Date: 26 November 2013
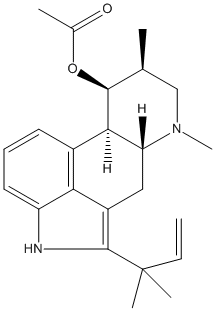
Secondary metabolites, structure diagram: Trivial name – fumigaclavine C
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
Species: A. fumigatusSystematic name: Ergolin-9-ol, 2-(1,1-dimethyl-2-propenyl)-6,8-dimethyl-, acetate (ester), (8-beta,9-beta)-Molecular formulae: C23H30N2O2Molecular weight: 366.497Chemical abstracts number: 62867-47-4Selected references: COLE RJ ; KIRKSEY JW ; DORNER JW ; WILSON DM ; JOHNSON J C JR ; JOHNSON AN ; BEDELL DM ; SPRINGER JP ; CHEXAL KK ; ET AL. J AGRIC FOOD CHEM; 25 (4). 1977 826-830. Mycotoxins produced by Aspergillus fumigatus species isolated from molded silage.Toxicity: The clavine alkaloids, fumigaclavine A, a new alkaloid designated fumigaclavine C and several tremorgens belonging to the fumitremorgen group were produced by A. fumigatus strains isolated from molded silage. The LD50 of fumigaclavine C was about 150 mg/kg oral dose in day-old cockerels. Calves dosed with crude extracts of A. fumigatus cultures experienced severe diarrhea, irritability and loss of appetite. Postmortem examination showed serous enteritis and evidence of interstitial changes in the lungs; abnormal changes were not found in other tissues.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
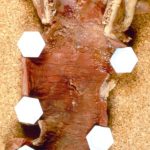
Pt FT. Autopsy appearance of the trachea, after the adherent pseudomembrane had been removed, revealing confluent ulceration superiorly with small green plaques of Aspergillus growth on the trachea inferiorly.
-
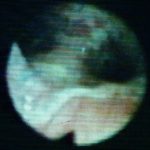
This view was obtained in a lung transplant recipient at bronchoscopy. Aspergillus fumigatus was grown from bronchial lavage but invasion was not demonstrated on bronchial biopsy. Symptoms improved with itraconazole therapy and abnormal appearances had resolved within 2 weeks.

-
Bronchoscopic view of Aspergillus tracheobronchitis. Bronchial lavage revealed hyphae in microscopy and cultures grew A.fumigatus. This man had received a lung transplant a few weeks before. Invasion of mucosa, but not cartilage, was demonstrated histologically. He responded rapidly to oral itraconazole.
-
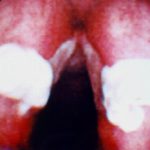
This view from indirect laryngoscopy illustrates bilateral lesions on the larynx that on biopsy were shown to be due to Aspergillus. This is a rare disease in non-immunocompromised patients.
-
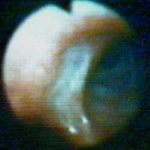
Bronchoscopic view of a deep bronchial ulcer in a lung transplant patient. Biopsies through the ulcer yielded cartilage with hyphae invading it. Fungal cultures of bronchial lavage grew Aspergillus fumigatus. He responded to oral itraconazole therapy.
-
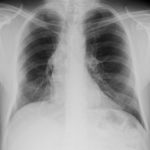
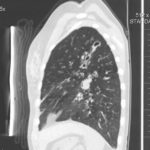
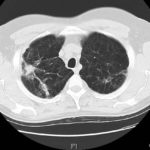
Patient had life threatening pneumonia, cavity formation was later observed. He later presented with a fungal ball. The aspergilloma was removed by surgical resection of the right upper lobe.
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,