Date: 26 November 2013
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
Dr. Balajee is a graduate of the University of Madras (India) and completed her post doctoral training in Dr. Kieren Marr’s laboratory at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, Seattle, US. Currently she leads the Molecular Epidemiology Unit within the Mycotic Diseases Branch at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Dr. Balajee’s dynamic research program is focused on public health mycology that includes studies on the molecular epidemiology of medically important fungi, specifically the genus Aspergillus. Another area of interest is understanding the role of mycotoxins, specifically aflatoxin elaborated by Aspergillus in mediating adverse health effects in humans. Dr. Balajee has published over 25 peer-reviewed articles and several book chapters and is committed to creating a learning environment for budding public health mycologists in her laboratory. Dr. Balajee is the convenor for an international working group on A. terreus to gather and disseminate scientific knowledge in this field and is a member of the working group on species concepts inAspergillus.
Key Contributions to recent literature:
- Balajee SA, Weaver M, Imhof A, Gribskov J, Marr KA. Aspergillus fumigatus variant with decreased susceptibility to multiple antifungals. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004 Apr;48(4):1197-203.
- Balajee SA, Imhof A, Gribskov JL, Marr KA. Determination of antifungal drug susceptibilities of Aspergillus species by a fluorescence-based microplate assay. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2005 Jan;55(1):102-5.
- Balajee SA, Gribskov JL, Hanley E, Nickle D, Marr KA. Aspergillus lentulus sp. nov., a new sibling species of A. fumigatus.Eukaryot Cell. 2005 Mar; 4(3):625-32.
- Bok JW, Chung D, Balajee SA, Marr KA, Andes D, Nielsen KF, Frisvad JC, Kirby KA, Keller NP. GliZ, a transcriptional regulator of gliotoxin biosynthesis, contributes to Aspergillus fumigatusvirulence. Infect Immun. 2006 Dec; 74(12):6761-8.
- Balajee SA, Nickle D, Varga J, Marr KA. Molecular studies reveal frequent misidentification of Aspergillus fumigatus by morphotyping. 2006 Oct; 5(10):1705-12.Eukaryot Cell.
- Balajee SA, Lindsley MD, Iqbal N, Ito J, Pappas PG, Brandt ME. A non-sporulating clinical isolate identified as Petromyces alliaceus (anamorph Aspergillus alliaceus) by morphological and sequence based methods. J Clin Microbiol. 2007 Aug; 45(8):2701-3.
- Balajee SA, Tay ST, A Lasker B, Hurst SF, Rooney AP.Characterization of a novel gene for strain typing reveals substructuring of Aspergillus fumigatus across North America.Eukaryot Cell. 2007 Aug; 6 (8):1392-9.
- Balajee SA, L Sigler and ME Brandt. DNA and the classical way: identification of medically important molds in the 21st century.Med Mycol 2007; 45: 1-16
- Balajee SA, SS Magill, ME Brandt. The role of molecular methods in the identification of fungal infections. Curr Fung Infect Reports 2007; 1: in press.
- Kano R, K Itamoto, M Okuda, H Inokuma, A Hasegawa, SA Balajee. Isolation of Aspergillus udagawae from a fatal case of feline orbital aspergillosis. Mycoses 2008 (in press).
- Balajee S.A, J. Houbraken, P.E. Verweij, S-B. Hong, T. Yaghuchi, J. Varga and R.A. Samson2. Aspergillus species identification in the clinical setting. Studies in Mycology. 59: 39–46. 2007.
- Balajee SA, de Valk HA, Lasker BA, Meis JF, Klaassen CH. J Microbiol Methods. 2008 Feb 23. Epub. Utility of a microsatellite assay for identifying clonally related outbreak isolates ofAspergillus fumigatus.
Arun Balajee Ph.D.
Chief, Molecular Epidemiology Unit,
Mycotic Diseases Branch,
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Mail stop – G 11 1600 Clifton Road, Atlanta, GA – 30333
Email fir3@cdc.gov
Phone – 404 639 3337
Fax – 404 639 3546
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
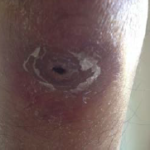
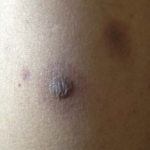
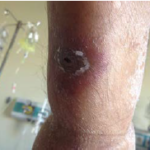
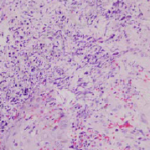
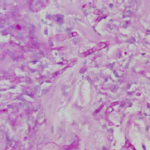
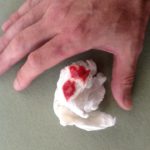
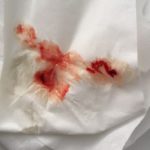
Images and abstract taken from Mert D et.al., Hematol Rep. 2017 Jun 1;9(2):6997. doi: 10.4081/hr.2017.6997. Invasive Aspergillosis with Disseminated Skin Involvement in a Patient with Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Rare Case.
Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis is most commonly seen in immunocompromised patients. Besides, skin lesions may also develop due to invasive aspergillosis in those patients. A 49-year-old male patient was diagnosed with acute myeloid leukemia.
The patient developed bullous and zosteriform lesions on the skin after the 21st day of hospitalization. The skin biopsy showed hyphae. Disseminated skin aspergillosis was diagnosed to the patient.
Voricanazole treatment was initiated. The patient was discharged once the lesions started to disappear.
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
-
A pile of woodchip stored for use in a garden usually as a weed suppressing mulch. The heat building up in the pile is illustrated by the plumes of steam eminating from the top of the pile.
Aspergillus fumigatus is particularly well adapted to grow in the heat (up to 60C) found in such piles of rotting organic material and this characteristic, an adaption for its life in its natural environment also enables it to survive and grow in warm mammalian bodies at 37C. Most fungi cannot grow or survive at those temperatures
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
-
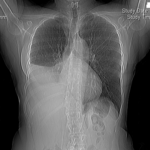
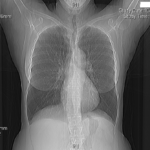
MK is 59 years old and presented with right sided pleuritic chest pain and coughing over 1 week. A chest Xray and then CT scan revealed complete collapse of her right lower lobe and middle lobes. Mucous retention is seen just proximal to the abrupt cutoff. There was mild bronchiectasis.
 ,
, 



 ,
,  ,
,