Date: 26 November 2013
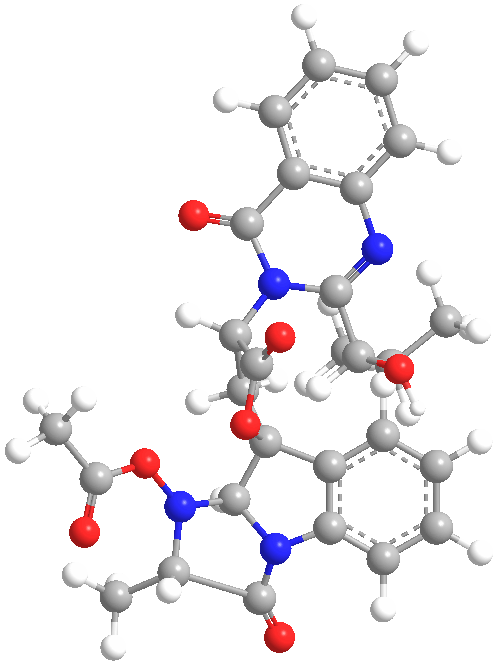
Secondary metabolites, 3D structure: Trivial name – Norisotryptoquivaline
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
Species A. fumigatusSystematic name Spiro[furan-2(5H),9′-[9H]imidazo[1,2-a]indole]-3′,5(2’H)-dione, 1′-(acetyloxy)-1′,3,4,9’a-tetrahydro-4-[2-[(1S)-1-hydroxy-2-methylpropyl]-4-oxo-3(4H)-quinazolinyl]-2′-methyl-, (2S,2’S,4R,9’aS)-Molecular formulae C28H28N4O7Molecular weight 532Chemical abstracts number 61897-84-5Selected references Yamazaki, Mikio; Okuyama, Emi; Maebayashi, Yukio (Res. Inst. Chemobiodyn., Chiba Univ., Chiba, Japan). Chem. Pharm. Bull., 27(7), 1611-17 (English) 1979.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
BAL specimen showing hyaline, septate hyphae consistent with Aspergillus, stained with Blankophor

-
Mucous plug examined by light microscopy with KOH, showing a network of hyaline branching hyphae typical of Aspergillus, from a patient with ABPA.

-
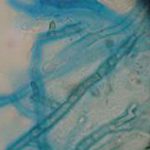
Corneal scraping stained with lactophenol cotton blue showing beaded septate hyphae not typical of either Fusarium spp or Aspergillus spp, being more consistent with a dematiceous (ie brown coloured) fungus
-
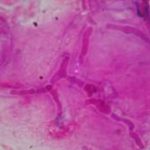
Corneal scrape with lactophenol cotton blue shows separate hyphae with Fusarium spp or Aspergillus spp.
-
A filamentous fungus in the CSF of a patient with meningitis that grew Candida albicans in culture subsequently.

-
Transmission electron micrograph of a C. neoformans cell seen in CSF in an AIDS patients with remarkably little capsule present. These cells may be mistaken for lymphocytes.
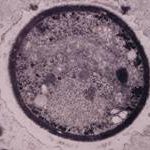
-
India ink preparation of CSF showing multiple yeasts with large capsules, and narrow buds to smaller daughter cells, typical of C. neoformans