Date: 21 January 2014
Further details
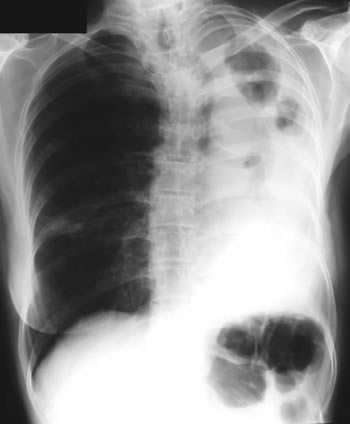
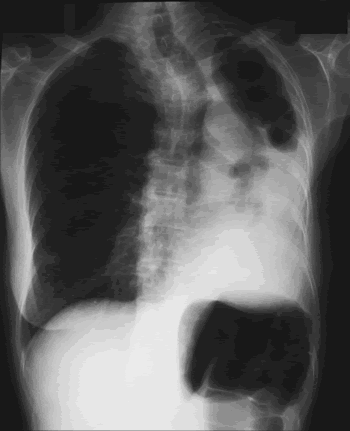
Image B. Additional cavities are apparent inferior to this large cavity and are in communication both with the bronchi and the additional cavities. Some of the apparent cavities are probably dilated bronchi. The left lower lung is completely opacified otherwise. The degree of pleural fibrosis surrounding the left apical cavity is reduced slightly over the interval of four months.
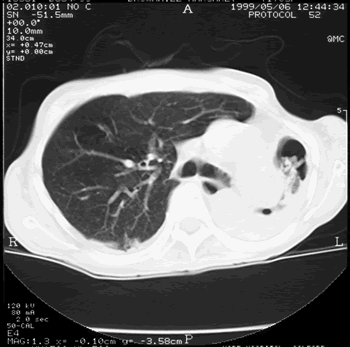
Image C. This shows an almost normal hyperexpanded right lung with a very substantially contracted left lung with one large airway visible and probably incontinuity with a slightly irregular cavity containing some debris, presumably fungal tissue. Other levels show very large left apical cavity with numerous subsections containing debris or fibrotic tissue and almost complete fibrosis of the lung below the level of the carina on the left, with some calcification within the fibrotic lung tissue.
Copyright: n/a
Notes: n/a
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Light microscopical appearance of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis showing vessel occlusion with thrombus and distal infarction (Haematoxylin and eosin, x100)

-
Light microscopical appearance of vessel thrombus showing fungal element within it (Haematoxylin and eosin, x400).

-
Medium power view (H&E) of lung tissue in patient with invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in which many of the fungal hyphae are seen in cross section.
Pulmaonary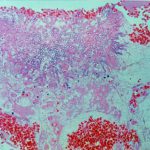
-
Light microscopical appearance of conidial head of A. fumigatus at an air interface in pulmonary tissue (Haematoxylin and eosin, x250).