
, 
 ,
,