Date: 26 November 2013
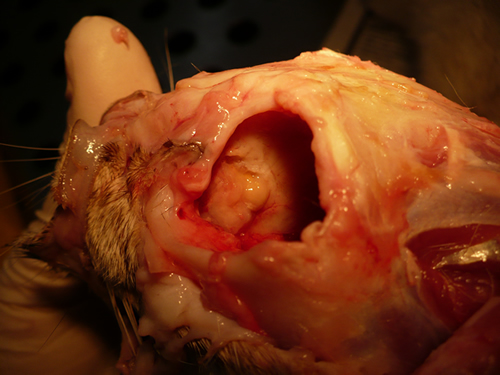
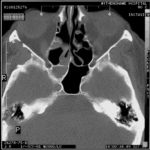
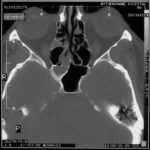
Nasal, sinus and orbital aspergillosis in a cat. The left nasal cavity and sinus were full of pus and debris and there was severe bone erosion from the nasal cavity into the rostromedial orbitthrough which pus was protruding
Copyright:
(Kindly provided by Martin L. Whitehead, BSc, PhD, BVSc, CertSAM, MRCVS & Peter W. Kettlewell, BVSc, MSc, MRCVS. Chipping Norton Veterinary Hospital, Albion Street, Chipping Norton, Oxon, OX7 5BN.)
Notes:
History : Nasal aspergillosis is relatively common in dogs but rare in cats. Our veterinary hospital in Oxfordshire was recently presented with a 13-year old female Burmilla cat with a history of left-side unilateral nasal discharge, a watery left eye with slight blepharospasm, occasional ‘twitching movements’ of the head, weight loss, inappetance and depression. Clinical examination was unremarkable except for left-side mucopurulent nasal discharge, left-side mild serous ocular discharge, and a soft subcutaneous swelling over the left frontal sinus. Haematology, blood biochemistry and urinalysis revealed diabetes mellitus but was otherwise unremarkable. Radiography under general anaesthesia revealed a diffuse soft tissue density within the left nasal cavity and left frontal sinus. Rhinoscopy revealed mucopurulent discharge on the left side but was otherwise unremarkable. Aspiration of the swelling over the left frontal sinus produced pus and this abscess was lanced and flushed. The frontal sinus was trephined and the sinus and nasal cavity flushed with saline. Tests for feline immunodeficiency virus and feline leukaemia virus and serology for Aspergillus were not carried out. The cat was started on insulin, ibafloxacin (Ibaflin, Intervet) and meloxicam (Metacam, Boehringer). Cytology of the material flushed from the frontal sinus and nasal cavity revealed fungal hyphae consistent with Aspergillus species and culture of this material yielded growth of a fungus which was morphologically similar to A. candidus (Awaiting molecular typing results). The cat was then started on oral itraconazole (Itrafungol, Janssen) 10 mg/kg p.o. SID. The abscess over the rostral frontal sinus did not heal and a second abscess appeared over the nasal bone just dorsal to the nose. Infusion of the frontal sinus and nasal cavity with topical antifungal medication was discussed with the owners, but as the cat was deteriorating they requested euthanasia. On post-mortem examination the right nasal cavity, frontal sinus and orbit were unaffected. The left nasal cavity and sinus were full of pus and debris and there was severe bone erosion from the nasal cavity into the rostromedial orbit through which pus was protruding. There was also severe bone erosion rostrally through the nasal bone and less severe bone erosion dorsally over the rostral part of the frontal sinus, these sites of bone erosion being at the location of the two subcutaneous abscesses.Feline nasal aspergillosis is extremely rare in the UK and to our knowledge this is the first reported case of orbital aspergillosis in the UK although nasal aspergillosis has been reported in other countries.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
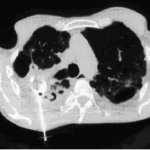
Image A. Scan shows large bore needle in one of the cavities on the right. The contrast media is mixed with amphotericin B and is whiter than surrounding lung tissue and fungal ball. The contrast surrounds the aspergilloma present in this cavity. Some of the contrast has fallen by gravity in another cavity anteriorly below the one being injected, showing communication between the cavities.
Image B. Scan showing contrast media mixed with amphotericin B injected into a multicystic cavity in the right upper lobe. The contrast (white) flows around the aspergilloma present in this cavity. The contrast falls by gravity posteriorly.
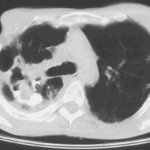
Image C. The opposite lung shows multiple empty cystic spaces with little normal lung.
Image D. There is substantial pleural thickening surrounding the irregular cavity containing the aspergilloma.
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
-
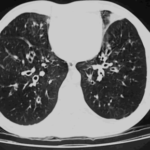
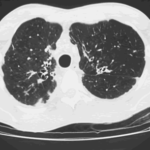
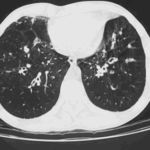
Extensive multilobar, varicose bronchiectasis, with some cyst formation most marked on the left anteriorly. Also some inhomogeneity of the pulmonary parenchyma secondary to air trapping in several affected segments.
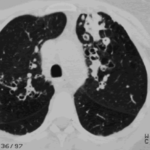
-
CT scans of thorax. Anterior left-sided bronchiectasis with extensive mucous plugging and with some proximal bronchiectasis and plugging on the right.

-
Bilateral multilobar varicose bronchiectasis affecting the segmental and small order bronchi, with some distal plugging.
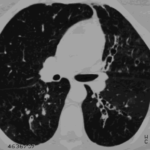
-
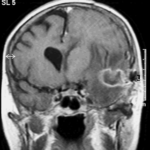
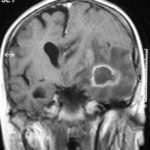
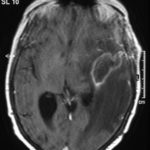
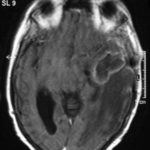
T1 weighted, gadolinium enhanced magnetic resonance brain scan. This 43 year-old alcoholic woman underwent laparoscopic cholecystectomy in January 2001. Ten days after surgery, she became confused, dysphasic and eventually had tonic-clonic seizures. A CT scan showed non-communicating hydrocephalus with ventriculitis. She underwent many complicated neurosurgical interventions, and received long term broad-spectrum antimicrobials and dexamethasone. One month later, she had generalized seizures, and a large abscess was observed on scan (see images). A heavy growth of A. fumigatus was retrieved from the abscess, and amphotericin B and 5-flucytosine were started. Antifungal therapy was changed voriconazole due to intolerance to amphotericin B and worsening disorientation. Voriconazole dosing (which varied from 300mg to 100mg twice daily) was guided by plasma concentrations as enzyme induction with rifampicin and carbamazepine, and reduction in clearance with alcoholic liver disease complicated her voriconazole dosing. Steroids were gradually reduced. She had a good recovery and completed 9 months of voriconazole.
Despite air filtration in the operating rooms, she apparently acquired an intra-operative infection, probably accelerated in presentation by concurrent dexamethasone. Rapid diagnosis and optimization of voriconazole dosing lead to a good outcome.
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
-
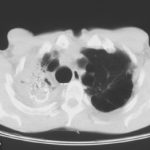
Allergic Broncho-pulmonary aspergillosis. Pt CT. Extensive severe saccular bronchiectasis of the left lower lobe and to a lesser extent of the left upper and right lower lobe.
-
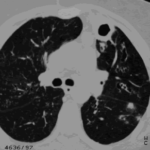
Ct scan of chest. This patient with severe ABPA, serologically and radiologically, developed a spectrum of lesions in the lung. In this cut, a cavitating infiltrate in the anterior segment of the left upper lobe was visualised together with some bronchial thickening and bronchiectasis in the left upper and lower lobe.


 ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,