Date: 26 November 2013
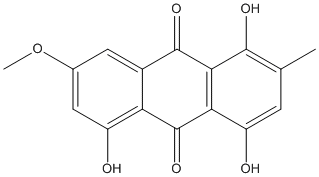
Secondary metabolites, structure diagram: trivial name – erythroglaucin
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
Species: A. chevalieriSystematic name: ANTHRAQUINONE, 7-METHOXY-2-METHYL-1,4,5-TRIHYDROXY- 1,4,5-Trihydroxy-7-methoxy-2-methylanthra-9,10-quinone 9,10-Anthracenedione, 1,4,5-trihydroxy-7-methoxy-2-methyl-Molecular formulae: C16H12O6Molecular weight: 300.263Chemical abstracts number: 476-57-3Selected references: Bachmann M, Blaser P, Luthy J, Schlatter C. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 1992 Mar-Apr;11(2):49-52. Toxicity and mutagenicity of anthraquinones from Aspergillus chevalieri.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
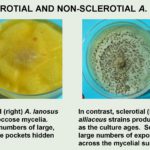
Sclerotial strains produce bright yellow, floccose mycelia. Sclerotial strains produce small numbers of large, fused sclerotial bodies in discrete pockets hidden within the mycelium.

-
Aspergillus alliaceus. No branching was observed in A. alliaceus conidiophores. Sclerotial strains typically produce large numbers of exposed, uniformly-shaped sclerotia across the mycelial surface.

-
Aspergillus alliaceus – Sclerotial. A. alliaceus strains produce flat, pale mycelia that darken as the culture ages.Sclerotial strains typically produce large numbers of exposed, uniformly-shaped sclerotia across the mycelial surface.

-
A. alliaceus strains produce flat, pale mycelia that darken as the culture ages.Sclerotial strains typically produce large numbers of exposed, uniformly-shaped sclerotia across the mycelial surface.