Date: 26 November 2013
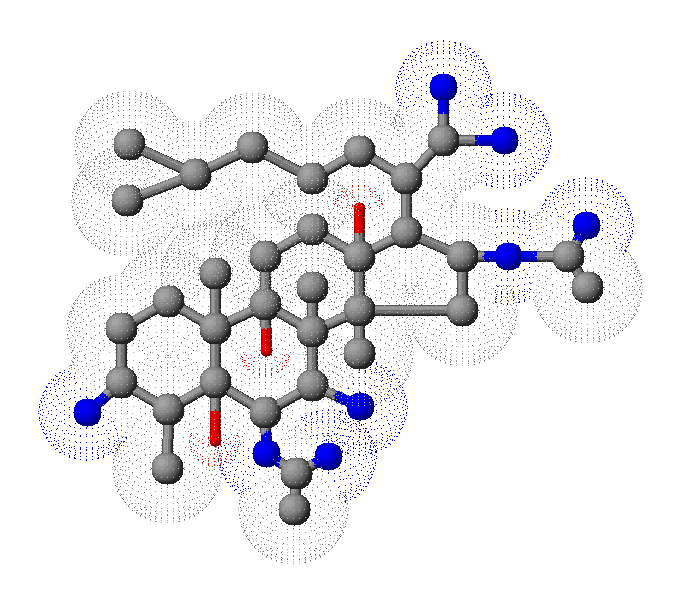
Secondary metabolites, 3D structure: Trivial name – helvolic acid
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
Species: A. fumigatiaffinis, A. fumigatus, A. novofumigatusSystematic name: 29-Nordammara-1,17(20),24-trien-21-oic acid, 6,16-bis(acetyloxy)-3,7-dioxo-, (4a,6b,8a,9b,13a,14b,16b,17Z)- (9CI)Helvolic acid (6CI, 7CI); (Z)-6b,16b-Dihydroxy-3,7-dioxo-29-nor-8a,9b,13a,14b-dammara-1,17(20),24-trien-21-oic acid diacetate; FumigacinMolecular formulae: C33H44O8Molecular weight: 568.698Chemical abstracts number: 29400-42-8Selected references: Waksman SA , et al. The production of two antibacterial substances, fumigacin and clavacin. Science 96: 202-203, 1942WILLIAMS TI.Biochem J. 1952 Jul;51(4):538-42. Some chemical properties of helvolic acid.OKUDA S, IWASAKI S, TSUDA K, SANO Y, HATA T, UDAGAWA S, NAKAYAMA Y, YAMAGUCHI H. THE STRUCTURE OF HELVOLIC ACID.Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 1964 Jan;12:121-4. Amitani R, Taylor G, Elezis EN, Llewellyn-Jones C, Mitchell J, Kuze F, Cole PJ, Wilson R. Purification and characterization of factors produced by Aspergillus fumigatus which affect human ciliated respiratory epithelium. Infect Immun. 1995 Sep;63(9):3266-71.Toxicity: mouse LD50 intraperitoneal 400mg/kg (400mg/kg) Antibiotics: Origin, Nature, and Properties, Korzyoski, T., et al., eds., Washington, DC, American Soc. for Microbiology, 1978Vol. 3, Pg. 1837, 1978. mouse LDLo intravenous 500mg/kg (500mg/kg) Antibiotics: Origin, Nature, and Properties, Korzyoski, T., et al., eds., Washington, DC, American Soc. for Microbiology, 1978Vol. 3, Pg. 1837, 1978.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
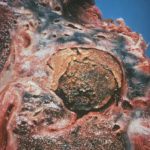
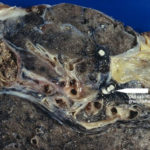
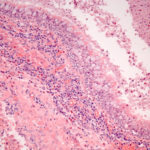
Macroscopic view medial aspect of left upper lobe of lung showing segmental collapse and congestion of lower segments, with mucus extruding from incised bronchi.
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
-
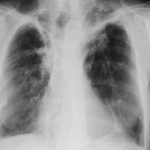
Born 75 years ago, Pt HK had 3 episodes of tuberculosis as a child and teenager, being treated with PAS and streptomycin. He suffered a ‘bad chest’ all his life and retired aged 54. Presenting with worsening and more frequent chest infections, he was referred with ‘bronchiectasis and Aspergillus sensitisation’. A diagnosis of chronic pulmonary aspergillosis was made in June 2009 on the basis of his chest radiograph and strongly positive Aspergillus precipitins (IgG antibodies) (titre 1/16). He also had Pseudomonas aeruginosa colonisation. His oxygen saturation was 87% and his pO2 6.8, pCO2 6.2 KPa.
His chest radiograph (see above, November 2009) was reported as showing; “ The lung fields are over-inflated. Bilateral apical fibrotic change secondary to old TB. No cavity seen.” At clinic, bilateral apical cavities were seen, with some associated pleural thickening at the left apex, without any evidence of a fungal ball.
He started posaconazole 400mg twice daily with therapeutic levels at subsequent visits. Sputum cultures never grew Aspergillus. Over the following 9 months he had no chest infections requiring antibiotics, his breathlessness worsened gradually and he remained easily fatigued. His Aspergillus antibody titres fell. Overall he felt better, but was concerned about declining respiratory status.