Date: 26 November 2013
Born 75 years ago, Pt HK had 3 episodes of tuberculosis as a child and teenager, being treated with PAS and streptomycin. He suffered a ‘bad chest’ all his life and retired aged 54. Presenting with worsening and more frequent chest infections, he was referred with ‘bronchiectasis and Aspergillus sensitisation’. A diagnosis of chronic pulmonary aspergillosis was made in June 2009 on the basis of his chest radiograph and strongly positive Aspergillus precipitins (IgG antibodies) (titre 1/16). He also had Pseudomonas aeruginosa colonisation. His oxygen saturation was 87% and his pO2 6.8, pCO2 6.2 KPa.
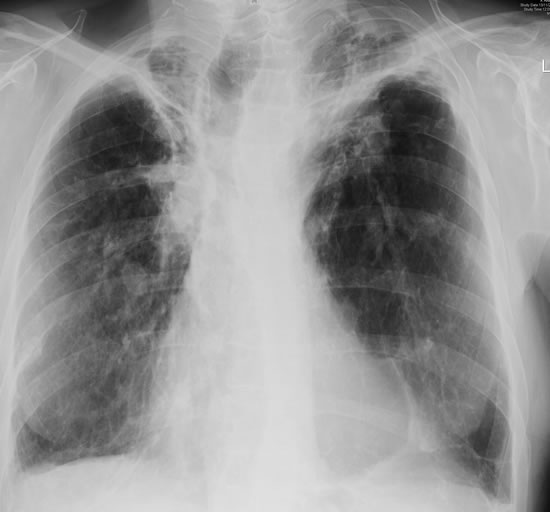
His chest radiograph (see above, November 2009) was reported as showing; “ The lung fields are over-inflated. Bilateral apical fibrotic change secondary to old TB. No cavity seen.” At clinic, bilateral apical cavities were seen, with some associated pleural thickening at the left apex, without any evidence of a fungal ball.
He started posaconazole 400mg twice daily with therapeutic levels at subsequent visits. Sputum cultures never grew Aspergillus. Over the following 9 months he had no chest infections requiring antibiotics, his breathlessness worsened gradually and he remained easily fatigued. His Aspergillus antibody titres fell. Overall he felt better, but was concerned about declining respiratory status.
Copyright:
Fungal Research Trust
Notes: n/a
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
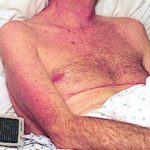
Itraconazole rash – macropopular rash after 7 days treatment with Itraconazole, in a patient with AIDS
-
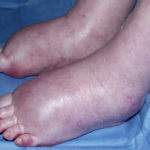
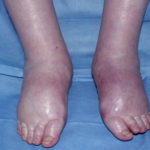
A 72 year-old male patient had been in treatment for many years for severe asthma with relatively good exercise tolerance. Over the past two years he had increasing problems of shortness of breath, cough and productive sputum. There was no history of chest pain, haemoptysis or fever. His total IgE was 680.0 IU/l, and specific IgE against Aspergillus fumigatus was 14.6 IU/l. Precipitins against A. fumigatus were weakly positive (titre 1/2), and there was no eosinophilia. Computed tomography revealed marked emphysema but only mild bronchiectasis. Based on these results he was diagnosed with severe asthma with fungal sensitisation (SAFS) and itraconazole was started (SporanoxTM 200mg bds). Itraconazole dosage was reduced to 200 mg daily one month later due to progressive bilateral ankle oedema. Itraconazole levels by bioassay were 17.5 mg/l at that time (normal range 5-15 mg/l). Despite showing improvement on his chest symptoms, peripheral oedema became a major negative impact on patient’s quality of life. There were no signs of heart failure. Figure 1 was taken 2 months after itraconazole was started, when drug levels were 9.8 mg/l. Itraconazole was replaced by voriconazole. Concomitant medications included furosemide (80 mg daily) and spironolactone (100 mg daily). After discontinuing itraconazole, the oedema quickly subsided.
Ankle oedema is an uncommon complication of therapy with itraconazole. It has occurred in about 4% of patients treated in clinical trials involving this drug. This complication seems to be more frequent in patients concomitantly receiving calcium channel blockers, which was not the case for our patient. The mechanism is unknown. It usually does not represent cardiac failure, another reported side effect of itraconazole, but this must be excluded. Marked oedema requiring drug suspension is a rare phenomenon, and has not been previously reported in association with itraconazole.
 ,
,  ,
, 
-
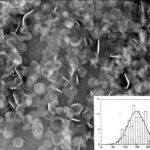
The insert shows the size of the discs. These discs dissociate after infusion to release amphotericin B preferentially into the reticuloendothelial system and lung. This form of amphotericin B is marketed as either Amphotec or Amphocil, depending on the country.