Date: 26 November 2013
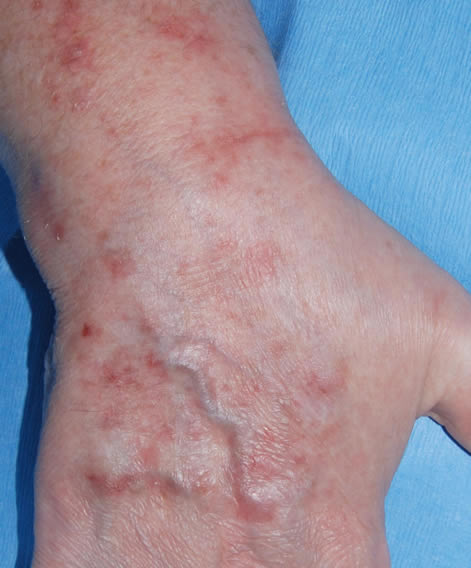
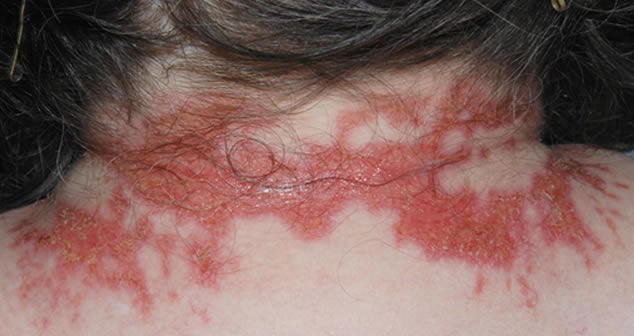
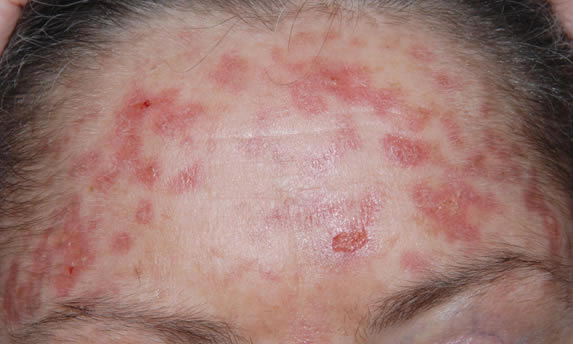
This patient with ABPA and chronic cavitary pulmonary aspergillosis has been stabilized on voriconazole treatment for >5 years. She had a degree of photosensitivity most of that time, noticed early in the course of voriconazole treatment. She is oxygen and wheelchair dependent and doesn’t go outside very much, so most of her light exposure has been indoor light. She developed rough scaly patches over her face, neck and lower arms. Dermatological review indicated multiple solar keratoses”. Skin biopsy from the right forearm confirmed this clinical diagnosis – “skin showing hyperkeratosis with a little parakeratosis and acanthosis. The keratinocytes have a glassy appearance but show nuclear atypia with dyskeratotic cells, and occasional suprabasal mitoses. The intraepidermal sweat ducts are spared. Appearances suggest an actinic keratosis with moderate to severe dysplasia.” These features are characteristic of a low grade premalignant change.
She was treated with local 5-fluorouracil cream (Efudix) (3 cycles) to the affected lesions. These photos were taken at the apogee of inflammation. The inflammation resolved after discontinuing the cream. This reaction is expected with application of this mild chemotherapy agent. Alternative or supplementary treatments include cryotherapy, curettage and cautery, if necessary. Following treatment her skin was much softer and considerably improved. Voriconazole has been stopped, and posaconazole substituted.
Copyright:
DW Denning and JE Ferguson, University Hospital of South Manchester. 22/07/08
Notes: n/a
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
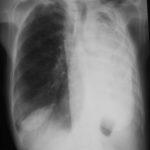
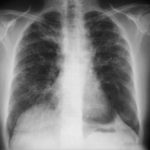
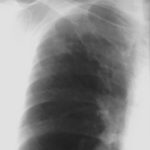
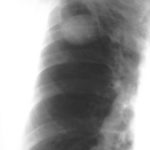
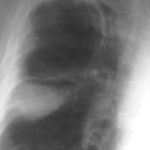
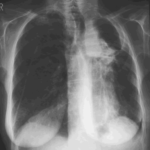
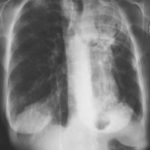
Pt AR Interval development of chronic cavitary pulmonary aspergillosis in the context of sarcoidosis
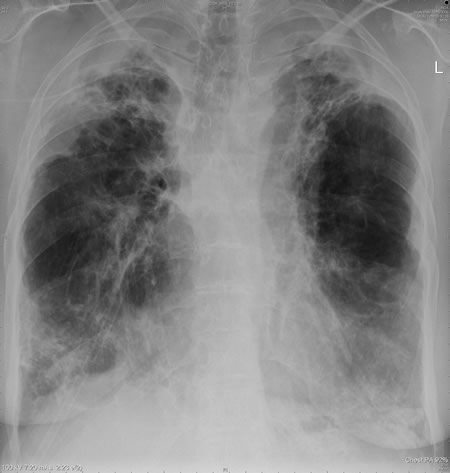
This patient was diagnosed with sarcoid after developing a chronic cough with the attached chest X-ray. In February 2003 the X-ray demonstrated bilateral extensive changes consistent with fibrocystic sarcoidosis with a complex cavitary area in both apices, more marked on the right. She was given a course of corticosteroids.
-
Further details
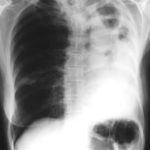
Image B. Additional cavities are apparent inferior to this large cavity and are in communication both with the bronchi and the additional cavities. Some of the apparent cavities are probably dilated bronchi. The left lower lung is completely opacified otherwise. The degree of pleural fibrosis surrounding the left apical cavity is reduced slightly over the interval of four months.
Image C. This shows an almost normal hyperexpanded right lung with a very substantially contracted left lung with one large airway visible and probably incontinuity with a slightly irregular cavity containing some debris, presumably fungal tissue. Other levels show very large left apical cavity with numerous subsections containing debris or fibrotic tissue and almost complete fibrosis of the lung below the level of the carina on the left, with some calcification within the fibrotic lung tissue.
 ,
,  ,
, 
-
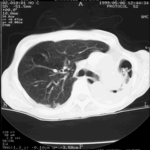
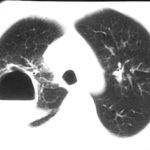
Transverse sections through the thorax of a patient with AIDS, hepatitis C and a left tempero-parietal cerebral lymphoma. His CD4 cell count was 45 x 106 / l. The lymphoma was proven by biopsy after a poor response to anti-toxoplasma therapy. He was given dexamethasone to cover the surgery and then developed diabetes mellitus. He did not receive chemotherapy for his lymphoma but did have 2 cerebral radiotherapy treatments (1.8 Gy each). Three weeks after the biopsy he developed dyspnoea and fever. Shortly after this he developed a right-sided hemiparesis, became comatose and died 2 days later.Autopsy showed a cerebral lymphoma and pulmonary and renal aspergillosis. Aspergillus nidulans was recovered from cultures of lungs and kidney.
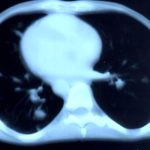 ,
, 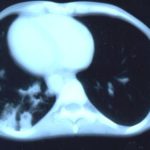 ,
,  ,
, 
-
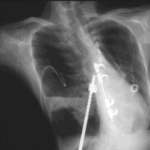
Fever chart of Pt CA -heart transplant pt with candidemia on amphotericin therapy, who developed pulmonary aspergillosis.

-
A Colonies on MEA + 20% sucrose after two weeks; B ascomata, x 40; C conidia and conidiophore, x 920; D ascospores and conidia x2330; E portion of ascoma with asci x920

-
A 66 yr old patient in good general health developed onychomycosis. Samples taken from the affected nail were grown by culture and examined by microscopy. Oral itraconazole pulse therapy was given to the patient (200 mg twice daily for 1 week, with 3 weeks off between successive pulses, for four pulses) and treatment was successful.
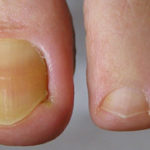


 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
 ,
,  ,
,