Date: 26 November 2013
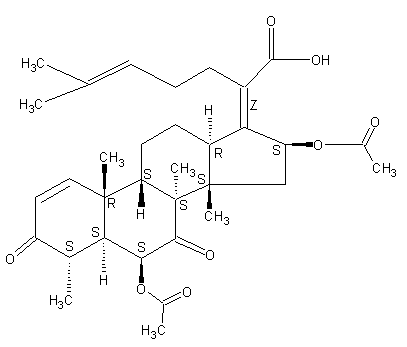
Secondary metabolites, structure diagram: Trivial name – helvolic acid
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
Species: A. fumigatiaffinis, A. fumigatus, A. novofumigatusSystematic name: 29-Nordammara-1,17(20),24-trien-21-oic acid, 6,16-bis(acetyloxy)-3,7-dioxo-, (4a,6b,8a,9b,13a,14b,16b,17Z)- (9CI)Helvolic acid (6CI, 7CI); (Z)-6b,16b-Dihydroxy-3,7-dioxo-29-nor-8a,9b,13a,14b-dammara-1,17(20),24-trien-21-oic acid diacetate; FumigacinMolecular formulae: C33H44O8Molecular weight: 568.698Chemical abstracts number: 29400-42-8Selected references: Waksman SA , et al. The production of two antibacterial substances, fumigacin and clavacin. Science 96: 202-203, 1942WILLIAMS TI.Biochem J. 1952 Jul;51(4):538-42. Some chemical properties of helvolic acid.OKUDA S, IWASAKI S, TSUDA K, SANO Y, HATA T, UDAGAWA S, NAKAYAMA Y, YAMAGUCHI H. THE STRUCTURE OF HELVOLIC ACID.Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 1964 Jan;12:121-4. Amitani R, Taylor G, Elezis EN, Llewellyn-Jones C, Mitchell J, Kuze F, Cole PJ, Wilson R. Purification and characterization of factors produced by Aspergillus fumigatus which affect human ciliated respiratory epithelium. Infect Immun. 1995 Sep;63(9):3266-71.Toxicity: mouse LD50 intraperitoneal 400mg/kg (400mg/kg) Antibiotics: Origin, Nature, and Properties, Korzyoski, T., et al., eds., Washington, DC, American Soc. for Microbiology, 1978Vol. 3, Pg. 1837, 1978. mouse LDLo intravenous 500mg/kg (500mg/kg) Antibiotics: Origin, Nature, and Properties, Korzyoski, T., et al., eds., Washington, DC, American Soc. for Microbiology, 1978Vol. 3, Pg. 1837, 1978.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
BAL specimen showing hyaline, septate hyphae consistent with Aspergillus, stained with Blankophor

-
Mucous plug examined by light microscopy with KOH, showing a network of hyaline branching hyphae typical of Aspergillus, from a patient with ABPA.

-
Corneal scraping stained with lactophenol cotton blue showing beaded septate hyphae not typical of either Fusarium spp or Aspergillus spp, being more consistent with a dematiceous (ie brown coloured) fungus
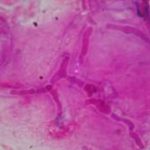
-
Corneal scrape with lactophenol cotton blue shows separate hyphae with Fusarium spp or Aspergillus spp.
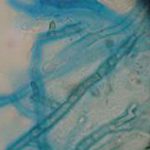
-
A filamentous fungus in the CSF of a patient with meningitis that grew Candida albicans in culture subsequently.

-
Transmission electron micrograph of a C. neoformans cell seen in CSF in an AIDS patients with remarkably little capsule present. These cells may be mistaken for lymphocytes.
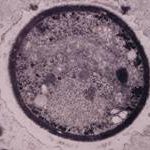
-
India ink preparation of CSF showing multiple yeasts with large capsules, and narrow buds to smaller daughter cells, typical of C. neoformans