Date: 26 November 2013
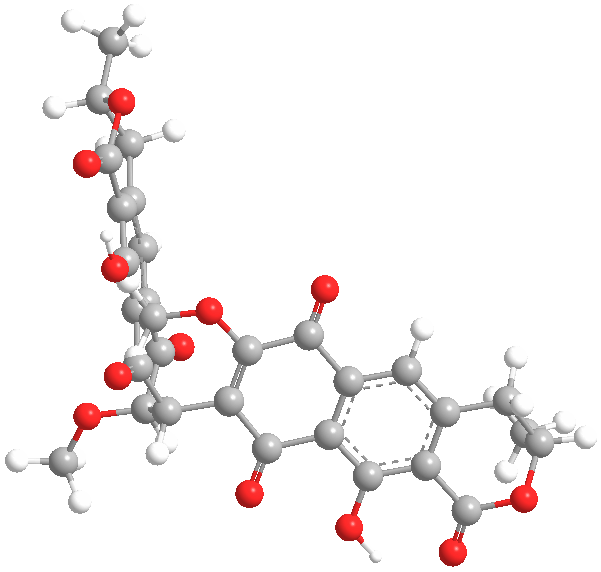
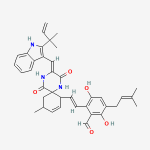
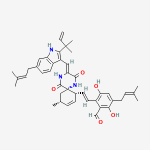
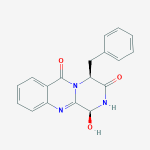
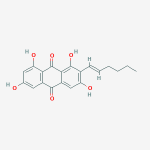
Secondary metabolites, 3D structure: Trivial name – xanthomegnin
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
Species: A. melleus, A. ochraceus, A. sulphureusSystematic name: (8,8′-Bi-1H-naphtho(1,2-c)pyran)-1,1′,7,7′,10,10′-hexone, 3,3′,4,4′-tetrahydro-6,6′-dihydroxy-9,9′-dimethoxy-3,3′-dimethyl-, (3R,3’R)- (8CI) (8,8′-BI-1H-NAPHTHO(2,3-c)PYRAN)-1,1′,6,6′,9,9′-HEXONE, 3,3′,4,4′-TETRAHYDRO-10, (8,8′-Bi-1H-naphtho(2,3-c)pyranMolecular formulae: C30H22O12Molecular weight: 574.488Chemical abstracts number: 1685-91-2Selected references: Durley RC, MacMillan J, Simpson TJ, Glen AT, Turner WB. Fungal products. Part XIII. Xanthomegnin, viomellin, rubrosulphin, and viopurpurin, pigments from Aspergillus sulphureus and Aspergillus melleus. J Chem Soc [Perkin 1]. 1975;(2):163-9. Stack ME, Mislivec PB. Production of xanthomegnin and viomellein by isolates of Aspergillus ochraceus, Penicillium cyclopium, and Penicillium viridicatum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Oct;36(4):552-4.Toxicity: Doses of 448 mg/kg body-weight in mice caused symptoms of liver damage including jaundice, necrotising cholangitis and other histological alterations. Robbers JE, Hong S, Tuite J, Carlton WW. Production of xanthomegnin and viomellein by species of Aspergillus correlated with mycotoxicosis produced in mice. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Dec;36(6):819-23.
Images library
-
Title
Legend