Date: 26 November 2013
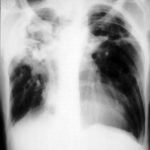
Born 75 years ago, Pt HK had 3 episodes of tuberculosis as a child and teenager, being treated with PAS and streptomycin. He suffered a ‘bad chest’ all his life and retired aged 54. Presenting with worsening and more frequent chest infections, he was referred with ‘bronchiectasis and Aspergillus sensitisation’. A diagnosis of chronic pulmonary aspergillosis was made in June 2009 on the basis of his chest radiograph and strongly positive Aspergillus precipitins (IgG antibodies) (titre 1/16). He also had Pseudomonas aeruginosa colonisation. His oxygen saturation was 87% and his pO2 6.8, pCO2 6.2 KPa.
His chest radiograph (see above, November 2009) was reported as showing; “ The lung fields are over-inflated. Bilateral apical fibrotic change secondary to old TB. No cavity seen.” At clinic, bilateral apical cavities were seen, with some associated pleural thickening at the left apex, without any evidence of a fungal ball.
He started posaconazole 400mg twice daily with therapeutic levels at subsequent visits. Sputum cultures never grew Aspergillus. Over the following 9 months he had no chest infections requiring antibiotics, his breathlessness worsened gradually and he remained easily fatigued. His Aspergillus antibody titres fell. Overall he felt better, but was concerned about declining respiratory status.
Copyright:
Fungal Research Trust
Notes: n/a
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
Late (venous) phase angiogram of a right intercostal artery showing persistence of vascular blush and further filling of a branch of the pulmonary artery.
-
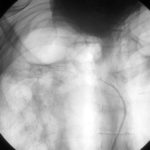
Catheter tip in a right posterior intercostal artery on screening film.
-
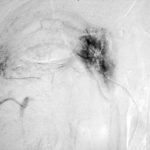
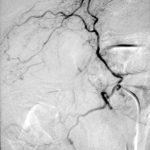
Angiogram of a right bronchial artery on subtraction film in the early arterial phase showing filling hypervascular circulation superiorly and communications with a pulmonary arterial radical.
-
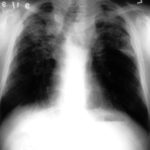
This patient with severe pulmonary sarcoidosis has bilateral aspergillomas. A rim of air is visible around parts of the aspergillomas on both sides. This patient was recruited into the NIAID Mycoses Study Group multicentre study of the treatment of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis with itraconazole but not analysed because invasive disease was not demonstrated. Denning DW, Lee JY, Hostetler JS, Pappas P, Kauffman CA, Dewsnup DH, Galgiani JN, Graybill JR, Sugar AM, Catanzaro A, Gallis H, Perfect JR, Dockery B, Dismukes WE, Stevens DA, NIAID Mycoses Study Group multicenter trial of oral itraconazole therapy of invasive aspergillosis. Am J Med 1994; 97: 135-144
-
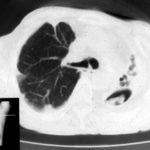
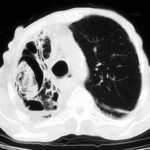
Extensive pleural thickening is demonstrated at the left apex on this CT scan of a woman who had previously had tuberculosis and whose large cavity gradually became obliterated by pleural thickening. An aspergilloma is demonstrable within the cavity
-
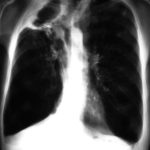
This chest radiograph (AMBER film) demonstrates the typical extensive pleural thickening at the right apex, seen in patients with aspergillomas. The cavity appears not to contain an aspergilloma but on CT scan had some ‘debris’ and Aspergillus antibiotics (precipitins) were strongly positive. The differential diagnosis lies between an aspergilloma and chronic invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. The extensive pleural thickening is heavily in favour of an aspergilloma, even without a well demonstrated fungal ball in the cavity.
-
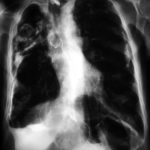
Image C. Another example of a severe apical aspergilloma with remarkably little pleural thickening on plain chest radiograph (AMBER film). Severe distortion of the trachea is demonstrated.
 ,
,  ,
, 
-
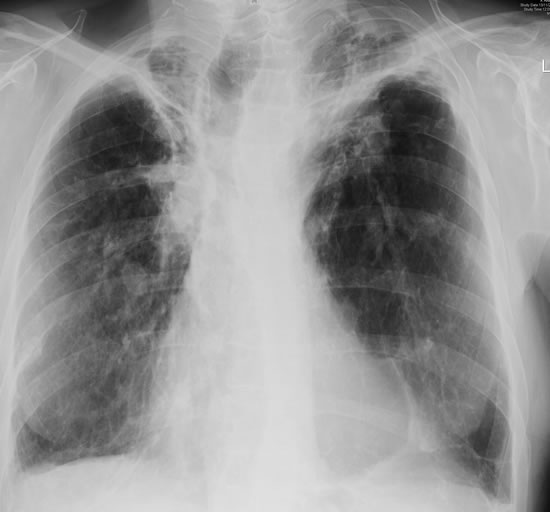
Right apical aspergilloma, patient WC. Plain chest radiograph of patient with right apical aspergilloma in an old, large tuberculous cavity. Severe haemoptysis and respiratory insufficiency together constituted the indications for embolisation which was done in one session over a 3 hour period (see images 1-6).