Date: 26 November 2013
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
Dr. Balajee is a graduate of the University of Madras (India) and completed her post doctoral training in Dr. Kieren Marr’s laboratory at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, Seattle, US. Currently she leads the Molecular Epidemiology Unit within the Mycotic Diseases Branch at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Dr. Balajee’s dynamic research program is focused on public health mycology that includes studies on the molecular epidemiology of medically important fungi, specifically the genus Aspergillus. Another area of interest is understanding the role of mycotoxins, specifically aflatoxin elaborated by Aspergillus in mediating adverse health effects in humans. Dr. Balajee has published over 25 peer-reviewed articles and several book chapters and is committed to creating a learning environment for budding public health mycologists in her laboratory. Dr. Balajee is the convenor for an international working group on A. terreus to gather and disseminate scientific knowledge in this field and is a member of the working group on species concepts inAspergillus.
Key Contributions to recent literature:
- Balajee SA, Weaver M, Imhof A, Gribskov J, Marr KA. Aspergillus fumigatus variant with decreased susceptibility to multiple antifungals. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004 Apr;48(4):1197-203.
- Balajee SA, Imhof A, Gribskov JL, Marr KA. Determination of antifungal drug susceptibilities of Aspergillus species by a fluorescence-based microplate assay. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2005 Jan;55(1):102-5.
- Balajee SA, Gribskov JL, Hanley E, Nickle D, Marr KA. Aspergillus lentulus sp. nov., a new sibling species of A. fumigatus.Eukaryot Cell. 2005 Mar; 4(3):625-32.
- Bok JW, Chung D, Balajee SA, Marr KA, Andes D, Nielsen KF, Frisvad JC, Kirby KA, Keller NP. GliZ, a transcriptional regulator of gliotoxin biosynthesis, contributes to Aspergillus fumigatusvirulence. Infect Immun. 2006 Dec; 74(12):6761-8.
- Balajee SA, Nickle D, Varga J, Marr KA. Molecular studies reveal frequent misidentification of Aspergillus fumigatus by morphotyping. 2006 Oct; 5(10):1705-12.Eukaryot Cell.
- Balajee SA, Lindsley MD, Iqbal N, Ito J, Pappas PG, Brandt ME. A non-sporulating clinical isolate identified as Petromyces alliaceus (anamorph Aspergillus alliaceus) by morphological and sequence based methods. J Clin Microbiol. 2007 Aug; 45(8):2701-3.
- Balajee SA, Tay ST, A Lasker B, Hurst SF, Rooney AP.Characterization of a novel gene for strain typing reveals substructuring of Aspergillus fumigatus across North America.Eukaryot Cell. 2007 Aug; 6 (8):1392-9.
- Balajee SA, L Sigler and ME Brandt. DNA and the classical way: identification of medically important molds in the 21st century.Med Mycol 2007; 45: 1-16
- Balajee SA, SS Magill, ME Brandt. The role of molecular methods in the identification of fungal infections. Curr Fung Infect Reports 2007; 1: in press.
- Kano R, K Itamoto, M Okuda, H Inokuma, A Hasegawa, SA Balajee. Isolation of Aspergillus udagawae from a fatal case of feline orbital aspergillosis. Mycoses 2008 (in press).
- Balajee S.A, J. Houbraken, P.E. Verweij, S-B. Hong, T. Yaghuchi, J. Varga and R.A. Samson2. Aspergillus species identification in the clinical setting. Studies in Mycology. 59: 39–46. 2007.
- Balajee SA, de Valk HA, Lasker BA, Meis JF, Klaassen CH. J Microbiol Methods. 2008 Feb 23. Epub. Utility of a microsatellite assay for identifying clonally related outbreak isolates ofAspergillus fumigatus.
Arun Balajee Ph.D.
Chief, Molecular Epidemiology Unit,
Mycotic Diseases Branch,
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Mail stop – G 11 1600 Clifton Road, Atlanta, GA – 30333
Email fir3@cdc.gov
Phone – 404 639 3337
Fax – 404 639 3546
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
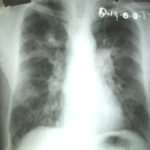
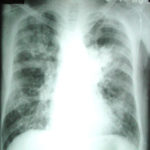
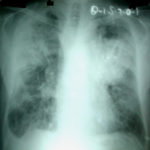
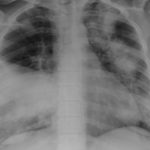
The chest X rays showed a rapid progression of lung disease- with bilateral upper zone and midzone consolidation and bilateral pleural effusion. Both lower lobes showed bronchiectasis in a central distribution along with centrilobular nodules and tree-in-bud pattern.
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
-
Patient EG Intraluminal aspergilloma in cystic fibrosis (12 months follow up)
The 21 year old woman with cystic fibrosis developed an aspergilloma in her left lower lobe bronchus. CF was diagnosed at 6 months of age (sweat chloride 78 and 100 mmol/L) and CFTR mutations δ508 and W1282X and she developed diabetes mellitus at age 12 years. Age 15 years ABPA was diagnosed. Her serum IgE at the time of diagnosis was 5060 IU/L, skin prick test for aspergillus was positive, and serum was positive for precipitating antibodies to Aspergillus. She was treated with oral prednisone (1 mg/kg/day) for first two weeks followed by prednisone at 0.5 mg/kg every other day for at least 6 months with some clinical and serologic improvement. Over the following 5 years, she presented with a pattern of repeated episodic exacerbations with wheezing and crackles, increases in IgE and need to increase prednisone dosage.
In the 12 months before the aspergillomas were found, she started to experience frequent pulmonary exacerbations, which have prompted intensive therapies. She has also been on oral prednisone & itraconazole for at least 9 months for her ABPA relapse with some clinical & serologic improvement. She then developed severe protracted coughing spells associated with minor hemoptysis, low grade intermittent fever, and weight loss. Her FEV1 declined in a 3 months period from 56% to 33%. A recent chest-x ray did not reveal any new changes when compared to the one obtained almost a year before. A CT scan of the chest, however shows an ovoid soft tissue density within an ectatic bronchi in the anterior basal segment of the lower left lobe, felt to be an aspergilloma. [Link here].
She was started on voriconazole 200 mg twice daily. This dose gave a random serum level of 5ug/L. Her prednisone was weaned to 5 mgs/day and her FEV1 increased to 46% of predicted. In January 2009, her IgE level was 3053 kU/L; one year later, her IgE level was 1167 kU/L. A lung transplant surgeon attempted unsuccessfully to remove the aspergilloma via flexible bronchoscopy. It took a while for her to recover from that procedure. She then had a pulmonary exacerbation. She tolerated voriconazole reasonably well and gaining some weight. By mid 2010, her IgE level was 637 IU/L.
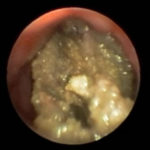
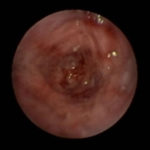
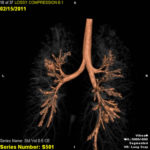
In early 2011, her aspergilloma (yellow friable material) in the anterior segment of the left lower lobe was removed completely (Fig a and b). It took a little time, but with biopsy forceps and some mincing and homogenization, it was all sucked out. The 3D reconstruction (Fig c) only shows the area of bronchiectasis, not the aspergilloma.Dr. Turcios is the director of pediatric pulmonology/cystic fibrosis in Somerville, NJ.
 ,
,  ,
, 
-
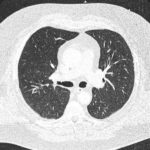
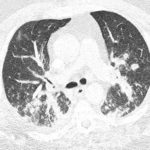
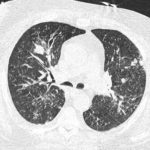
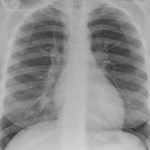
This patient is a 70 yr old, obese diabetic with aortic stenosis and COPD. He was admitted in early March 09, with collapse and loss of conciousness. His lungs appeared normal at this time – CT and X-ray 1. 10 days later he was admitted with increasing shortness of breath and chest X ray (F) showing widespread patchy consolidation. CT scan (B) showed bronchial dilatation, mucus plugging, nodular and bibasal consolidation. Multiple sputum samples grew Aspergillus fumigatus. The patient required intubation and remained in ITU for 160 days.
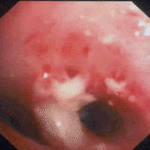
Bronchoscopy showed plaques in the major airways with more distal airways plugged with secretions resembling “cottage cheese”.There was severe contact bleeding and oedematous mucosa (I & J). Biopsy of the plaques showed fungal hyphae with a branching pattern consistent with aspergillus infection (G & H).
The patient was initially given IV and nebulised amphotericin B whilst on doses of hydrocortisone from 100-400 mg/day. Voriconazole was added with dose optimisation, and amphotericin discontinued. The patient improved gradually with voriconazole treatment over several months and for the latter month, gamma interferon was added into his regime which further improved his CT scan although some shadowing and bronchial wall thickening was still seen (D).
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
-
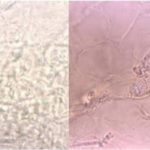
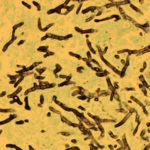
Hyphal septate club-like enlargements from culture on CYA 25°C medium (mag x100)
-
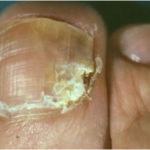
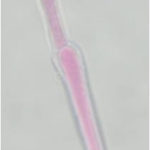
G Potassium hydroxide preparation of a nail specimen with onychomycosis- examined by microscopy