Date: 21 January 2014
Further details
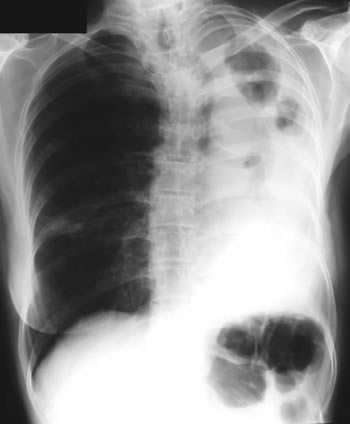
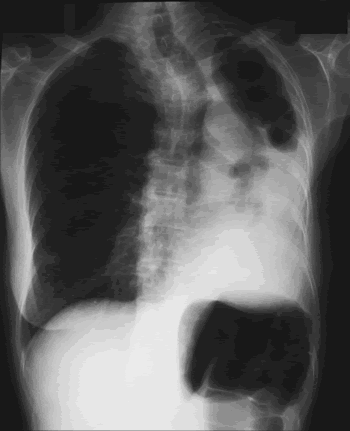
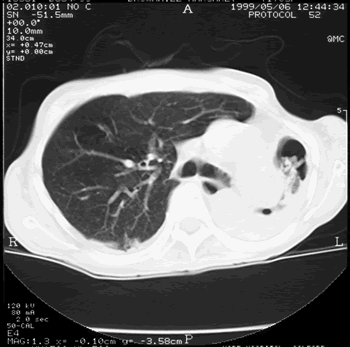
Image B. Additional cavities are apparent inferior to this large cavity and are in communication both with the bronchi and the additional cavities. Some of the apparent cavities are probably dilated bronchi. The left lower lung is completely opacified otherwise. The degree of pleural fibrosis surrounding the left apical cavity is reduced slightly over the interval of four months.
Image C. This shows an almost normal hyperexpanded right lung with a very substantially contracted left lung with one large airway visible and probably incontinuity with a slightly irregular cavity containing some debris, presumably fungal tissue. Other levels show very large left apical cavity with numerous subsections containing debris or fibrotic tissue and almost complete fibrosis of the lung below the level of the carina on the left, with some calcification within the fibrotic lung tissue.
Copyright: n/a
Notes: n/a
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
Light microscopic image of hyphae in an aspergilloma (10x magnification)

-
Light microscopic image of hyphae in an aspergilloma (400x magnification)
-
An aspergilloma (or fungal ball) is a mass of fungus found inside the body, for example inside cavities such as the lungs or sinuses, or as abscesses in organs such as the brain or kidney. They are made up of threadlike fungal strands (hyphae) that are densely packed but only around 1/200 of a millimetre in diameter. A mass of hyphae is called a mycelium.
In this image, a slice through an aspergilloma has been imaged using a transmission electron microscope.
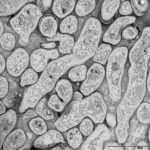
-
Aspergillus can punch through the lining of the lungs and invade the blood vessels below, in a process called angioinvasion. It can result in blockage (occlusion) of the blood vessel and damage to the local tissue through lack of oxygen (infarction). In severely immunocompromised patients, fragments can even break off and travel to other organs in the body.
In this image, a tissue section through a blocked blood vessel has been stained with the dyes haematoxylin (purple, binds DNA) and eosin (pink, binds proteins).
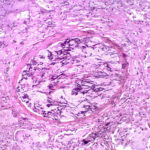
-
Showing the edge of a colony of aspergillus forming a fungal ball. The fungal hyphae exhibit dichotomous 45 degree angle branching and septae typical of Aspergillus.
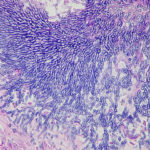
-
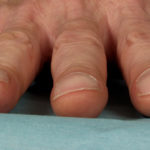
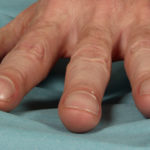
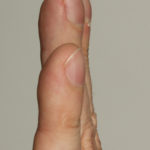
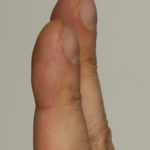
Pt CJ finger clubbing, this patient had chronic cavitary pulmonary aspergillosis, with an aspergilloma since 1988, following an episode of haemoptysis. Currently patient still has symptomatic disease.
Images E,F Blood stained sputum samples from this patient.
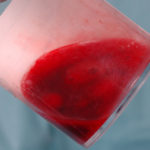 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
-
Disseminated, invasive aspergillosis showing dichotomously branching hyphae. Original magnification x300. Stained with Gomori Methenamine Silver (GMS).
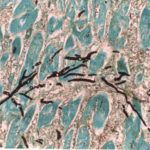
-
Disseminated, invasive aspergillosis showing dichotomously branching hyphae. Original magnification x150. Stained with Gomori Methenamine Silver (GMS).

-
Disseminated, invasive aspergillosis showing dichotomously branching hyphae. Original magnification x50. Stained with Gomori Methenamine Silver (GMS).

-
Light microscopical appearance of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis showing vessel occlusion with thrombus and distal infarction (Haematoxylin and eosin, x100)