Date: 26 November 2013
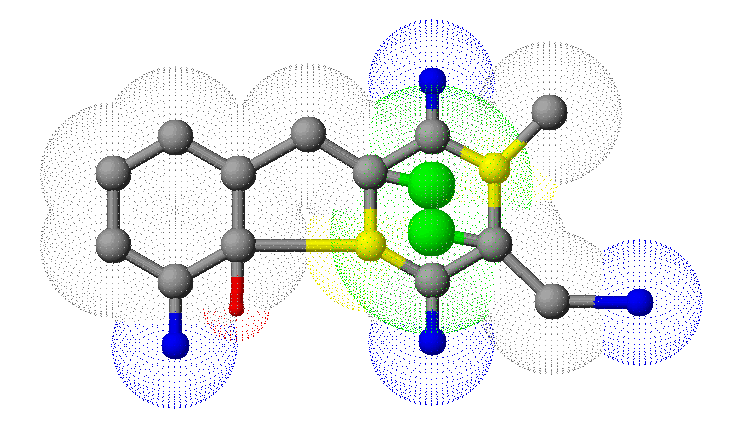
Secondary metabolites, 3D structure: Trivial name – gliotoxin
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
Species: A. flavus, A. fumigatus, A. niger, A. terreus, Eurotium chevalieri, Neosartorya pseudofischeriSystematic name: 10H-3,10a-Epidithiopyrazino[1,2-a]indole-1,4-dione, 2,3,5a,6-tetrahydro-6-hydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methyl-, (3R,5aS,6S,10aR)-Molecular formulae: C13H14N2O4S2Molecular weight: 326.393Chemical abstracts number: 67-99-2Selected references: Larsen TO, Smedsgaard J, Nielsen KF, Hansen MA, Samson RA, Frisvad JC. Production of mycotoxins by Aspergillus lentulus and other medically important and closely related species in section Fumigati. Med Mycol. 2007 May;45(3):225-32. Belkacemi, L.; Barton, R. C.; Hopwood, V.; Evans, E. G. V. (CORPORATE SOURCE PHLS Mycology Reference Laboratory, Department of Microbiology, University of Leeds, Leeds, UK). SOURCE Med. Mycol., 37(4), 227-233 (English) 1999 Blackwell Science Ltd. Lewis RE, Wiederhold NP, Lionakis MS, Prince RA, Kontoyiannis DP.J Clin Microbiol. 2005 Dec;43(12):6120-2. Frequency and species distribution of gliotoxin-producing Aspergillus isolates recovered from patients at a tertiary-care cancer center.Toxicity: Gliotoxin posseses a spectrum of biological activities including antibacterial and antiviral activities, and it is also a potent immunomodulating agent. Gliotoxin is also an inducer of apoptotic cell death in a number of cell types, and it has been found to be associated with some diseases attributed directly or indirectly to fungal infections. It is a secondary metabolite produced by a number of Aspergillus and Penicillium species.It is a potent immunosuppressive metabolite and brings about apoptosis in cells. Because of its effects on the immune system it may have a place in transplant surgery. There is limited evidence for its occurrence in moulded cereals. A. fumigatus is a potent pathogen which can colonise the lungs and other body tissues after ingestion of spores. There is some limited evidence that gliotoxin may be formed in situ in such circumstances. hamster LDLo oral 25mg/kg (25mg/kg) Veterinary and Human Toxicology. Vol. 32(Suppl), Pg. 63, 1990. mouse LD50 intraperitoneal 32mg/kg (32mg/kg) Chemotherapia. Vol. 10, Pg. 12, 1965. mouse LD50 intravenous 7800ug/kg (7.8mg/kg) Chemotherapia. Vol. 10, Pg. 12, 1965. mouse LD50 oral 67mg/kg (67mg/kg) Chemotherapia. Vol. 10, Pg. 12, 1965. mouse LD50 subcutaneous 25mg/kg (25mg/kg) Chemotherapia. Vol. 10, Pg. 12, 1965. rabbit LDLo intravenous 45mg/kg (45mg/kg) VASCULAR: BP LOWERING NOT CHARACTERIZED IN AUTONOMIC SECTION. GASTROINTESTINAL: HYPERMOTILITY, DIARRHEA Journal of the American Chemical Society. Vol. 65, Pg. 2005, 1943. rat LDLo intravenous 45mg/kg (45mg/kg) Veterinary and Human Toxicology. Vol. 32(Suppl), Pg. 63, 1990. rat LDLo unreported 50mg/kg (50mg/kg) BEHAVIORAL: ALTERED SLEEP TIME (INCLUDING CHANGE IN RIGHTING REFLEX) Journal of the American Chemical Society. Vol. 65, Pg. 2005, 1943.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
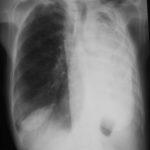
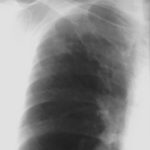
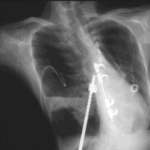
Pt AR Interval development of chronic cavitary pulmonary aspergillosis in the context of sarcoidosis
This patient was diagnosed with sarcoid after developing a chronic cough with the attached chest X-ray. In February 2003 the X-ray demonstrated bilateral extensive changes consistent with fibrocystic sarcoidosis with a complex cavitary area in both apices, more marked on the right. She was given a course of corticosteroids.
-
Further details
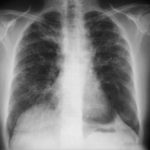
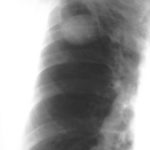
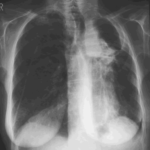
Image B. Additional cavities are apparent inferior to this large cavity and are in communication both with the bronchi and the additional cavities. Some of the apparent cavities are probably dilated bronchi. The left lower lung is completely opacified otherwise. The degree of pleural fibrosis surrounding the left apical cavity is reduced slightly over the interval of four months.
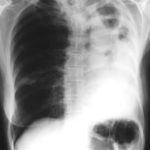
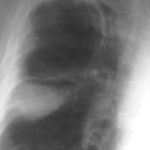
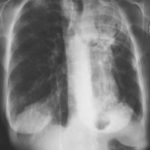
Image C. This shows an almost normal hyperexpanded right lung with a very substantially contracted left lung with one large airway visible and probably incontinuity with a slightly irregular cavity containing some debris, presumably fungal tissue. Other levels show very large left apical cavity with numerous subsections containing debris or fibrotic tissue and almost complete fibrosis of the lung below the level of the carina on the left, with some calcification within the fibrotic lung tissue.
 ,
,  ,
, 
-
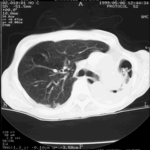
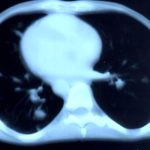
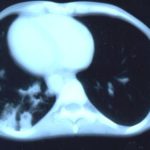
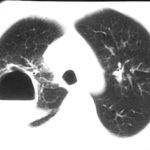
Transverse sections through the thorax of a patient with AIDS, hepatitis C and a left tempero-parietal cerebral lymphoma. His CD4 cell count was 45 x 106 / l. The lymphoma was proven by biopsy after a poor response to anti-toxoplasma therapy. He was given dexamethasone to cover the surgery and then developed diabetes mellitus. He did not receive chemotherapy for his lymphoma but did have 2 cerebral radiotherapy treatments (1.8 Gy each). Three weeks after the biopsy he developed dyspnoea and fever. Shortly after this he developed a right-sided hemiparesis, became comatose and died 2 days later.Autopsy showed a cerebral lymphoma and pulmonary and renal aspergillosis. Aspergillus nidulans was recovered from cultures of lungs and kidney.
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
-
Fever chart of Pt CA -heart transplant pt with candidemia on amphotericin therapy, who developed pulmonary aspergillosis.

-
A Colonies on MEA + 20% sucrose after two weeks; B ascomata, x 40; C conidia and conidiophore, x 920; D ascospores and conidia x2330; E portion of ascoma with asci x920

-
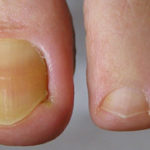
A 66 yr old patient in good general health developed onychomycosis. Samples taken from the affected nail were grown by culture and examined by microscopy. Oral itraconazole pulse therapy was given to the patient (200 mg twice daily for 1 week, with 3 weeks off between successive pulses, for four pulses) and treatment was successful.


 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
 ,
,  ,
,