Date: 26 November 2013
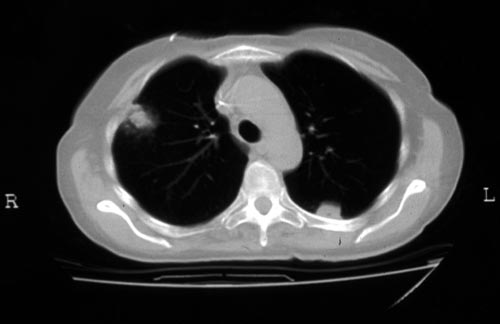
Halo sign in IPA
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
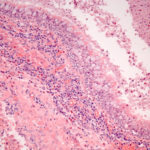
CT scan of a neutropenia patient with leukaemia who has 2 lesions. One, on the right, is nodular, abuts on the pleura and is surrounded by a (grey) low attenuation area, referred to as the “halo” sign. This is virtually only seen in invasive fungal infections of the lung, especially early in the course of the disease, during neutropenia. The other lesion visible on this scan, posteriorly on the left, is also typical of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in that it is pleura-based and has sharply angulated sides typical of vascular invasion and infarction of small lung segments. There is the suggestion of a “halo” sign anteriorly, but there is less confidence in this appearance (compared with the other) because it is only on one side of the lesion.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
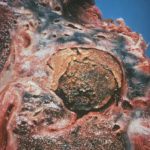
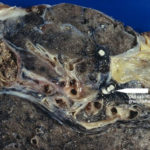
Macroscopic view medial aspect of left upper lobe of lung showing segmental collapse and congestion of lower segments, with mucus extruding from incised bronchi.
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
-
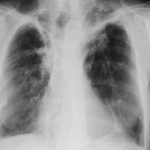
Born 75 years ago, Pt HK had 3 episodes of tuberculosis as a child and teenager, being treated with PAS and streptomycin. He suffered a ‘bad chest’ all his life and retired aged 54. Presenting with worsening and more frequent chest infections, he was referred with ‘bronchiectasis and Aspergillus sensitisation’. A diagnosis of chronic pulmonary aspergillosis was made in June 2009 on the basis of his chest radiograph and strongly positive Aspergillus precipitins (IgG antibodies) (titre 1/16). He also had Pseudomonas aeruginosa colonisation. His oxygen saturation was 87% and his pO2 6.8, pCO2 6.2 KPa.
His chest radiograph (see above, November 2009) was reported as showing; “ The lung fields are over-inflated. Bilateral apical fibrotic change secondary to old TB. No cavity seen.” At clinic, bilateral apical cavities were seen, with some associated pleural thickening at the left apex, without any evidence of a fungal ball.
He started posaconazole 400mg twice daily with therapeutic levels at subsequent visits. Sputum cultures never grew Aspergillus. Over the following 9 months he had no chest infections requiring antibiotics, his breathlessness worsened gradually and he remained easily fatigued. His Aspergillus antibody titres fell. Overall he felt better, but was concerned about declining respiratory status.