Date: 26 November 2013
Further details
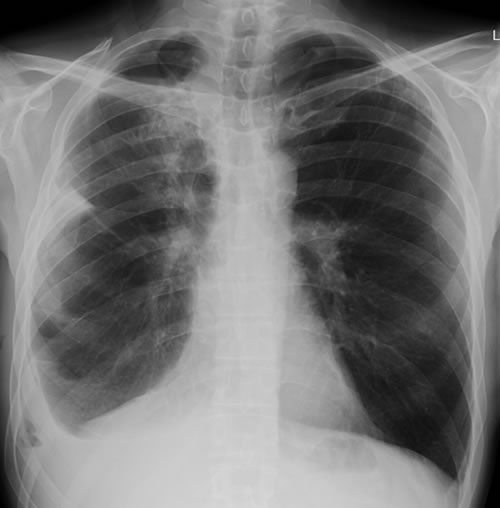
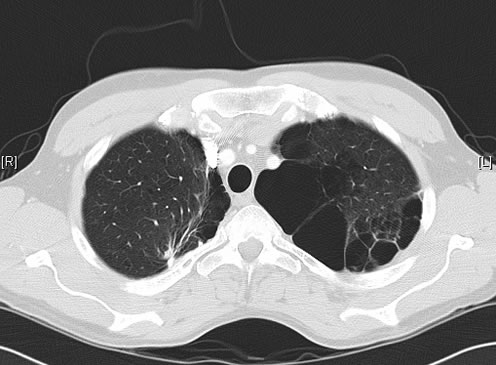
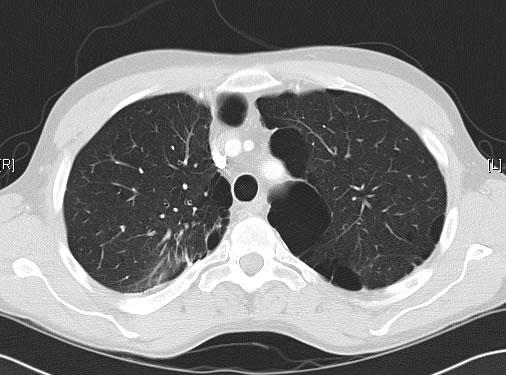
June 2009 – CT scan of the chest (two images D & E). These scans show residual large bullae, particularly notable in the apex of the left lung on both cuts. Small residual bullae remain in the right apex following a bullectomy which greatly reduced the size and number of these lesions.
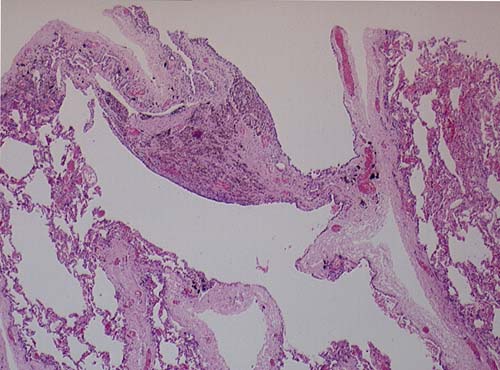
Pt RK Lung bullae caused by cannabis smoking complicated by pneumothorax and chronic cavitary pulmonary aspergillosis.
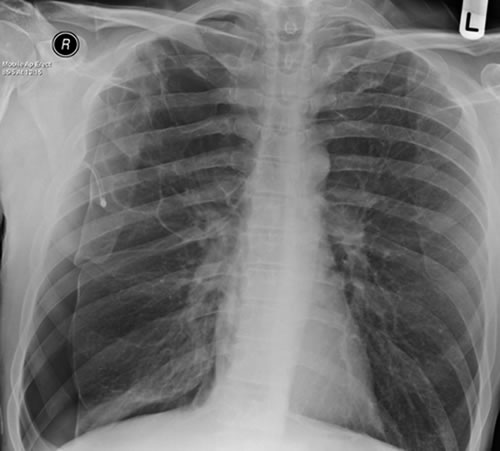
February 2009 – Chest x-ray showing bilateral apical bullae most marked on the right in association with a right pneumothorax. A chest drain is in-situ.
Late February 2009 – persistent apical bullae right upper zone with resolving pneumothorax. Chest drain still in-situ. Increasing right upper lobe shadowing possibly representing infection or haemorrhage.
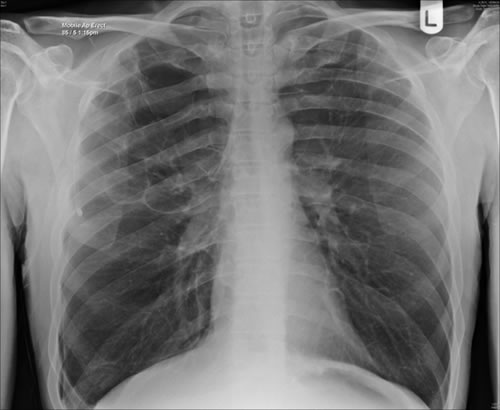
April 2009 – Post-operative chest x-ray showing post apical bullectomy on the right, resolved pneumothorax but the interval development of fluid in the right costo-phrenic angle with air fluid levels consistent with recent surgery. Great reduction in apical bullae in the right apex but increasing consolidation proximally in the right upper zone and some fluid in the horizontal fissure. These findings are following an apical bullectomy and pleurodesis of his prior significant pneumothorax.
June 2009 – CT scan of the chest (two images – see above). These scans show residual large bullae, particularly notable in the apex of the left lung on both cuts. Small residual bullae remain in the right apex following a bullectomy which greatly reduced the size and number of these lesions.
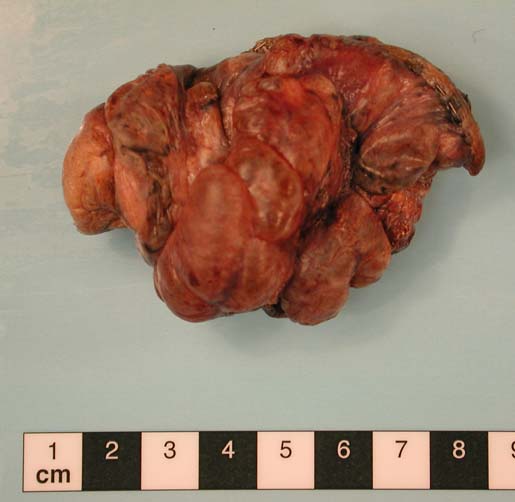
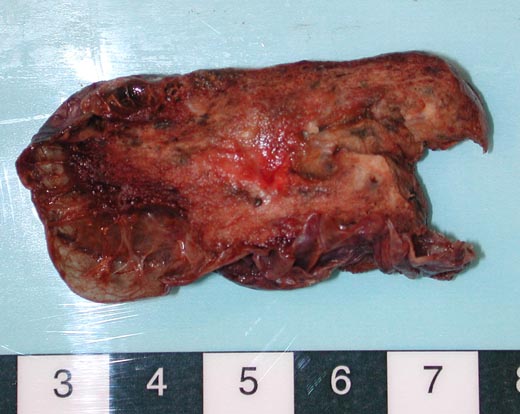
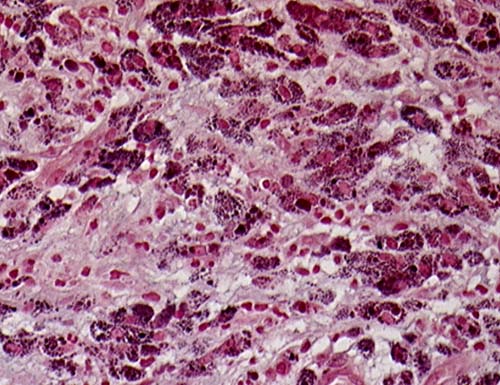
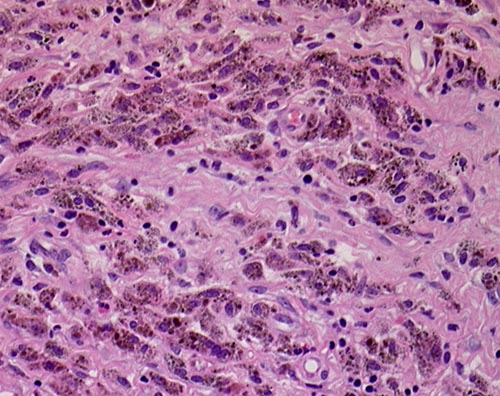
This patient underwent a bullectomy to remove part of the lung after developing lung bullae associated with cannabis smoking. The transverse section (G) of the specimen clearly shows the bullae along the left side and lower edge of the section. I and J demonstrate the dark pigment seen in accumulated macrophages. Tobacco smoking alone also causes a dark pigment, but evidence suggests that in marijuana smokers this pigment accumulates much faster and even with reduced exposure. The manner in which marijuana is smoked ie. without a filter and extended holding of the breath may contribute to this observation.
Copyright: n/a
Notes: n/a
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
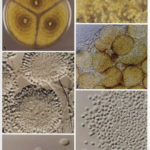
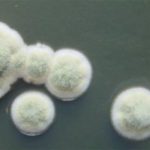
Pigmentation of Aspergillus versicolor colonies ranged from pale green to greenish-beige, pink-green, dark green and brown. Reverse is usually reddish. The growth rate is usually slow. Cultured on Sabouraud dextrose agar with chloramphenicol.

-
A Colonies on MEA after one week; B, C conidial heads with tip of conidiophire, x920; D conidial head, x 2330; E conidial heads x920
![aspvers[2] aspvers2](https://www.aspergillus.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/aspvers2-150x150.jpg)
-
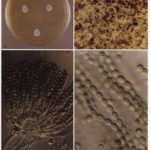
A Colonies on MEA + 20% sucrose after one week; B detail of colony showing columnar conidial heads x 44 ; C conidial heads x 920; D conidia x2330
-
Cultures are grown on malt extract agar for 5-7 days at 30°C.
Light microscopy-1000x stained with lacto-phenol and cotton blue.
-
A Colonies on MEA +20% sucrose after one week; B ascomata x 40; C conidiophores x 920; D ascospores x2330; E ascoma x 230; F portion of ascoma with asci and ascospores, x 920.