Date: 26 November 2013
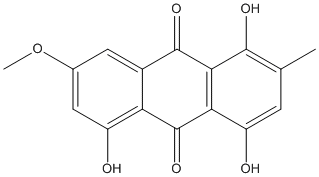
Secondary metabolites, structure diagram: trivial name – erythroglaucin
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
Species: A. chevalieriSystematic name: ANTHRAQUINONE, 7-METHOXY-2-METHYL-1,4,5-TRIHYDROXY- 1,4,5-Trihydroxy-7-methoxy-2-methylanthra-9,10-quinone 9,10-Anthracenedione, 1,4,5-trihydroxy-7-methoxy-2-methyl-Molecular formulae: C16H12O6Molecular weight: 300.263Chemical abstracts number: 476-57-3Selected references: Bachmann M, Blaser P, Luthy J, Schlatter C. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 1992 Mar-Apr;11(2):49-52. Toxicity and mutagenicity of anthraquinones from Aspergillus chevalieri.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
BAL specimen showing hyaline, septate hyphae consistent with Aspergillus, stained with Blankophor

-
Mucous plug examined by light microscopy with KOH, showing a network of hyaline branching hyphae typical of Aspergillus, from a patient with ABPA.

-
Corneal scraping stained with lactophenol cotton blue showing beaded septate hyphae not typical of either Fusarium spp or Aspergillus spp, being more consistent with a dematiceous (ie brown coloured) fungus
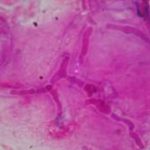
-
Corneal scrape with lactophenol cotton blue shows separate hyphae with Fusarium spp or Aspergillus spp.
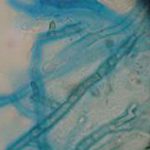
-
A filamentous fungus in the CSF of a patient with meningitis that grew Candida albicans in culture subsequently.

-
Transmission electron micrograph of a C. neoformans cell seen in CSF in an AIDS patients with remarkably little capsule present. These cells may be mistaken for lymphocytes.
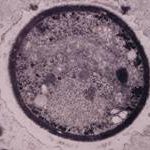
-
India ink preparation of CSF showing multiple yeasts with large capsules, and narrow buds to smaller daughter cells, typical of C. neoformans