Date: 26 November 2013
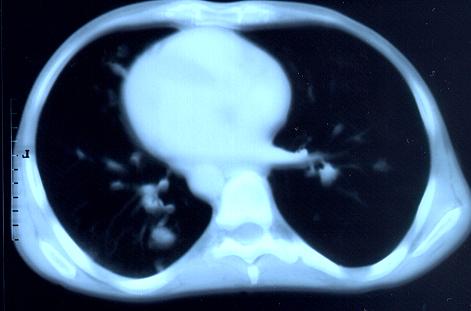
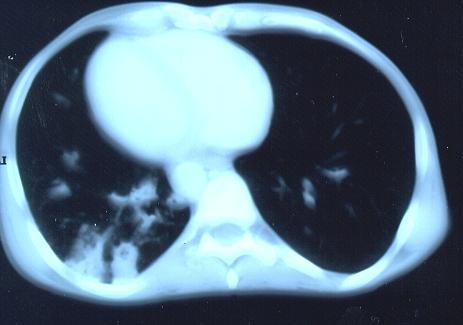
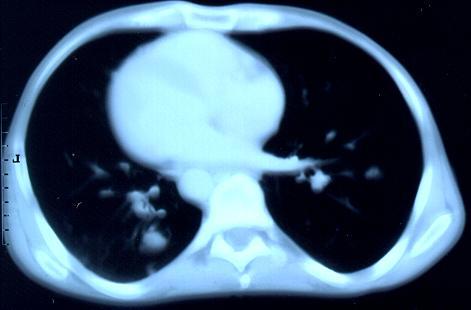
Transverse sections through the thorax of a patient with AIDS, hepatitis C and a left tempero-parietal cerebral lymphoma. His CD4 cell count was 45 x 106 / l. The lymphoma was proven by biopsy after a poor response to anti-toxoplasma therapy. He was given dexamethasone to cover the surgery and then developed diabetes mellitus. He did not receive chemotherapy for his lymphoma but did have 2 cerebral radiotherapy treatments (1.8 Gy each). Three weeks after the biopsy he developed dyspnoea and fever. Shortly after this he developed a right-sided hemiparesis, became comatose and died 2 days later.Autopsy showed a cerebral lymphoma and pulmonary and renal aspergillosis. Aspergillus nidulans was recovered from cultures of lungs and kidney.
Copyright:
Images submitted by Dr. Cornelia Lass-Floerl, University of Innsbruck – Institute of Hygiene; the case team includes: Dr. Mario Sarcletti, Dr. Alfons Stöger and Prof. Hans Maier all at the University of Innsbruck.
Notes: n/a
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
Light microscopic image of hyphae in an aspergilloma (10x magnification)

-
Light microscopic image of hyphae in an aspergilloma (400x magnification)
-
An aspergilloma (or fungal ball) is a mass of fungus found inside the body, for example inside cavities such as the lungs or sinuses, or as abscesses in organs such as the brain or kidney. They are made up of threadlike fungal strands (hyphae) that are densely packed but only around 1/200 of a millimetre in diameter. A mass of hyphae is called a mycelium.
In this image, a slice through an aspergilloma has been imaged using a transmission electron microscope.
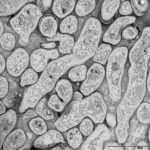
-
Aspergillus can punch through the lining of the lungs and invade the blood vessels below, in a process called angioinvasion. It can result in blockage (occlusion) of the blood vessel and damage to the local tissue through lack of oxygen (infarction). In severely immunocompromised patients, fragments can even break off and travel to other organs in the body.
In this image, a tissue section through a blocked blood vessel has been stained with the dyes haematoxylin (purple, binds DNA) and eosin (pink, binds proteins).
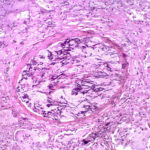
-
Showing the edge of a colony of aspergillus forming a fungal ball. The fungal hyphae exhibit dichotomous 45 degree angle branching and septae typical of Aspergillus.
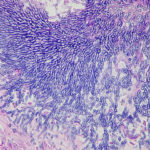
-
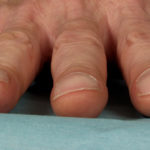
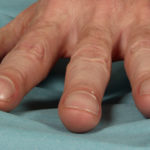
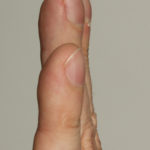
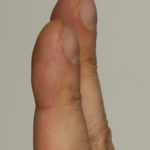
Pt CJ finger clubbing, this patient had chronic cavitary pulmonary aspergillosis, with an aspergilloma since 1988, following an episode of haemoptysis. Currently patient still has symptomatic disease.
Images E,F Blood stained sputum samples from this patient.
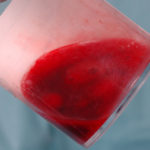 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
-
Disseminated, invasive aspergillosis showing dichotomously branching hyphae. Original magnification x300. Stained with Gomori Methenamine Silver (GMS).
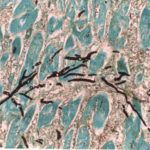
-
Disseminated, invasive aspergillosis showing dichotomously branching hyphae. Original magnification x150. Stained with Gomori Methenamine Silver (GMS).

-
Disseminated, invasive aspergillosis showing dichotomously branching hyphae. Original magnification x50. Stained with Gomori Methenamine Silver (GMS).

-
Light microscopical appearance of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis showing vessel occlusion with thrombus and distal infarction (Haematoxylin and eosin, x100)