Date: 26 November 2013
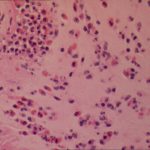
Facial erythema: Voriconazole rash in ABPA patient resistant to corticosteroids, treated with voriconazole 200mg BID. Serum voriconazole levels were very low and the dose was raised to 250mg BID. Within 3 weeks patient had developed remarkable facial erythema. His trough voriconazole concentration at this time was 370ng/ml. When voriconazole was stopped because of the facial erythema and lack of impact on his ABPA his facial erythema resolved over 4 weeks.
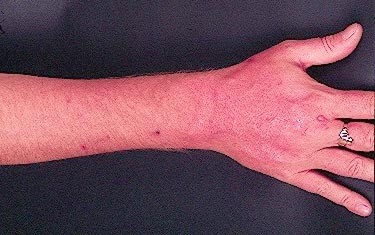
Forearm erythema related to voriconazole. As with facial erythema patient developed remarkable forearm erythema with lesions similar to porphyria cutanea tarda all of which resolved with stopping voriconazole.
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
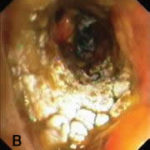
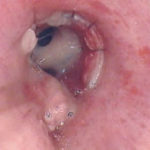
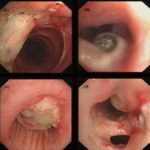
Bronchoscopic manifestations of Aspergillus tracheobronchitis. (a) Type I. Inflammatory infiltration, mucosa hyperaemia and plaques of pseudomembrane formation in the lumen without obvious airway occlusion. (b) Type II. Deep ulceration of the bronchial wall. (c) Type III. Significant airway occlusion by thick mucous plugs full of Aspergillus without definite deeper tissue invasion. (d) Type IV. Extensive tissue necrosis and pseudomembrane formation in the lumen with airway structures and severe airway occlusion (Wu 2010).
-
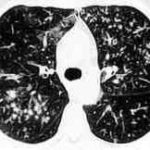
High resolution CT showing centrilobular nodular opacities and branching linear opacities (tree-in-bud appearance) (Al-Alawi 2007).
-
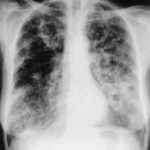
Chest X-ray showing poorly defined bilateral nodular opacities (Al-Alawi 2007).
-
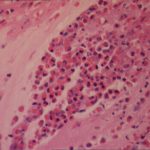
Gross pathologic specimen from autopsy shows the bronchial lumen covered by multiple whitish endobronchial nodules (arrows) (Franquet 2002).

-
Invasive tracheobronchitis showing numerous nodules seen during bronchoscopy (Ronan D’Driscoll).

-
Pseudomembranous seen overlying the bronchial mucosa (Tasci 2006).