Date: 3 April 2014
PAS stain. An example of Aspergillus fumigatus.
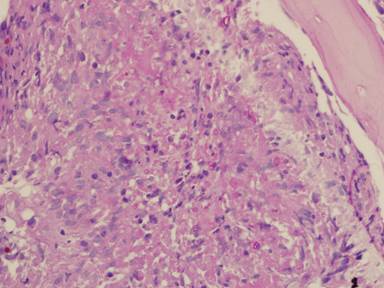
(PAS-stained) in a patient with chronic granulomatous disease showing a 45 degree branching hypha within a giant cell. Rather bulbous hyphal ends are also seem, which is sometimes found inAspergillus spp. infections, histologically. (x800)
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
Comparison of GMS and PAS stains. Patient with disseminated Trichosporon spp. infection. Both x60. In the GMS image, substantial background staining of elastin is seen, with more prominent yeasts superimposed. In contrast, the PAS stain shows the tissue morphology, with bright pink yeasts also visible.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
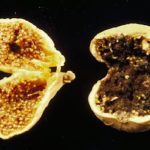
Fresh fruit: Fig. A. niger infected Calimyrna fig (smutted right fig) and a healthy fig (left)
-
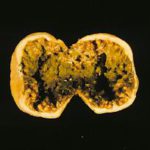
Fresh fruit: Fig. A. niger and A. parasiticus in the same Calimyrna fig
-
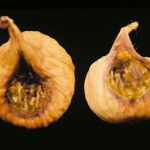
Fresh fruit: Fig. A. flavus contact (external) spot on Calimyrna figs
-
Fresh fruit: Fig. A. carbonarius (felt top), A. niger (top right), A. japonicus (bottom) on Calimyrna figs

-
Dried fruit: Peach. Sclerotia of A. niger on mummified peach

-
Dried fruit: Peach. Naturally developed sclerotia of A. niger on a peach which then mummified
-
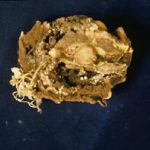
Dried fruit: Peach. A mummy of Elegant Lady peach infected with A. niger (loaded with sclerotia)

-
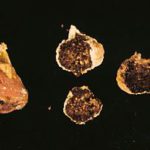
Dried fruit: Fig. Mummies of Calimyrna figs following infection by A. niger
-
Vegetables: Chili Pepper. A. niger on chili pepper