Date: 3 April 2014
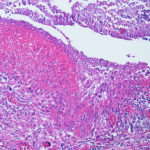
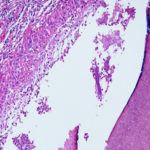
PAS stain. An example of Aspergillus fumigatus.
(PAS-stained) in a patient with chronic granulomatous disease showing a 45 degree branching hypha within a giant cell. Rather bulbous hyphal ends are also seem, which is sometimes found inAspergillus spp. infections, histologically. (x800)
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
Comparison of GMS and PAS stains. Patient with disseminated Trichosporon spp. infection. Both x60. In the GMS image, substantial background staining of elastin is seen, with more prominent yeasts superimposed. In contrast, the PAS stain shows the tissue morphology, with bright pink yeasts also visible.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
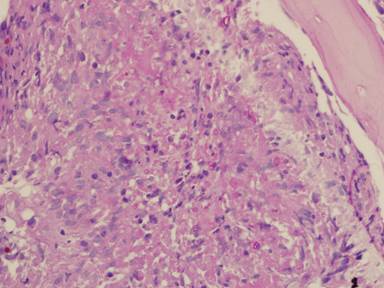
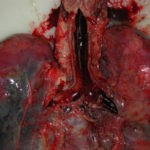
Subacute IPA in rheumatoid nodules of the lung. in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. Histology sections stained with H&E
-
Subacute IPA in rheumatoid nodules of the lung. in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. Histology sections stained with H&E.
-
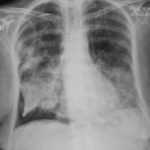
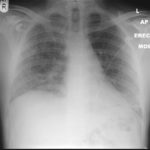
22/09/08 This chest radiograph shows bilateral hazy diffuse airspace disease predominating in the lower lungs with subtle nodularity in upper zones.
-
Further details
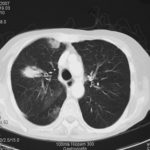
Images 3a,b,c 02/07/07
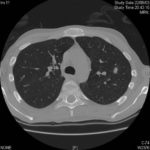
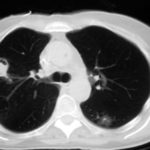
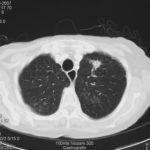
CT thorax, after 2 weeks high dose erythromycin, showing a 2.8cm speculated lesion in the right upper lobe with a further 1.6cm similar mass on the left upper lobe also with a tendency for a central cavitation, and ill defined consolidation involving the peripheral aspect of both upper lobes and to a lesser extent right middle and both lower lobes.History:
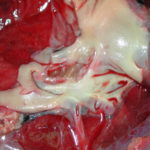
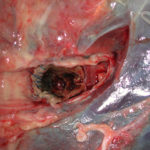
A 71 year old woman presents with persistent dry cough. Her second CT scan of thorax shows lesions in the right and left upper lobes with ill defined consolidation in other areas (see images 3a, 3b and 3c). A PET scan is positive. She underwent right thoracotomy and sub-lobar wedge resection. Aspergillus grown from tissue and sputum grows Pseudomonas. Histology confirms the nodule to be non-small cell carcinoma (adenocarcinoma) but other lung areas show organizing pneumonia and another abscess formation with a cluster of branching septate hyphae. Despite starting itraconazole and oral ciprofloxacin she deteriorated with Type 1 respiratory failure. She was intubated and ventilated and switched to intravenous voriconazole and ceftazidime. She developed acute renal failure and then Enterococcus faecium bacteremia and she died 3 days later.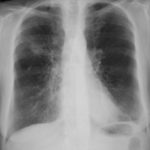 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,