Date: 3 April 2014
PAS stain. An example of Aspergillus fumigatus.
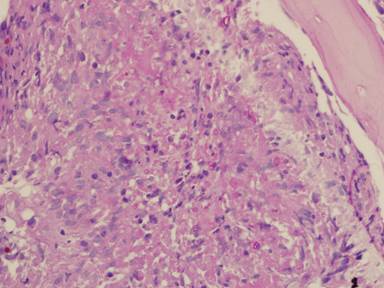
(PAS-stained) in a patient with chronic granulomatous disease showing a 45 degree branching hypha within a giant cell. Rather bulbous hyphal ends are also seem, which is sometimes found inAspergillus spp. infections, histologically. (x800)
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
Comparison of GMS and PAS stains. Patient with disseminated Trichosporon spp. infection. Both x60. In the GMS image, substantial background staining of elastin is seen, with more prominent yeasts superimposed. In contrast, the PAS stain shows the tissue morphology, with bright pink yeasts also visible.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
Pt FT. Autopsy appearance of the trachea, after the adherent pseudomembrane had been removed, revealing confluent ulceration superiorly with small green plaques of Aspergillus growth on the trachea inferiorly.
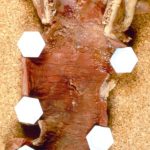
-
This view was obtained in a lung transplant recipient at bronchoscopy. Aspergillus fumigatus was grown from bronchial lavage but invasion was not demonstrated on bronchial biopsy. Symptoms improved with itraconazole therapy and abnormal appearances had resolved within 2 weeks.

-
Bronchoscopic view of Aspergillus tracheobronchitis. Bronchial lavage revealed hyphae in microscopy and cultures grew A.fumigatus. This man had received a lung transplant a few weeks before. Invasion of mucosa, but not cartilage, was demonstrated histologically. He responded rapidly to oral itraconazole.
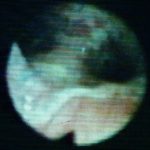
-
This view from indirect laryngoscopy illustrates bilateral lesions on the larynx that on biopsy were shown to be due to Aspergillus. This is a rare disease in non-immunocompromised patients.
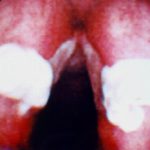
-
Bronchoscopic view of a deep bronchial ulcer in a lung transplant patient. Biopsies through the ulcer yielded cartilage with hyphae invading it. Fungal cultures of bronchial lavage grew Aspergillus fumigatus. He responded to oral itraconazole therapy.
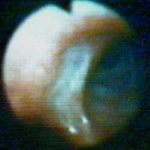
-
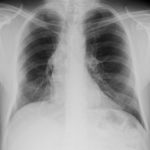
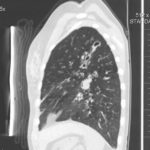
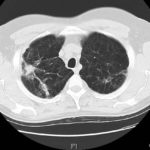
Patient had life threatening pneumonia, cavity formation was later observed. He later presented with a fungal ball. The aspergilloma was removed by surgical resection of the right upper lobe.
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,