Date: 26 November 2013
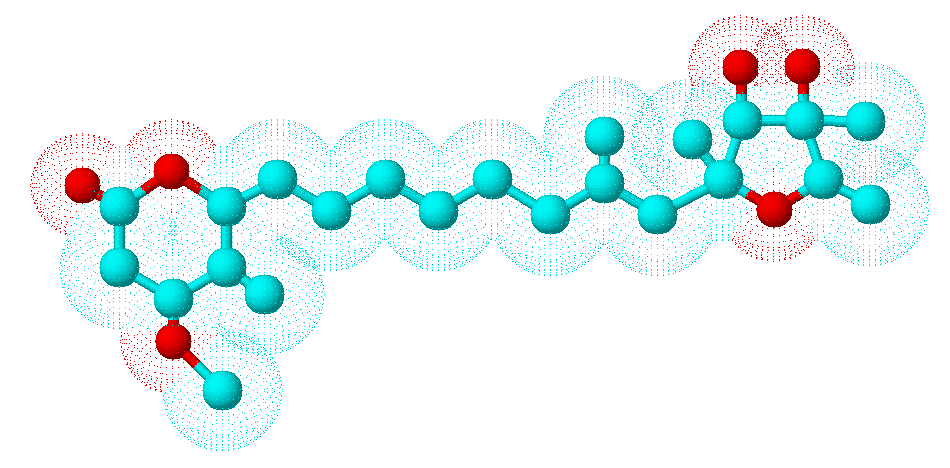
Secondary metabolites, 3D structure: Trivial name – citreoviridin
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
Species: A. terreusSystematic name: D-Iditol, 2,5-anhydro-1,6-dideoxy-2-C-[(1E,3E,5E,7E)-8-(4-methoxy-5-methyl-2-oxo-2H-pyran-6-yl)-2-methyl-1,3,5,7-octatetraenyl]-4-C-methyl- (9CI)Molecular formulae: C23H30O6Molecular weight: 402.481Chemical abstracts number: 25425-12-1Selected references: Franck B, Gehrken HP. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 1980;19(6):461-2 Citreoviridins from Aspergillus terreus.Toxicity: Citreoviridin is produced by P. citreonigrum (synonyms P. citreoviride and P. toxicarium), particularly in rice after harvest. It can cause cardiac beriberi in man. Acute cardiac beriberi in Japan is now only of historical interest although P. citreonigrum and citreoviridin are still reported in other parts of Asia. The fungus is said to be favoured by the lower temperatures and shorter hours of daylight occurring in the more temperate rice growing areas. The toxin is also produced by P. ochrosalmoneum. Citreoviridin has been found in un-harvested corn in the USA. Citreoviridin is an unusual molecule consisting of a lactone ring conjugated to a furan ring, with a molecular weight of 402. It is a neurotoxin. Nishie K, Cole RJ, Dorner JW. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1988 Jan;59(1):31-52.Toxicity of citreoviridin.
Images library
-
Title
Legend