Date: 26 November 2013
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
Professor
Department of Medical Microbiology
University of Wisconsin
My research focus lies in genetically dissecting those aspects of Aspergillus spp. that render them potent pathogens and superb natural product machines. My laboratory’s research includes elucidation of fungal sporulation and host/pathogen interactions; processes intimately linked to secondary metabolite (e.g. mycotoxin) production. My tactic has been to use the genetic model Aspergillus nidulans to elucidate important biological processes in this genus and then carry this information to the plant pathogens A. flavus and A. parasiticus and the human pathogen A. fumigatus. The former two pathogens contaminate seed crops worldwide with aflatoxin, the most potent naturally occurring carcinogen known. The latter pathogen is now tied with Candida as the most serious human mycopathogen in developed countries where it can cause invasive aspergillosis, a disease with a mortality rate ranging from 50 to 90%.
Areas of fungal biology that my lab has been central in developing include:
I. Genetic Regulation of Secondary Metabolism and the Role of Toxic Metabolites in Fungal Virulence.
- Bok J.-W, Balajee S A, Marr K A, Andes D, Fog Nielsen K. Frisvad J C. Keller N P (2005) LaeA, a regulator of morphogenetic fungal virulence factors. Euk Cell 4:1574-1582.
- Perrin RM, Fedorova ND, Bok JW, Cramer RA, Wortman JR, Kim HS, Nierman WC, Keller NP. (2007) Transcriptional regulation of chemical diversity in Aspergillus fumigatus by LaeA. PloS Pathogens Apr;3(4):e50.
- Shwab E., Bok JW, Tribus M, Galehr J, Graessle S, Keller NP. (2007) Histone deacetylase activity regulates chemical diversity in Aspergillus. Euk Cell 6:1656-64
II. Gene silencing processes.
- Hammond T M, Bok J-W, Andrewski MD, Reyes-Domínguez Y, Scazzocchio C, Keller NP. (2008) RNA silencing gene truncation in the filamentous fungus Aspergillus nidulans. Euk Cell Dec 7(2):339-49
- Hammond T M, Andrewski MD, Roossinck M, Keller NP. (2008) Aspergillus mycoviruses are targets and suppressors of RNA silencing. Euk Cell 2007 7(2):350-7
- Bok JW, Noordermeer D, Kale S P, Keller NP (2006) Secondary metabolic gene cluster silencing in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Microbiol 61:1636-1645
III. Host/fungal signaling.
- Tsitsigiannis D I, Bok J-W, Andes D, Fog Nielsen K, Frisvad J C, Keller N P (2005) Aspergillus cyclooxygenase-like enzymes are associated with prostaglandin production and virulence. Infect Immun: 73:4548-4559.
- Brodhagen M, Tsitsigiannis D, Hornung E, Goebel C, Feussner I, Keller NP. (2008) Reciprocal oxylipin-mediated cross talk in the Aspergillus/seed pathosystem. Mol Microbiol 67:378-391
Contact details:
Nancy Keller
Professor
3476 Microbial Science Building
Department Medical Microbiology and Immunology
Department of Plant Pathology
UW-Madison
1550 Linden Dr., Madison, WI 53706
phone (608) 262-9795
fax (608) 262-8418
npk@plantpath.wisc.edu
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
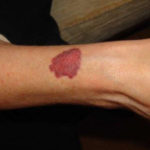
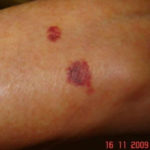
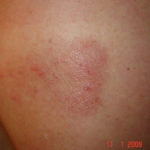
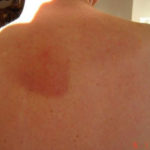
Drug rashes: Drug interactions between steroids and anti-fungal drugs – (ecchymosis)
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
-
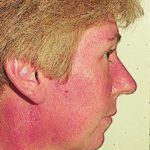
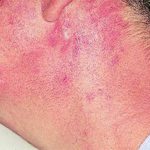
Reference: Muco-cutaneous retinoid effects and facial erythema related to the novel triazole antifungal agent voriconazole. Denning, DW & Griffiths, CEM. Clin.Exp Dermatol 2001, 26(8), 648-53.
Courtesy of Dr D Denning, Wythenshawe Hospital, Manchester.(© Fungal Research Trust)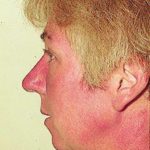 ,
,  ,
, 
-
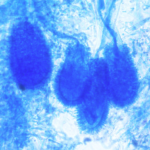
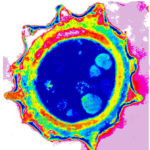
Micrographs of A. niger conidia & conidial heads provided by Amaliya Stepanova, Head of Laboratory pathomorphology and cytology at Kashkin Research Institute, Russian Federation.
 ,
, 
-
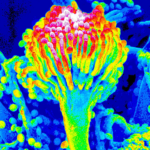
Micrographs of A. terreus conidia & conidial heads provided by Amaliya Stepanova, , Head of Laboratory pathomorphology and cytology at Kashkin Research Institute, Russian Federation.
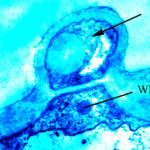 ,
,  ,
, 
-
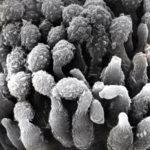
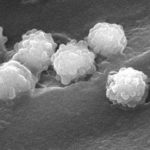
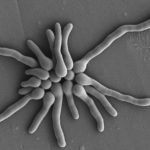
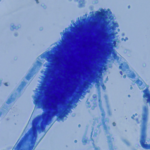
Micrographs of A. fumigatus conidia & conidial heads provided by Amaliya Stepanova, , Head of Laboratory pathomorphology and cytology at Kashkin Research Institute, Russian Federation.
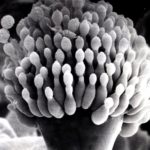 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
-
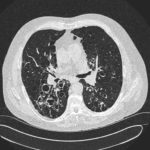
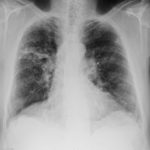
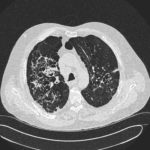
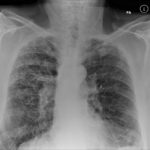
Patients has history of ABPA complicating long standing asthma. His total IgE has fluctuated between 2,200 and 4,600 KU/L, his Aspergillus IgE between 36.3 and 65.4 kAU/L and Aspergillus IgG from 87-154 mg/L. He has been taking long term itraconazole.
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 



 ,
,  ,
,