Date: 26 November 2013
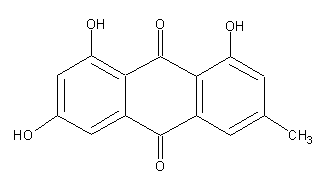
Secondary metabolites, structure diagram: Trivial name – Emodin/Archin/Emodol/Frandulic Acid
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
Species: A. aureus, A. sclerotiorum, A. terreus, A. wentiiSystematic name: 9,10-Anthracenedione, 1,3,8-trihydroxy-6-methyl- (9CI)Molecular formulae: C15H10O5Molecular weight: 270.237Chemical abstracts number: 518-82-1Selected references: Kiriyama, Noriki; Nitta, Keiichi; Sakaguchi, Yoshiaki; Taguchi, Yasuhisa; Yamamoto, Yuzuru (Fac. Pharm. Sci., Kanazawa Univ., Kanazawa, Japan). Chem. Pharm. Bull., 25(10), 2593-601 (English) 1977.Toxicity: Mean lethal dose of emodin orally administered to 1-day-old DeKalb cockerels was 3.7 mg/kg.BACKGROUND: Emodin, a widely available herbal remedy, was evaluated for potential effects on pregnancy outcome. METHODS: Emodin was administered in feed to timed-mated Sprague-Dawley (CD) rats (0, 425, 850, and 1700 ppm; gestational day [GD] 6-20), and Swiss Albino (CD-1) mice (0, 600, 2500 or 6000 ppm; GD 6-17). Ingested dose was 0, 31, 57, and approximately 80-144 mg emodin/kg/day (rats) and 0, 94, 391, and 1005 mg emodin/kg/day (mice). Timed-mated animals (23-25/group) were monitored for body weight, feed/water consumption, and clinical signs. At termination (rats: GD 20; mice: GD 17), confirmed pregnant dams (21-25/group) were evaluated for clinical signs: body, liver, kidney, and gravid uterine weights, uterine contents, and number of corpora lutea. Fetuses were weighed, sexed, and examined for external, visceral, and skeletal malformations/variations. RESULTS: There were no maternal deaths. In rats, maternal body weight, weight gain during treatment, and corrected weight gain exhibited a decreasing trend. Maternal body weight gain during treatment was significantly reduced at the high dose. In mice, maternal body weight and weight gain was decreased at the high dose. CONCLUSIONS: Prenatal mortality, live litter size, fetal sex ratio, and morphological development were unaffected in both rats and mice. At the high dose, rat average fetal body weight per litter was unaffected, but was significantly reduced in mice. The rat maternal lowest observed adverse effect level (LOAEL) was 1700 ppm; the no observed adverse effect level (NOAEL) was 850 ppm. The rat developmental toxicity NOAEL was > or =1700 ppm. A LOAEL was not established. In mice, the maternal toxicity LOAEL was 6000 ppm and the NOAEL was 2500 ppm. The developmental toxicity LOAEL was 6000 ppm (reduced fetal body weight) and the NOAEL was 2500 ppm. Copyright 2004 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
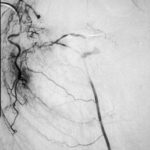
Embolisation 7 – patient WC. Angiogram of the lateral thoracic artery on subtraction film showing grossly abnormal vasculature inferiorly shunting along several anterior intercostal arteries to the internal mammary artery. In addition a pseudoaneurysm is shown.
-
Embolisation 6 – patient WC. Catheter tip in the lateral thoracic artery on screening film.
-
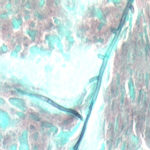
Grocott (silver) stain showing branching septate hyphae fairly typical of Aspergillus in mucus. The apparent right angle branching is unusual.
-
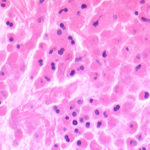
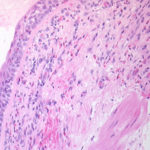
Bronchial mucosa under H & E stain showing numerous eosinophils deep to the mucosa, and mucus in the lumen of the bronchiole.
-
Grocott (silver) stain showing branching septate hyphae fairly typical of Aspergillus in mucus. The apparent right angle branching is unusual.

-
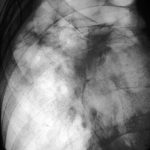
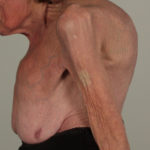
Severe kyphoscoliosis caused by greater than 40 years of prednisolone for ABPA and asthma.

-
These pictures show remarkable curvature of the spine as a result of collapse of the vertebral bodies of the thoracic vertebrae. This is a gross example of steroid-induced osteoporosis. The dose was not large in the last 10 years, typically 5-10mg daily, but multiple high dose courses and slow tapering lead to this outcome.
Her corticosteroid warning card is also demonstrated, as additional steroids are required for any significant illness or surgery, as her adrenal glands had completely atrophied.
Kindly supplied by Prof David Denning, South Manchester University Hospitals NHS Trust, Manchester UK
(© Fungal Research Trust)
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,