Date: 26 November 2013
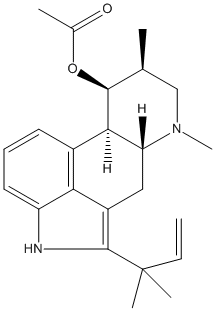
Secondary metabolites, structure diagram: Trivial name – fumigaclavine C
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
Species: A. fumigatusSystematic name: Ergolin-9-ol, 2-(1,1-dimethyl-2-propenyl)-6,8-dimethyl-, acetate (ester), (8-beta,9-beta)-Molecular formulae: C23H30N2O2Molecular weight: 366.497Chemical abstracts number: 62867-47-4Selected references: COLE RJ ; KIRKSEY JW ; DORNER JW ; WILSON DM ; JOHNSON J C JR ; JOHNSON AN ; BEDELL DM ; SPRINGER JP ; CHEXAL KK ; ET AL. J AGRIC FOOD CHEM; 25 (4). 1977 826-830. Mycotoxins produced by Aspergillus fumigatus species isolated from molded silage.Toxicity: The clavine alkaloids, fumigaclavine A, a new alkaloid designated fumigaclavine C and several tremorgens belonging to the fumitremorgen group were produced by A. fumigatus strains isolated from molded silage. The LD50 of fumigaclavine C was about 150 mg/kg oral dose in day-old cockerels. Calves dosed with crude extracts of A. fumigatus cultures experienced severe diarrhea, irritability and loss of appetite. Postmortem examination showed serous enteritis and evidence of interstitial changes in the lungs; abnormal changes were not found in other tissues.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
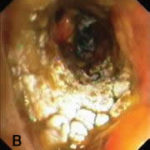
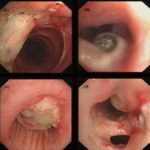
Bronchoscopic manifestations of Aspergillus tracheobronchitis. (a) Type I. Inflammatory infiltration, mucosa hyperaemia and plaques of pseudomembrane formation in the lumen without obvious airway occlusion. (b) Type II. Deep ulceration of the bronchial wall. (c) Type III. Significant airway occlusion by thick mucous plugs full of Aspergillus without definite deeper tissue invasion. (d) Type IV. Extensive tissue necrosis and pseudomembrane formation in the lumen with airway structures and severe airway occlusion (Wu 2010).
-
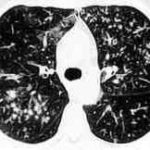
High resolution CT showing centrilobular nodular opacities and branching linear opacities (tree-in-bud appearance) (Al-Alawi 2007).
-
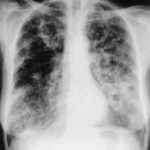
Chest X-ray showing poorly defined bilateral nodular opacities (Al-Alawi 2007).
-
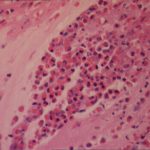
Gross pathologic specimen from autopsy shows the bronchial lumen covered by multiple whitish endobronchial nodules (arrows) (Franquet 2002).

-
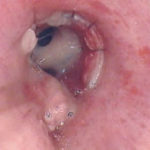
Invasive tracheobronchitis showing numerous nodules seen during bronchoscopy (Ronan D’Driscoll).

-
Pseudomembranous seen overlying the bronchial mucosa (Tasci 2006).