Date: 26 November 2013
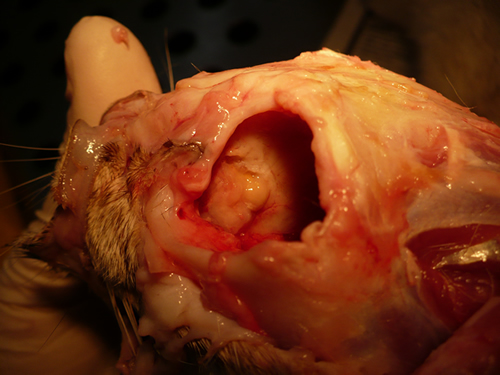
Nasal, sinus and orbital aspergillosis in a cat. The left nasal cavity and sinus were full of pus and debris and there was severe bone erosion from the nasal cavity into the rostromedial orbitthrough which pus was protruding
Copyright:
(Kindly provided by Martin L. Whitehead, BSc, PhD, BVSc, CertSAM, MRCVS & Peter W. Kettlewell, BVSc, MSc, MRCVS. Chipping Norton Veterinary Hospital, Albion Street, Chipping Norton, Oxon, OX7 5BN.)
Notes:
History : Nasal aspergillosis is relatively common in dogs but rare in cats. Our veterinary hospital in Oxfordshire was recently presented with a 13-year old female Burmilla cat with a history of left-side unilateral nasal discharge, a watery left eye with slight blepharospasm, occasional ‘twitching movements’ of the head, weight loss, inappetance and depression. Clinical examination was unremarkable except for left-side mucopurulent nasal discharge, left-side mild serous ocular discharge, and a soft subcutaneous swelling over the left frontal sinus. Haematology, blood biochemistry and urinalysis revealed diabetes mellitus but was otherwise unremarkable. Radiography under general anaesthesia revealed a diffuse soft tissue density within the left nasal cavity and left frontal sinus. Rhinoscopy revealed mucopurulent discharge on the left side but was otherwise unremarkable. Aspiration of the swelling over the left frontal sinus produced pus and this abscess was lanced and flushed. The frontal sinus was trephined and the sinus and nasal cavity flushed with saline. Tests for feline immunodeficiency virus and feline leukaemia virus and serology for Aspergillus were not carried out. The cat was started on insulin, ibafloxacin (Ibaflin, Intervet) and meloxicam (Metacam, Boehringer). Cytology of the material flushed from the frontal sinus and nasal cavity revealed fungal hyphae consistent with Aspergillus species and culture of this material yielded growth of a fungus which was morphologically similar to A. candidus (Awaiting molecular typing results). The cat was then started on oral itraconazole (Itrafungol, Janssen) 10 mg/kg p.o. SID. The abscess over the rostral frontal sinus did not heal and a second abscess appeared over the nasal bone just dorsal to the nose. Infusion of the frontal sinus and nasal cavity with topical antifungal medication was discussed with the owners, but as the cat was deteriorating they requested euthanasia. On post-mortem examination the right nasal cavity, frontal sinus and orbit were unaffected. The left nasal cavity and sinus were full of pus and debris and there was severe bone erosion from the nasal cavity into the rostromedial orbit through which pus was protruding. There was also severe bone erosion rostrally through the nasal bone and less severe bone erosion dorsally over the rostral part of the frontal sinus, these sites of bone erosion being at the location of the two subcutaneous abscesses.Feline nasal aspergillosis is extremely rare in the UK and to our knowledge this is the first reported case of orbital aspergillosis in the UK although nasal aspergillosis has been reported in other countries.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
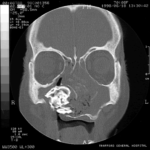
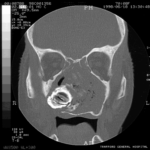
Patient MB X rays and CT scans. Chronic calcified maxillary sinusitis, patient had a palate defect.A. fumigatus cultured.
Images A&B Plain X rays antero-posterior and lateral, pre-operatively of Pt MB aged 76 who presented with unilateral nasal stuffiness and difficulty getting dentures fitted. She had hda these symptoms for many years. A large irregular calcified mass can be seen replacing the right maxillary sinus.
Images C D & E Coronal CT scan images of Pt MB showing a completely obstructed nasal cavity bilaterally and loss of internal nasal architecture. On the right side is large lamellar calcified lesion embedded in the extensive inflammatory material. Loss of bony margins is seen in numerous locations. This material was all removed surgically and showed mostly necrotic debris with Charcot-Leyden crystals and a few eosinophils and degenerate fungal hyphae. Aspergillus fumigatus was cultured from the material, especially infero-laterally on the right.
Image F Photograph through the mouth post-operatively showing the palate and a large defect in its right side. Through the defect can be seen the interior of the right maxillary sinus and nasal cavity with the inferior turbinate just visible.
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
-
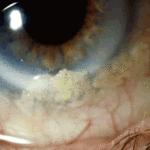
Aspergillus keratitis. Severe aspergillus infection with large area of corneal ulceration and deep stromal involvement

-
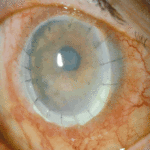
Sequence of images showing ocular surface change which unusually predisposed to severe fusarium keratitis in an elderly woman. Successful treatment involved full thickness corneal transplantation shown 2 weeks and then 2 years after surgery.

-
Sequence of images showing ocular surface change which unusually predisposed to severe fusarium keratitis in an elderly woman. Successful treatment involved full thickness corneal transplantation shown 2 weeks and then 2 years after surgery.
-
Sequence of images showing ocular surface change which unusually predisposed to severe fusarium keratitis in an elderly woman. Successful treatment involved full thickness corneal transplantation shown 2 weeks and then 2 years after surgery.
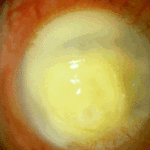
-
Sequence of images showing ocular surface change which unusually predisposed to severe fusarium keratitis in an elderly woman. Successful treatment involved full thickness corneal transplantation shown 2 weeks and then 2 years after surgery
-
Aspergillus keratitis. Shrunken eye as a consequence of this infection