Date: 26 November 2013
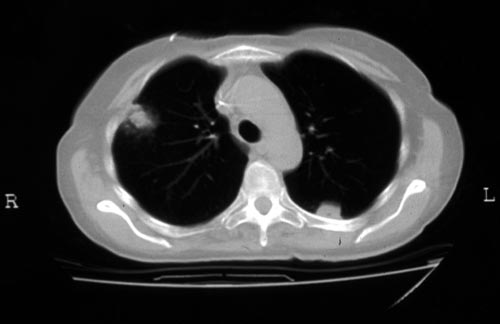
Halo sign in IPA
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
CT scan of a neutropenia patient with leukaemia who has 2 lesions. One, on the right, is nodular, abuts on the pleura and is surrounded by a (grey) low attenuation area, referred to as the “halo” sign. This is virtually only seen in invasive fungal infections of the lung, especially early in the course of the disease, during neutropenia. The other lesion visible on this scan, posteriorly on the left, is also typical of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in that it is pleura-based and has sharply angulated sides typical of vascular invasion and infarction of small lung segments. There is the suggestion of a “halo” sign anteriorly, but there is less confidence in this appearance (compared with the other) because it is only on one side of the lesion.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
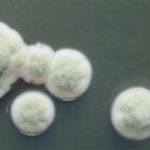
Cultures were grown on malt extract agar. Image kindly provided by Niall Hamilton.
-
A Colonies on MEA after one week, B conidial head x920, C atypical reduced conidial head x920, D conidial head x 920.

-
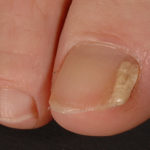
A case of onychomycosis associated with Aspergillus ochraceopetaliformis as described in Med Mycol. 2009 Mar 9:1-5, 2009,Brasch J, Varga J, Jensen JM, Egberts F & Tintelnot K
-
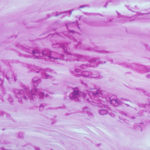
Histology of the infected nail (PAS stain) showing thick fungal elements and septate hyphae within nail material.
-
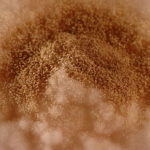
culture and identified in a case of onychomycosis – Culture at higher magnification.
-
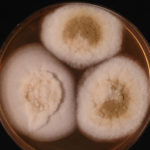
culture and identified in a case of onychomycosis – Culture of Aspergillus ochraceopetaliformis on Sabouraud agar with cycloheximide at 26C
-
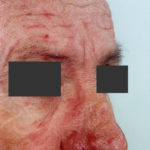
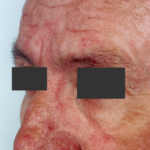
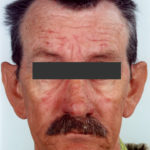
This patient with chronic cavitary pulmonary aspergillosis was treated with itraconazole, with some success, but considerable gastrointestinal disturbance (diarrhoea, flatulence and uncomfortable feeling in his abdomen). He also developed a facial rash. Itraconazole was stopped and he reverted to voriconazole which he was unable to take because of a severe feeling of being generally unwell. His facial rash resolved. Application was made for funding posaconazole. He started this and after 6 weeks an almost identical facial rash to that seen with itraconazole appeared. He tolerated posaconazole well in other respects, and his chronic cavitary pulmonary aspergillosis is now significantly better (symptomatically and serologically). July 2007
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,