Date: 26 November 2013
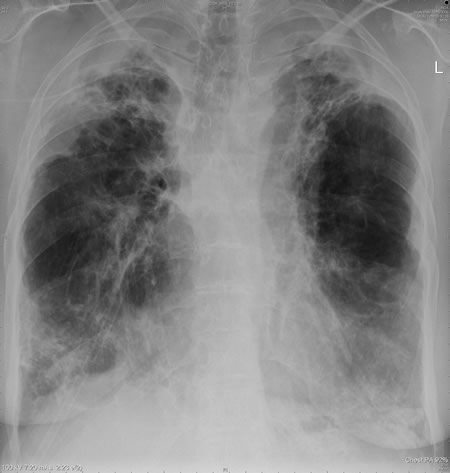
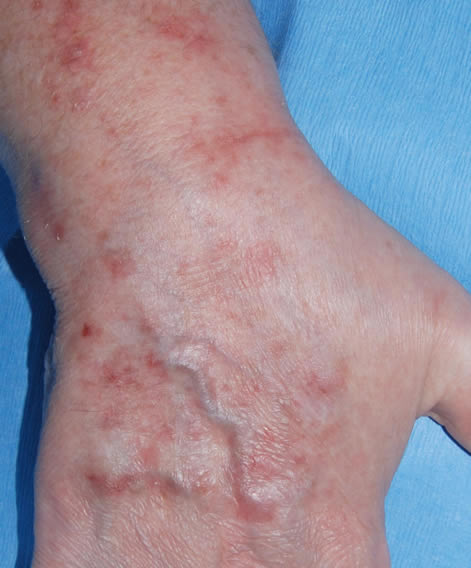
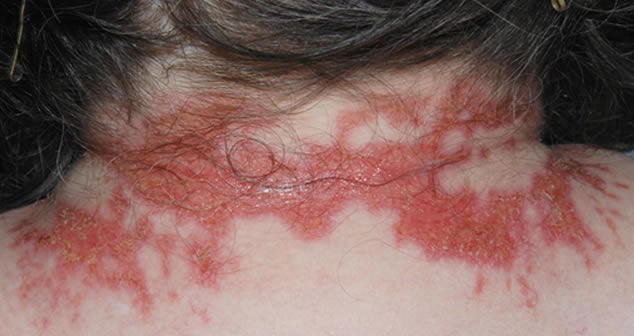
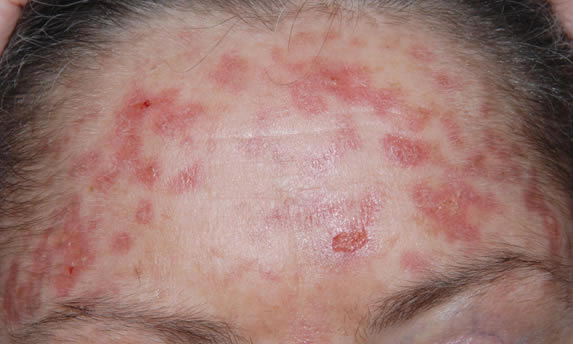
This patient with ABPA and chronic cavitary pulmonary aspergillosis has been stabilized on voriconazole treatment for >5 years. She had a degree of photosensitivity most of that time, noticed early in the course of voriconazole treatment. She is oxygen and wheelchair dependent and doesn’t go outside very much, so most of her light exposure has been indoor light. She developed rough scaly patches over her face, neck and lower arms. Dermatological review indicated multiple solar keratoses”. Skin biopsy from the right forearm confirmed this clinical diagnosis – “skin showing hyperkeratosis with a little parakeratosis and acanthosis. The keratinocytes have a glassy appearance but show nuclear atypia with dyskeratotic cells, and occasional suprabasal mitoses. The intraepidermal sweat ducts are spared. Appearances suggest an actinic keratosis with moderate to severe dysplasia.” These features are characteristic of a low grade premalignant change.
She was treated with local 5-fluorouracil cream (Efudix) (3 cycles) to the affected lesions. These photos were taken at the apogee of inflammation. The inflammation resolved after discontinuing the cream. This reaction is expected with application of this mild chemotherapy agent. Alternative or supplementary treatments include cryotherapy, curettage and cautery, if necessary. Following treatment her skin was much softer and considerably improved. Voriconazole has been stopped, and posaconazole substituted.
Copyright:
DW Denning and JE Ferguson, University Hospital of South Manchester. 22/07/08
Notes: n/a
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
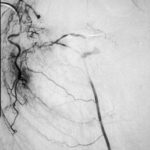
Embolisation 7 – patient WC. Angiogram of the lateral thoracic artery on subtraction film showing grossly abnormal vasculature inferiorly shunting along several anterior intercostal arteries to the internal mammary artery. In addition a pseudoaneurysm is shown.
-
Embolisation 6 – patient WC. Catheter tip in the lateral thoracic artery on screening film.
-
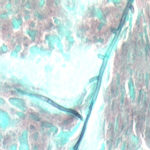
Grocott (silver) stain showing branching septate hyphae fairly typical of Aspergillus in mucus. The apparent right angle branching is unusual.
-
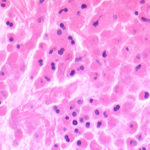
Bronchial mucosa under H & E stain showing numerous eosinophils deep to the mucosa, and mucus in the lumen of the bronchiole.
-
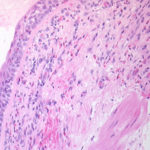
Grocott (silver) stain showing branching septate hyphae fairly typical of Aspergillus in mucus. The apparent right angle branching is unusual.

-
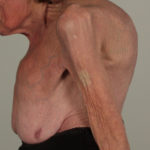
Severe kyphoscoliosis caused by greater than 40 years of prednisolone for ABPA and asthma.

-
These pictures show remarkable curvature of the spine as a result of collapse of the vertebral bodies of the thoracic vertebrae. This is a gross example of steroid-induced osteoporosis. The dose was not large in the last 10 years, typically 5-10mg daily, but multiple high dose courses and slow tapering lead to this outcome.
Her corticosteroid warning card is also demonstrated, as additional steroids are required for any significant illness or surgery, as her adrenal glands had completely atrophied.
Kindly supplied by Prof David Denning, South Manchester University Hospitals NHS Trust, Manchester UK
(© Fungal Research Trust)
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,