Date: 26 November 2013
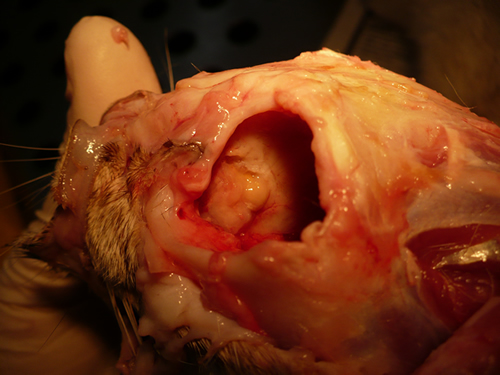
Nasal, sinus and orbital aspergillosis in a cat. The left nasal cavity and sinus were full of pus and debris and there was severe bone erosion from the nasal cavity into the rostromedial orbitthrough which pus was protruding
Copyright:
(Kindly provided by Martin L. Whitehead, BSc, PhD, BVSc, CertSAM, MRCVS & Peter W. Kettlewell, BVSc, MSc, MRCVS. Chipping Norton Veterinary Hospital, Albion Street, Chipping Norton, Oxon, OX7 5BN.)
Notes:
History : Nasal aspergillosis is relatively common in dogs but rare in cats. Our veterinary hospital in Oxfordshire was recently presented with a 13-year old female Burmilla cat with a history of left-side unilateral nasal discharge, a watery left eye with slight blepharospasm, occasional ‘twitching movements’ of the head, weight loss, inappetance and depression. Clinical examination was unremarkable except for left-side mucopurulent nasal discharge, left-side mild serous ocular discharge, and a soft subcutaneous swelling over the left frontal sinus. Haematology, blood biochemistry and urinalysis revealed diabetes mellitus but was otherwise unremarkable. Radiography under general anaesthesia revealed a diffuse soft tissue density within the left nasal cavity and left frontal sinus. Rhinoscopy revealed mucopurulent discharge on the left side but was otherwise unremarkable. Aspiration of the swelling over the left frontal sinus produced pus and this abscess was lanced and flushed. The frontal sinus was trephined and the sinus and nasal cavity flushed with saline. Tests for feline immunodeficiency virus and feline leukaemia virus and serology for Aspergillus were not carried out. The cat was started on insulin, ibafloxacin (Ibaflin, Intervet) and meloxicam (Metacam, Boehringer). Cytology of the material flushed from the frontal sinus and nasal cavity revealed fungal hyphae consistent with Aspergillus species and culture of this material yielded growth of a fungus which was morphologically similar to A. candidus (Awaiting molecular typing results). The cat was then started on oral itraconazole (Itrafungol, Janssen) 10 mg/kg p.o. SID. The abscess over the rostral frontal sinus did not heal and a second abscess appeared over the nasal bone just dorsal to the nose. Infusion of the frontal sinus and nasal cavity with topical antifungal medication was discussed with the owners, but as the cat was deteriorating they requested euthanasia. On post-mortem examination the right nasal cavity, frontal sinus and orbit were unaffected. The left nasal cavity and sinus were full of pus and debris and there was severe bone erosion from the nasal cavity into the rostromedial orbit through which pus was protruding. There was also severe bone erosion rostrally through the nasal bone and less severe bone erosion dorsally over the rostral part of the frontal sinus, these sites of bone erosion being at the location of the two subcutaneous abscesses.Feline nasal aspergillosis is extremely rare in the UK and to our knowledge this is the first reported case of orbital aspergillosis in the UK although nasal aspergillosis has been reported in other countries.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
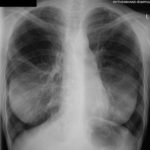
X-ray two months after initiating corticosteroids, showing the interval development of a fungal ball within a cavity at the right apex surrounded by some additional small cavities medially, pleural thickening and thick wall in the cavity.
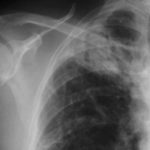
-
Pt AR Interval development of chronic cavitary pulmonary aspergillosis in the context of sarcoidosis
Follow-up film in July 2004 demonstrates the interval development of nearly confluent shadowing in the right apex with the suggestion of a fungal ball approximately 2-3cm across within the area of consolidation.
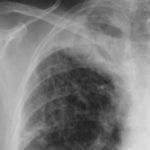
-
Pt AR Interval development of chronic cavitary pulmonary aspergillosis in the context of sarcoidosis
Close up view of adjacent X-ray
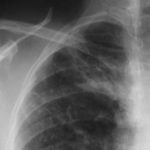
-
Chronic (Cavitary) Pulmonary Aspergillosis. Aspergillus plugs. pt. DS

-
Further details
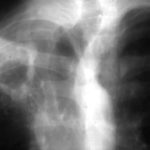
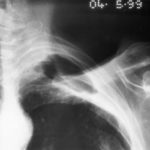
Image A. December 1991. The lesions were considered to be possibly malignant and surgically resected. Histological examination showed granulomata containing hyphae consistent with Aspergillus. Fungal cultures were not done.
Image B. June 1992 Despite resection of part of the right upper-lobe, invasive aspergillosis recurred six months later. Sputum cultures grew A.fumigatus and Aspergillus antibodies were detected in serum. He responded to itraconazole but subsequently progressed.
Image C. September 1992 Although the appearance suggests the formation of aspergillomas, the contemporaneous CT scan did not confirm this.
Image K. December 1991. There are no particular distinguishing characteristics of invasive aspergillosis. The right upper-lobe was resected and histological examination showed granulomata containing hyphae consistent with Aspergillus. Fungal cultures were not done.
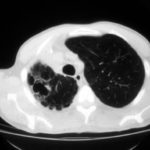
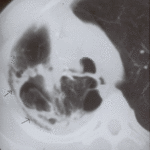
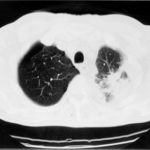
Image M & N. CT scan of thorax. Post RVL segmentectomy with chronic pulmonary aspergillosis. CT shows patchy consolidation with cavitation in the apical segment of right lower lobe. A tiny pneumothorax can be identified posterolaterally (arrows).
Image O. Reference: Muco-cutaneous retinoid effects and facial erythema related to the novel triazole antifungal agent voriconazole. Denning, DW & Griffiths, CEM. Clin.Exp Dermatol 2001, 26(8), 648-53.
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
-
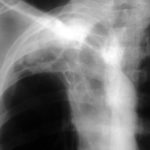
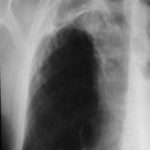
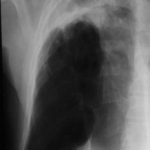
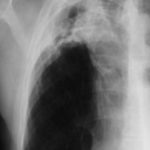
Primary pulmonary aspergillosis evolving into chronic cavitary pulmonary aspergillosis.

-
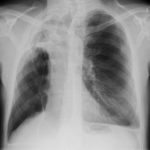
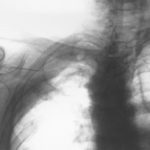
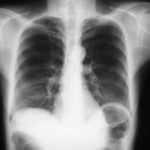
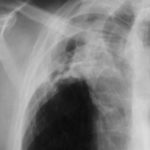
Image A. This man presented with fever and chest pain and was treated with antibiotics. His symptoms partially improved, but slowly. He was 62 years old and had drunk alcohol to excess in the past. He was a smoker. A small infiltrate is seen in the left apex.
Image B. He remained unwell and because the evolution of his chest X-ray was reminiscent of tuberculosis, was transferred to the infectious disease department. Sputum samples were negative for acid fast bacilli (and subsequently culture negative).
Image C. He continued to cough and had low grade fever. His chest X-ray now showed extensive cavitation at the left apex.
Image D. The patient’s symptoms had now resolved. The chest X-ray shows a pair of large thick walled cavities at the left apex. He was on therapy for primary Aspergillus pneumonia (a presumptive diagnosis) with itraconazole 200 mg twice daily.
Image E. A needle biopsy was done which yielded nonspecific chronic inflammatory tissue. He was being treated with itraconazole. Serology now showed one precipitin line to Aspergillus having been negative previously and his IgE was 6000 iu/ml (normal < 150 iu/ml).
Image F. The patient was now asymptomatic on itraconazole (which was given for 6 months). His chest X-ray shows continued resolution of the cavity infiltrate.
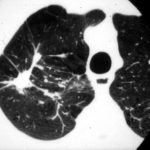
Image G. The CT scans show left apical consolidation with cavitation, with a loose infiltrate inferiorly. The features are consistent with an apical cavitating pneumonia.
Image H. The CT scan shows left apical consolidation with cavitation, with a loose infiltrate inferiorly. The features are consistent with an apical cavitating pneumonia.
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
-
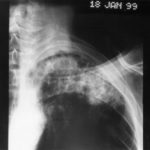
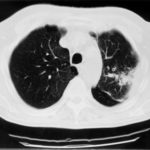
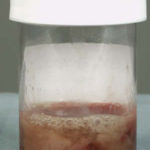
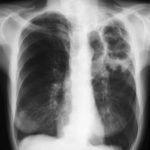
The patient’s blood-stained thick sputum is shown B. She had tuberculosis in 1955 treated with streptomyin for 1 year. She developed a severe cough with haemoptysis in 2003 and responded to itraconazole treatment given orally. In january 2006 she deteriorated with thick purulent sputum and some hameoptysis, and this has continued intermittently since then, despite itraconazole. Her serum contains a high titre of Aspergillus precipitating antibody.
Her chest X-ray shows almost complete fibrosis of the right upper lobe with pleural thickening and one or more large cavities filled with material likely to represent an aspergilloma.
 ,
, 

 ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 