Date: 26 November 2013
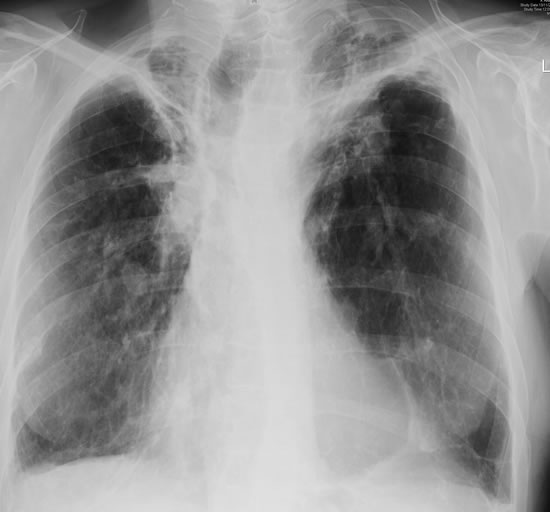
Born 75 years ago, Pt HK had 3 episodes of tuberculosis as a child and teenager, being treated with PAS and streptomycin. He suffered a ‘bad chest’ all his life and retired aged 54. Presenting with worsening and more frequent chest infections, he was referred with ‘bronchiectasis and Aspergillus sensitisation’. A diagnosis of chronic pulmonary aspergillosis was made in June 2009 on the basis of his chest radiograph and strongly positive Aspergillus precipitins (IgG antibodies) (titre 1/16). He also had Pseudomonas aeruginosa colonisation. His oxygen saturation was 87% and his pO2 6.8, pCO2 6.2 KPa.
His chest radiograph (see above, November 2009) was reported as showing; “ The lung fields are over-inflated. Bilateral apical fibrotic change secondary to old TB. No cavity seen.” At clinic, bilateral apical cavities were seen, with some associated pleural thickening at the left apex, without any evidence of a fungal ball.
He started posaconazole 400mg twice daily with therapeutic levels at subsequent visits. Sputum cultures never grew Aspergillus. Over the following 9 months he had no chest infections requiring antibiotics, his breathlessness worsened gradually and he remained easily fatigued. His Aspergillus antibody titres fell. Overall he felt better, but was concerned about declining respiratory status.
Copyright:
Fungal Research Trust
Notes: n/a
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
Patient MB X rays and CT scans. Chronic calcified maxillary sinusitis, patient had a palate defect.A. fumigatus cultured.
Images A&B Plain X rays antero-posterior and lateral, pre-operatively of Pt MB aged 76 who presented with unilateral nasal stuffiness and difficulty getting dentures fitted. She had hda these symptoms for many years. A large irregular calcified mass can be seen replacing the right maxillary sinus.
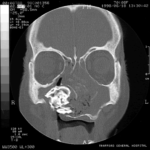
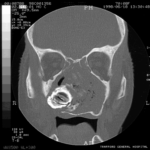
Images C D & E Coronal CT scan images of Pt MB showing a completely obstructed nasal cavity bilaterally and loss of internal nasal architecture. On the right side is large lamellar calcified lesion embedded in the extensive inflammatory material. Loss of bony margins is seen in numerous locations. This material was all removed surgically and showed mostly necrotic debris with Charcot-Leyden crystals and a few eosinophils and degenerate fungal hyphae. Aspergillus fumigatus was cultured from the material, especially infero-laterally on the right.
Image F Photograph through the mouth post-operatively showing the palate and a large defect in its right side. Through the defect can be seen the interior of the right maxillary sinus and nasal cavity with the inferior turbinate just visible.
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,