Date: 26 November 2013
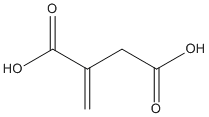
Secondary metabolites, structure diagram: Trivial name – Itaconic acid
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
Species: A. terreusSystematic name: 2-methylidenebutanedioic acidMolecular formulae: C5H6O4Molecular weight: 130.099Chemical abstracts number: 811Selected references: LARSEN H, EIMHJELLEN KE. The mechanism of itaconic acid formation by Aspergillus terreus. 1. The effect of acidity. Biochem J. 1955 May;60(1):135-9. EIMHJELLEN KE, LARSEN H. The mechanism of itaconic acid formation by Aspergillus terreus. 2. The effect of substrates and inhibitors. Biochem J. 1955 May;60(1):139-47.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
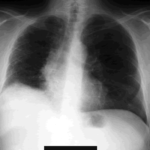
The chest x-ray shows a patient who had a left lung transplanted in May 2003 for cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis, which was diagnosed post-transplant as sarcoidosis.
-
Gross pathology demonstrating the great pleural thickness and two cavities (upper lobe and superior segment of lower lobe) with fragments of fungal mass.

-
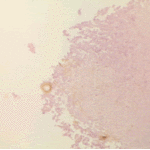
Histopathological appearance of a fungus ball. Note a conidial head resulting from fungal exposure to the air.
-
Histopathological appearance of a fungus ball caused by Scedosporium apiospermum. The presence of anneloconidia differentiates it from Aspergillus.

-
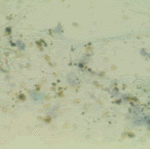
Chronic necrotising aspergillosis. Hyaline hyphal and calcium oxalate crystals obtained by needle aspirate biopsy from a diabetic patient with chronic necrotizing aspergillosis caused by Aspergillus niger (Papanicolaou, x 100).
-
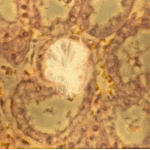
Aspergillus niger fungus ball and acute oxalosis. Higher magnification of adjacent replicate section.
-
Oxalate crystals within renal tubuli (H&E, phase contrast, x 100). This patient developed acute oxalosis.
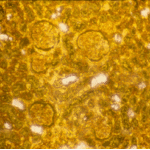
-
Lung surface. Fungus ball, severe parenchymal fibrosis and pleural thickening.


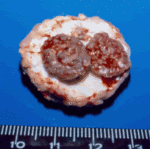 ,
, 
 ,
,  ,
, 