Date: 26 November 2013
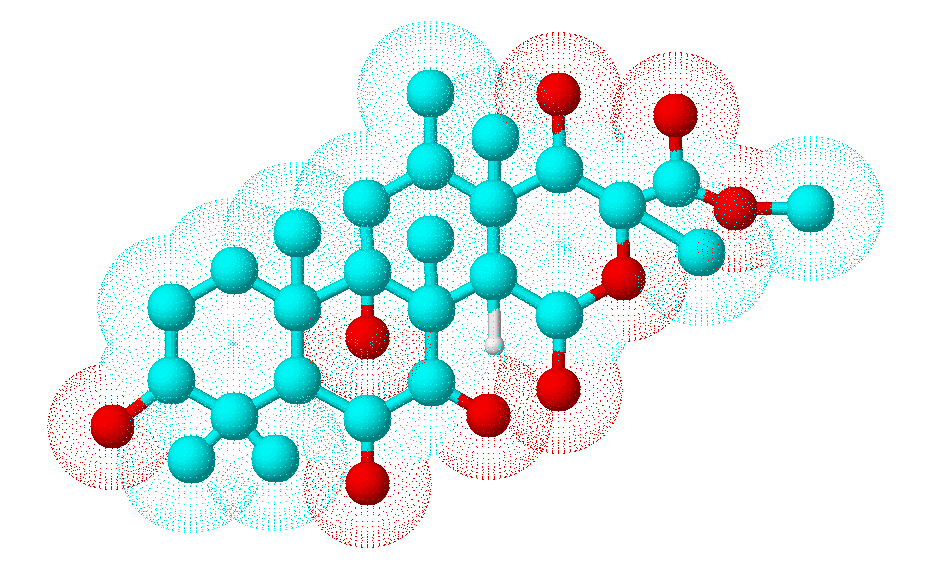
Secondary metabolites, 3D structure: Trivial name – terretonin
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
Species: A. terreusMolecular formulae: C26H3209Selected references: McIntyre, C.R.; Scott, F.E.; Simpson, T.J.; Trimble, L.A. and Vederas, J.C., Application of Stable Isotope Labelling Methodology to the Biosynthesis of the Mycotoxin, Terretonin, by Aspergillus terreus: Incorporation of 13C Labelled Acetates and Methionine, 2H and 13C, 18O Labelled Ethyl 3,5-Dimethylorsellinate and Oxygen-18 Tetrahedron 1989 45 () 2307-2321 J. P. Springer, J. W. Dorner, R. J. Cole, R. H. Cox Terretonin, a Toxic Compound from Aspergillus terreus J. Org. Chem. 1979 44 () 4852-4854
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
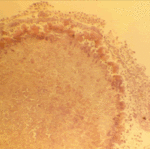
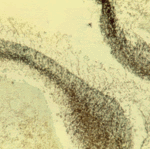
The periphery of the fungus ball is deeply eosinophilic because of the deposition of Splendore-Hoeppli material.
-
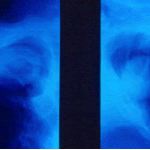
Single fungal ball, moving. Radiographic appearance of a fungus ball, showing movement as the patient’s position changes.
-
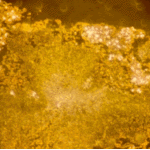
Oxalate crystals in the cavity wall surrounding an Aspergillus niger fungus ball (H&E, dark field, x 25).
-
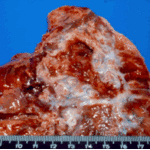
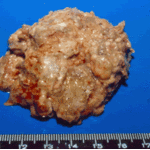
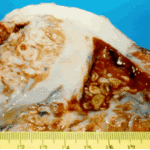
Aspergilloma patient. Gross pathology appearance of a fungus ball.
-
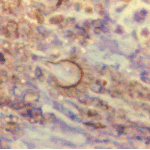
Conidiophores of Aspergillus fumigatus in the mass of the fungal ball surrounded by mycelia (H&E, x 400).
-
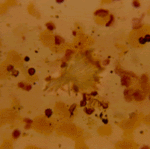
Aspergillus niger fungal ball. Calcium oxalate crystals in Aspergillus niger fungal ball. Also shown are darkly pigmented, rough-walled conidia associated with Aspergillus niger infection.
-
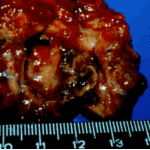
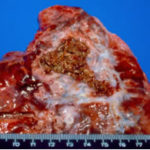
Aspergillus niger fungus ball within an old tuberculous cavern. This patient had diabetes, a disease commonly associated with A. niger infection.

 ,
, 
 ,
,