Date: 5 August 2014
Pt SD congestive heart failure 5 images
Copyright:
FIT
Notes:
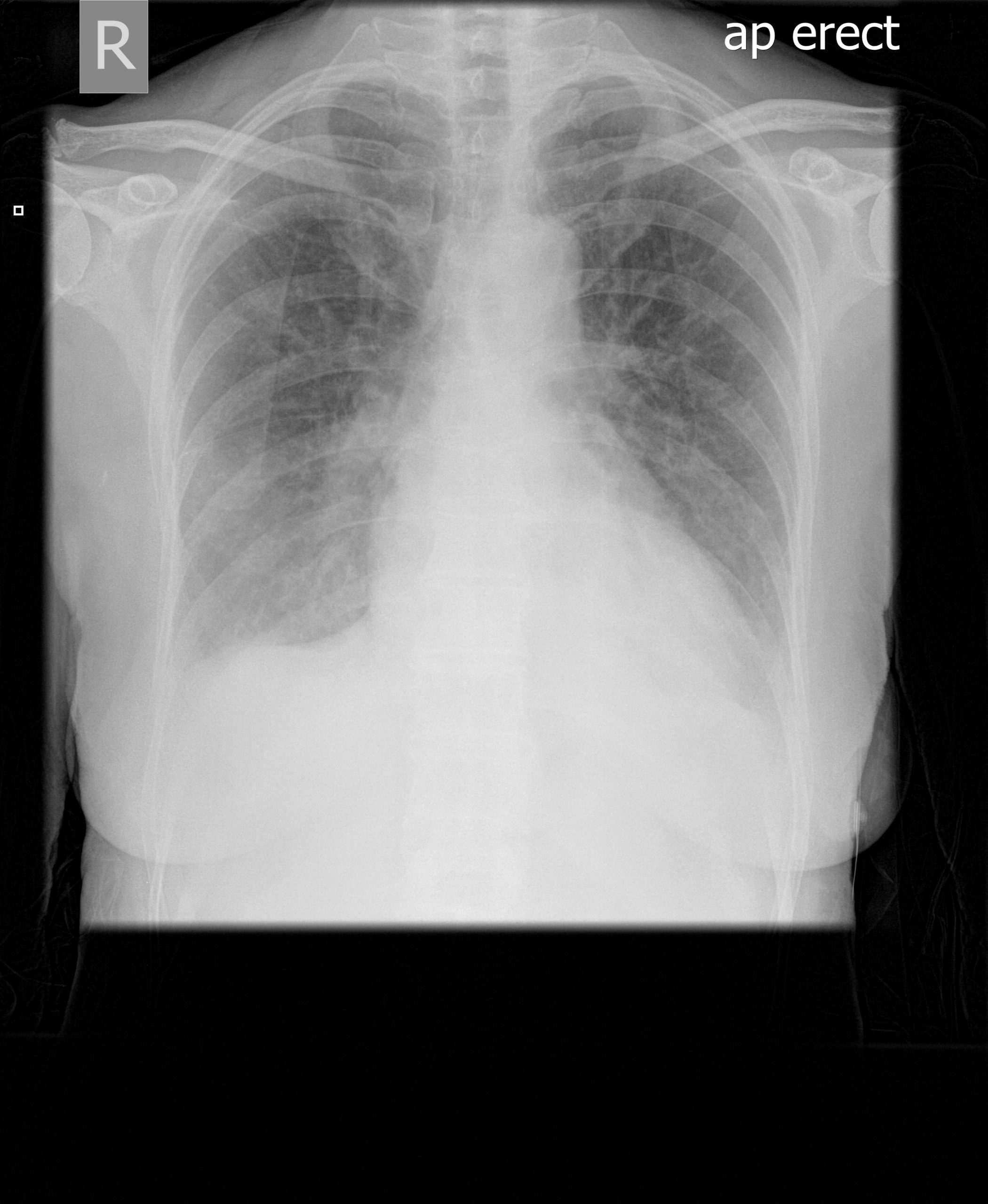
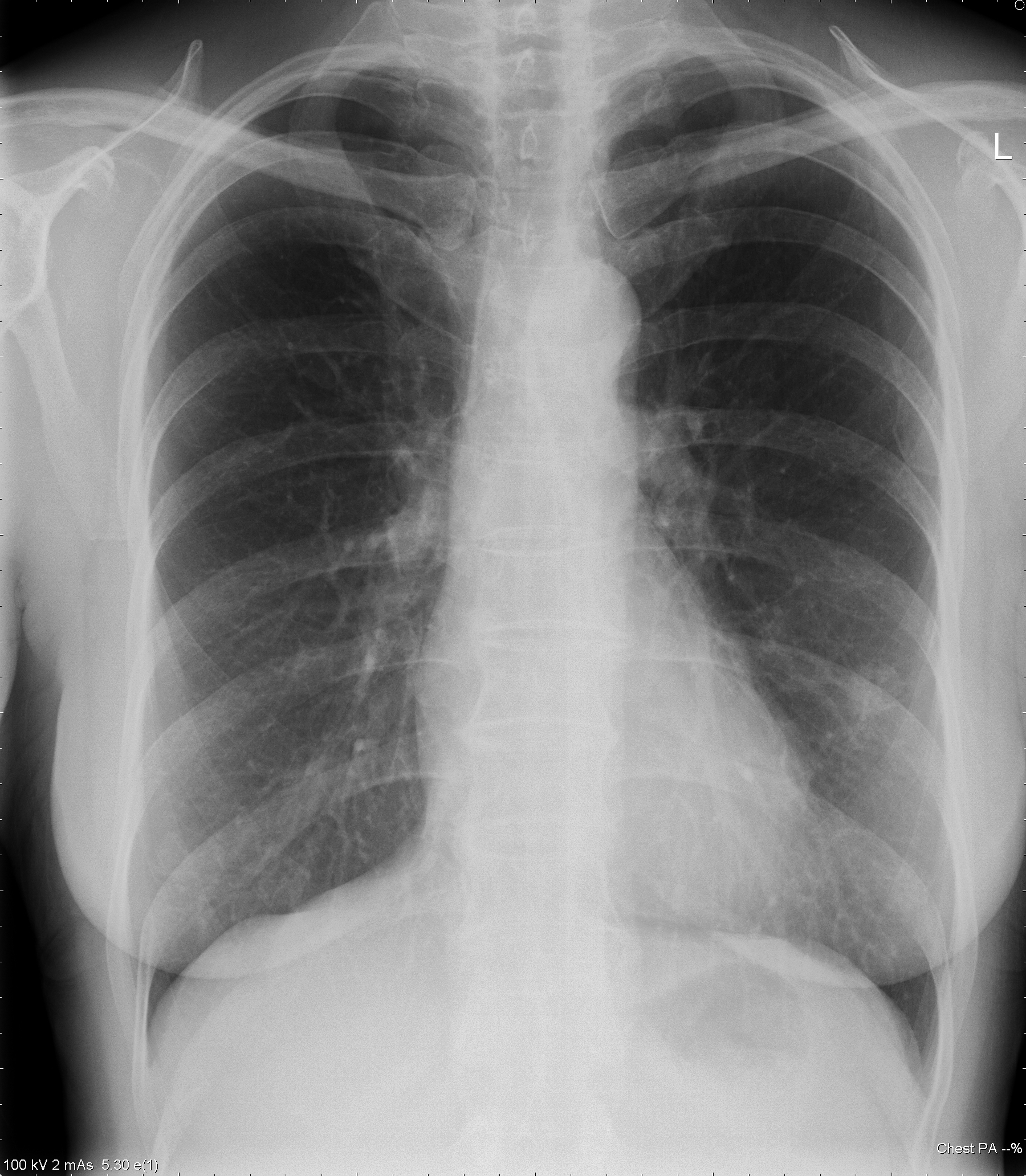
This 63 year old woman with a lung nodule, probably caused by Aspergillus, was treated with itraconazole 300mg daily. After 3 weeks, she noticed dizziness and her blood pressure was reduced at 100/60. A week later, she was complaining of headaches, feeling unwell and fluctuating blood pressure. Her BP was 133/62 and pulse 90/min and regular. Her thyroid replacement therapy was excessive and so reduced, as was her itraconazole dose, although subsequent itraconazole levels were in the therapeutic range. Six days later she was admitted to hospital very breathless with bilateral pleural effusions. Itraconazole was stopped.
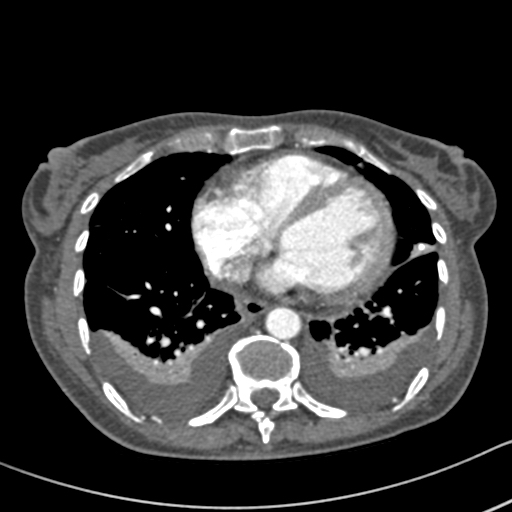
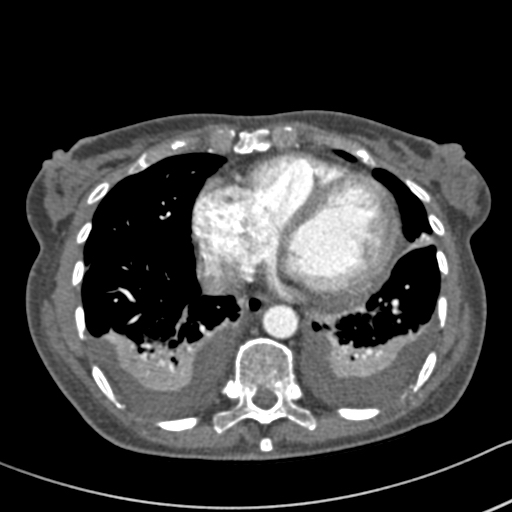
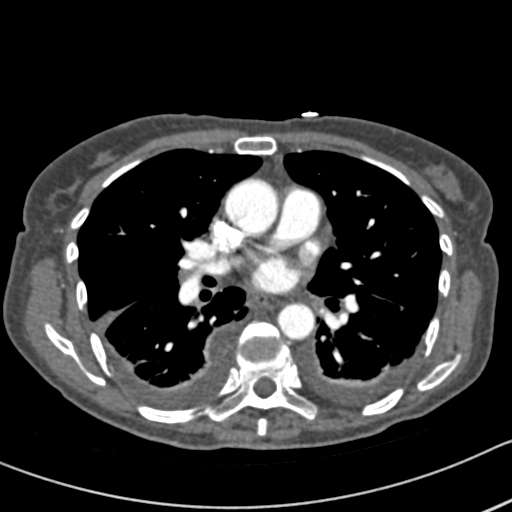
Her CXR shows bilateral effusions, probable cardiac enlargement and some upper lobe vessel fullness in the lungs. The CT scan confirms bilateral flexural effusions, with associated consolidated lung and fluid in the fissure on the right. The heart is enlarged and right ventricle dilated. In May, all had resolved and she is left with a nodule in the left lower lobe.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
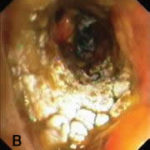
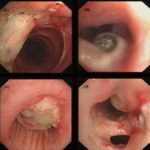
Bronchoscopic manifestations of Aspergillus tracheobronchitis. (a) Type I. Inflammatory infiltration, mucosa hyperaemia and plaques of pseudomembrane formation in the lumen without obvious airway occlusion. (b) Type II. Deep ulceration of the bronchial wall. (c) Type III. Significant airway occlusion by thick mucous plugs full of Aspergillus without definite deeper tissue invasion. (d) Type IV. Extensive tissue necrosis and pseudomembrane formation in the lumen with airway structures and severe airway occlusion (Wu 2010).
-
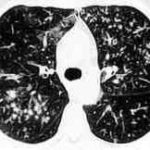
High resolution CT showing centrilobular nodular opacities and branching linear opacities (tree-in-bud appearance) (Al-Alawi 2007).
-
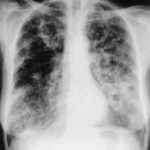
Chest X-ray showing poorly defined bilateral nodular opacities (Al-Alawi 2007).
-
Gross pathologic specimen from autopsy shows the bronchial lumen covered by multiple whitish endobronchial nodules (arrows) (Franquet 2002).

-
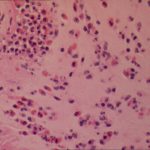
Invasive tracheobronchitis showing numerous nodules seen during bronchoscopy (Ronan D’Driscoll).

-
Pseudomembranous seen overlying the bronchial mucosa (Tasci 2006).