Date: 26 November 2013
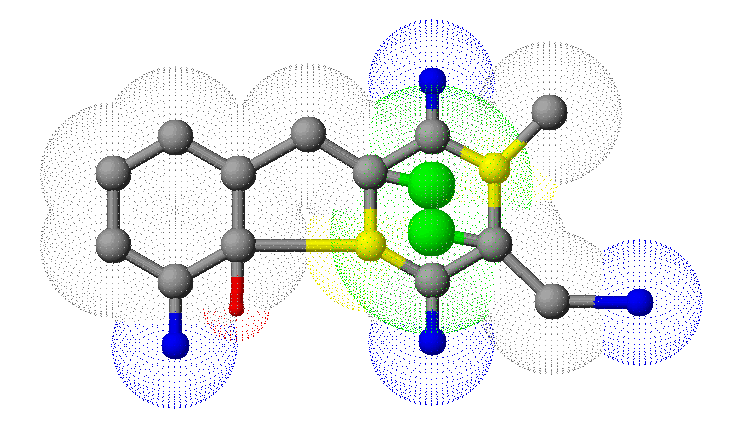
Secondary metabolites, 3D structure: Trivial name – gliotoxin
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
Species: A. flavus, A. fumigatus, A. niger, A. terreus, Eurotium chevalieri, Neosartorya pseudofischeriSystematic name: 10H-3,10a-Epidithiopyrazino[1,2-a]indole-1,4-dione, 2,3,5a,6-tetrahydro-6-hydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methyl-, (3R,5aS,6S,10aR)-Molecular formulae: C13H14N2O4S2Molecular weight: 326.393Chemical abstracts number: 67-99-2Selected references: Larsen TO, Smedsgaard J, Nielsen KF, Hansen MA, Samson RA, Frisvad JC. Production of mycotoxins by Aspergillus lentulus and other medically important and closely related species in section Fumigati. Med Mycol. 2007 May;45(3):225-32. Belkacemi, L.; Barton, R. C.; Hopwood, V.; Evans, E. G. V. (CORPORATE SOURCE PHLS Mycology Reference Laboratory, Department of Microbiology, University of Leeds, Leeds, UK). SOURCE Med. Mycol., 37(4), 227-233 (English) 1999 Blackwell Science Ltd. Lewis RE, Wiederhold NP, Lionakis MS, Prince RA, Kontoyiannis DP.J Clin Microbiol. 2005 Dec;43(12):6120-2. Frequency and species distribution of gliotoxin-producing Aspergillus isolates recovered from patients at a tertiary-care cancer center.Toxicity: Gliotoxin posseses a spectrum of biological activities including antibacterial and antiviral activities, and it is also a potent immunomodulating agent. Gliotoxin is also an inducer of apoptotic cell death in a number of cell types, and it has been found to be associated with some diseases attributed directly or indirectly to fungal infections. It is a secondary metabolite produced by a number of Aspergillus and Penicillium species.It is a potent immunosuppressive metabolite and brings about apoptosis in cells. Because of its effects on the immune system it may have a place in transplant surgery. There is limited evidence for its occurrence in moulded cereals. A. fumigatus is a potent pathogen which can colonise the lungs and other body tissues after ingestion of spores. There is some limited evidence that gliotoxin may be formed in situ in such circumstances. hamster LDLo oral 25mg/kg (25mg/kg) Veterinary and Human Toxicology. Vol. 32(Suppl), Pg. 63, 1990. mouse LD50 intraperitoneal 32mg/kg (32mg/kg) Chemotherapia. Vol. 10, Pg. 12, 1965. mouse LD50 intravenous 7800ug/kg (7.8mg/kg) Chemotherapia. Vol. 10, Pg. 12, 1965. mouse LD50 oral 67mg/kg (67mg/kg) Chemotherapia. Vol. 10, Pg. 12, 1965. mouse LD50 subcutaneous 25mg/kg (25mg/kg) Chemotherapia. Vol. 10, Pg. 12, 1965. rabbit LDLo intravenous 45mg/kg (45mg/kg) VASCULAR: BP LOWERING NOT CHARACTERIZED IN AUTONOMIC SECTION. GASTROINTESTINAL: HYPERMOTILITY, DIARRHEA Journal of the American Chemical Society. Vol. 65, Pg. 2005, 1943. rat LDLo intravenous 45mg/kg (45mg/kg) Veterinary and Human Toxicology. Vol. 32(Suppl), Pg. 63, 1990. rat LDLo unreported 50mg/kg (50mg/kg) BEHAVIORAL: ALTERED SLEEP TIME (INCLUDING CHANGE IN RIGHTING REFLEX) Journal of the American Chemical Society. Vol. 65, Pg. 2005, 1943.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
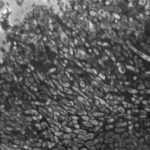
Light microscopic image of hyphae in an aspergilloma (10x magnification)

-
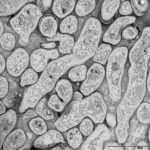
Light microscopic image of hyphae in an aspergilloma (400x magnification)
-
An aspergilloma (or fungal ball) is a mass of fungus found inside the body, for example inside cavities such as the lungs or sinuses, or as abscesses in organs such as the brain or kidney. They are made up of threadlike fungal strands (hyphae) that are densely packed but only around 1/200 of a millimetre in diameter. A mass of hyphae is called a mycelium.
In this image, a slice through an aspergilloma has been imaged using a transmission electron microscope.
-
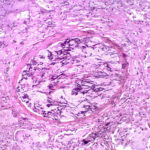
Aspergillus can punch through the lining of the lungs and invade the blood vessels below, in a process called angioinvasion. It can result in blockage (occlusion) of the blood vessel and damage to the local tissue through lack of oxygen (infarction). In severely immunocompromised patients, fragments can even break off and travel to other organs in the body.
In this image, a tissue section through a blocked blood vessel has been stained with the dyes haematoxylin (purple, binds DNA) and eosin (pink, binds proteins).
-
Showing the edge of a colony of aspergillus forming a fungal ball. The fungal hyphae exhibit dichotomous 45 degree angle branching and septae typical of Aspergillus.
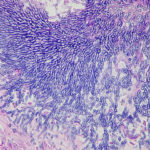
-
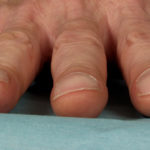
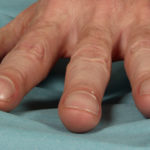
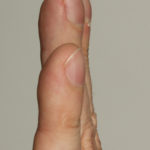
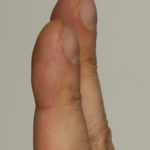
Pt CJ finger clubbing, this patient had chronic cavitary pulmonary aspergillosis, with an aspergilloma since 1988, following an episode of haemoptysis. Currently patient still has symptomatic disease.
Images E,F Blood stained sputum samples from this patient.
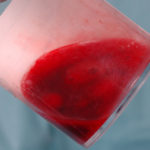 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
-
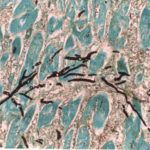
Disseminated, invasive aspergillosis showing dichotomously branching hyphae. Original magnification x300. Stained with Gomori Methenamine Silver (GMS).
-
Disseminated, invasive aspergillosis showing dichotomously branching hyphae. Original magnification x150. Stained with Gomori Methenamine Silver (GMS).

-
Disseminated, invasive aspergillosis showing dichotomously branching hyphae. Original magnification x50. Stained with Gomori Methenamine Silver (GMS).

-
Light microscopical appearance of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis showing vessel occlusion with thrombus and distal infarction (Haematoxylin and eosin, x100)