Date: 21 January 2014
Further details
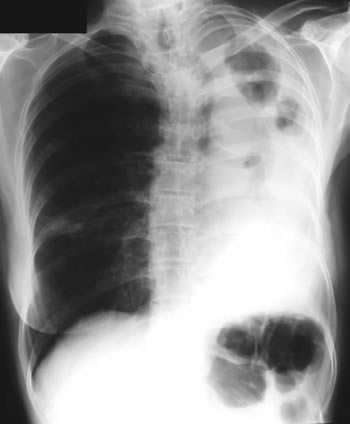
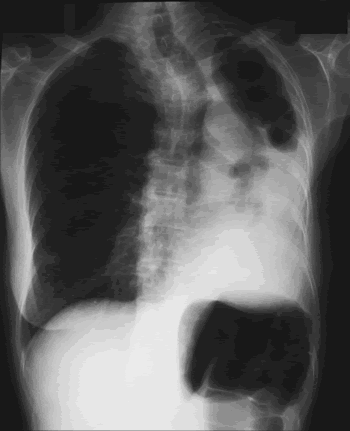
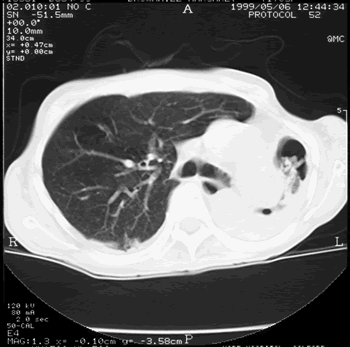
Image B. Additional cavities are apparent inferior to this large cavity and are in communication both with the bronchi and the additional cavities. Some of the apparent cavities are probably dilated bronchi. The left lower lung is completely opacified otherwise. The degree of pleural fibrosis surrounding the left apical cavity is reduced slightly over the interval of four months.
Image C. This shows an almost normal hyperexpanded right lung with a very substantially contracted left lung with one large airway visible and probably incontinuity with a slightly irregular cavity containing some debris, presumably fungal tissue. Other levels show very large left apical cavity with numerous subsections containing debris or fibrotic tissue and almost complete fibrosis of the lung below the level of the carina on the left, with some calcification within the fibrotic lung tissue.
Copyright: n/a
Notes: n/a
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
Corneal ulcer – gram stain. Corneal scrapings were taken from a 67 yr old farmer presenting with a corneal ulcer of the right eye. A piece of vegetable matter was embedded in the cornea and scrapings were done. Gram stain (500x magnification) showed numerous septate hyphae. Cultures grew a small amount of A fumigatus.

-
Corneal ulcer – gram stain. Corneal scrapings were taken from a 67 yr old farmer presenting with a corneal ulcer of the right eye. A piece of vegetable matter was embedded in the cornea and scrapings were done. Gram stain (500x magnification) showed numerous septate hyphae. Cultures grew a small amount of A fumigatus.
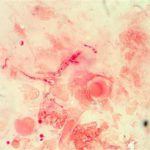
-
Corneal ulcer – gram stain. Corneal scrapings were taken from a 67 yr old farmer presenting with a corneal ulcer of the right eye. A piece of vegetable matter was embedded in the cornea and scrapings were done. Gram stain (500x magnification) showed numerous septate hyphae. Cultures grew a small amount of A fumigatus.

-
Aspergillus keratitis. Central lesion in aspergillus keratitis following a corneal foreign body which made a good response to topical treatment alone, albeit over 2 months intensive treatment.
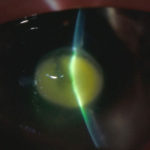
-
Aspergillus keratitis. B- Severe central aspergillus infection with a “cheesey†looking area of the lesion and hypopyon (fluid level of inflammatory cells in the anterior chamber)
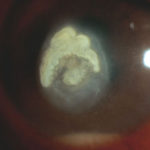
-
Aspergillus keratitis. A- Severe aspergillus infection with large area of corneal ulceration and deep stromal involvement
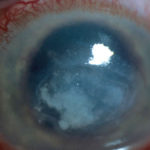
-
Candida keratitis. Focal candida keratitis as an unusual cause of a suture related infection following corneal transplantation for non infective indication
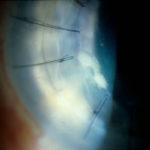
-
Candida keratitis. Subacute onset of candida keratitis in a young adult in whom dust blew into her eye in Greece. A slightly “feathery†edge to stromal involvement is suggestive of fungal infection
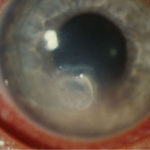
-
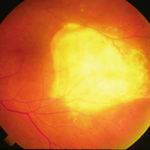
Aspergillus endopthalmitis. Temporal necrosis due to Aspergillus endopthalmitis as part of disseminated disease. No evidence of vitritis. Systemic treatment essential.
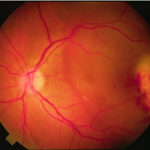
-
Aspergillus endopthalmitis. Large scarred area of the choroid following healing after Aspergillus endopthalmitis